- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Blog
Follow our blog and stay up to date.
Revolutionizing Patient Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-Generated Smart Forms
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The repetitive nature of filling out the same forms during each visit to a healthcare provider can be a time-consuming and tedious process for patients. However, Warp Core Health, an innovative healthcare technology company, is leading the charge in transforming the patient form experience. Through their groundbreaking AI-powered solutions, Warp Core Health is developing an AI-generated form that patients fill out once, and subsequently, only relevant information is presented for review and update based on the reason for the visit. This revolution in patient forms aims to streamline the healthcare experience, save time, and improve the overall efficiency of medical visits.
- The Current Challenge: Traditionally, patients are required to provide a comprehensive range of information during each visit, regardless of the reason for their appointment. This results in repetitive and time-consuming form filling, often causing frustration for patients who feel that the process is unnecessary and inefficient. Furthermore, healthcare providers must sift through extensive paperwork to locate the specific details relevant to the visit, creating an additional administrative burden.
- AI-Generated Smart Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms represent a significant advancement in the patient form process. With the power of artificial intelligence, these forms are designed to be dynamic and tailored to each patient’s specific needs. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, the smart forms intelligently analyze the reason for the visit and present only the relevant sections and questions for review and update.
- Personalized and Streamlined Experience: By eliminating the need to repeat previously provided information, patients can experience a more streamlined and personalized visit. With AI-generated smart forms, patients can focus on updating crucial details related to their current health condition, symptoms, or concerns. This targeted approach ensures that patients’ valuable time is maximized during their appointments, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering the most appropriate care.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Warp Core Health’s AI algorithms continually learn from patient data, allowing for improved accuracy and efficiency over time. As patients update their information during subsequent visits, the smart forms intelligently adapt and present new questions or prompts based on previous responses and the reason for the current visit. This iterative process ensures that patient information remains up-to-date and relevant, while minimizing redundant or unnecessary data entry.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems, creating a powerful synergy between patient information and form customization. As new data is added to the EHR, such as diagnoses, treatments, or test results, it further enhances the customization of smart forms for future visits. The AI algorithms analyze the updated EHR data and dynamically adjust the smart forms to ensure that patients are presented with the most relevant sections and questions specific to their follow-up or next visit. This dynamic customization optimizes the patient form experience, allowing for efficient updates and reviews of pertinent information while eliminating the need to navigate through irrelevant sections. By harnessing the power of EHR integration, Warp Core Health’s smart forms adapt to each patient’s evolving healthcare journey, ensuring a personalized and tailored experience throughout their medical visits.
- Data Security and Privacy: Warp Core Health places a high priority on maintaining the security and privacy of patient data. Their AI-generated smart forms are designed to adhere to stringent data protection regulations, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential. Robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards are implemented to safeguard patient privacy throughout the form-filling and data storage processes.
Conclusion: Warp Core Health’s pioneering efforts in developing AI-generated smart forms are set to revolutionize the patient form experience in healthcare. By leveraging artificial intelligence, these forms minimize repetitive data entry, present only relevant information for review and update, and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical visits. With seamless integration into electronic health record systems, Warp Core Health ensures that patient information remains up-to-date, contributing to improved continuity of care. As the healthcare industry embraces the power of AI technology, Warp Core Health’s innovative approach to patient forms promises to transform the patient experience, saving time, and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Author: Sharon Lojun, M.D., M.S.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
The Importance of AI in Advancing Global Health in 3rd World Countries
Introduction: In recent years, the world has witnessed the rapid advancements of artificial intelligence (AI) and its transformative potential across various industries. One area where AI holds immense promise is global health, particularly in third-world countries facing unique challenges in healthcare delivery. This article explores the importance of AI in addressing healthcare disparities, improving diagnosis and treatment, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, and ultimately saving lives in developing nations.
- Bridging Healthcare Disparities: Access to quality healthcare remains a significant challenge in many third-world countries. AI can play a pivotal role in bridging this gap by enabling remote healthcare services and telemedicine. Through AI-powered platforms, individuals in remote areas can receive medical consultations, access health information, and receive timely interventions, regardless of their physical location. This technology helps bring healthcare to underserved populations, reducing disparities and improving health outcomes.
- Enhancing Diagnosis and Treatment: AI has the potential to revolutionize diagnostic capabilities in resource-constrained settings. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including images, lab results, and patient records, to assist healthcare providers in accurate and timely diagnoses. AI can also support healthcare professionals in developing personalized treatment plans, predicting disease progression, and identifying potential complications, thereby improving patient care and reducing medical errors.
- Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure: Developing countries often face challenges in building and maintaining robust healthcare infrastructure. AI can support these efforts by optimizing resource allocation, streamlining patient flow, and improving operational efficiency. Predictive analytics can help anticipate disease outbreaks, allocate medical supplies, and optimize healthcare logistics. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide basic healthcare information, triage patients, and offer guidance, especially in areas with a shortage of healthcare professionals.
- Empowering Disease Surveillance and Prevention: AI technologies enable real-time monitoring of disease outbreaks, early detection of epidemics, and effective disease surveillance. Machine learning algorithms can analyze data from various sources, such as social media, online search trends, and healthcare databases, to identify patterns and potential threats. By empowering timely interventions and targeted preventive measures, AI can help prevent the spread of infectious diseases, improve vaccination campaigns, and strengthen public health responses.
- Facilitating Medical Research and Drug Discovery: AI accelerates medical research and drug discovery processes, offering hope for developing new treatments and therapies. Through AI-driven algorithms, vast amounts of biomedical data can be analyzed to identify potential drug targets, optimize clinical trials, and accelerate the development of cost-effective healthcare solutions. This not only benefits the local population but also contributes to the global scientific community, driving advancements in medicine and healthcare worldwide.
Conclusion: Artificial intelligence presents an unprecedented opportunity to revolutionize global health in third-world countries. By harnessing AI’s power, we can overcome healthcare disparities, enhance diagnosis and treatment, strengthen healthcare infrastructure, and empower disease surveillance and prevention efforts. As developing nations strive to improve the health and well-being of their populations, embracing AI in healthcare becomes crucial. Collaborative efforts among governments, healthcare providers, researchers, and technology experts are essential in unlocking the full potential of AI and creating a healthier future for all, regardless of geographical location or socioeconomic status.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Potential Impact of AI
by Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been making waves in the healthcare industry in recent years, with many experts predicting that it will revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered in the near future. From early disease detection to personalized treatment plans, AI has the potential to transform the healthcare landscape, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
One of the main areas where AI is expected to make a significant impact is in the early detection of diseases. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, such as medical images and genetic information, to identify patterns that may be indicative of a disease. For example, AI-powered imaging tools can help radiologists detect early signs of cancer, heart disease, and other conditions, allowing for earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
Another area where AI is expected to make a big impact is in personalized treatment plans. AI algorithms can analyze a patient’s medical history, genetic makeup, and other factors to create personalized treatment plans that are tailored to their specific needs. This can help healthcare providers deliver more effective treatments and reduce the risk of adverse reactions to medications.
AI can also help improve patient outcomes by predicting which patients are at risk of developing certain conditions. For example, AI algorithms can analyze patient data to identify those at high risk of developing diabetes or heart disease. This can help healthcare providers intervene early, providing preventive measures to reduce the risk of these conditions developing.
AI can also be used to improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery. For example, chatbots powered by AI can be used to provide patients with 24/7 access to basic medical information and advice, reducing the need for in-person consultations and freeing up healthcare providers to focus on more complex cases. AI-powered scheduling systems can also help healthcare providers manage their workload more efficiently, reducing waiting times for patients and improving the overall quality of care.
Despite the many potential benefits of AI in healthcare, there are also some challenges that need to be addressed. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that AI algorithms are accurate and reliable. To achieve this, it is important to ensure that the algorithms are based on high-quality data and that they are regularly tested and updated.
Another challenge is ensuring that AI is used in an ethical and responsible way. This means ensuring that patient data is kept secure and that AI algorithms are not used to discriminate against certain groups of people.
In conclusion, AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare in numerous ways. From early disease detection to personalized treatment plans, AI can help healthcare providers deliver more effective and efficient care, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. However, it is important to address the challenges associated with the use of AI in healthcare to ensure that it is used in an ethical and responsible way.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
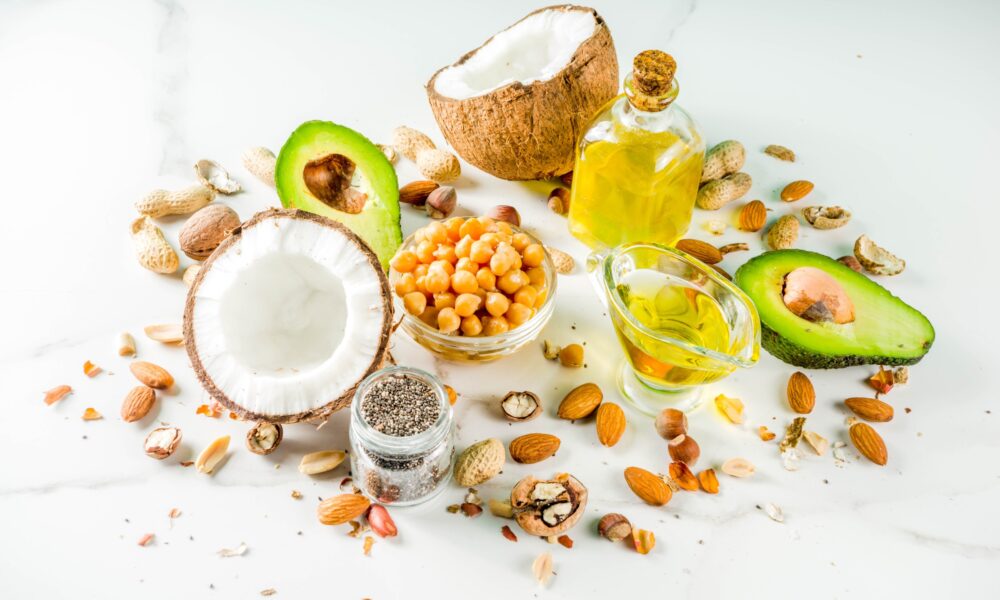
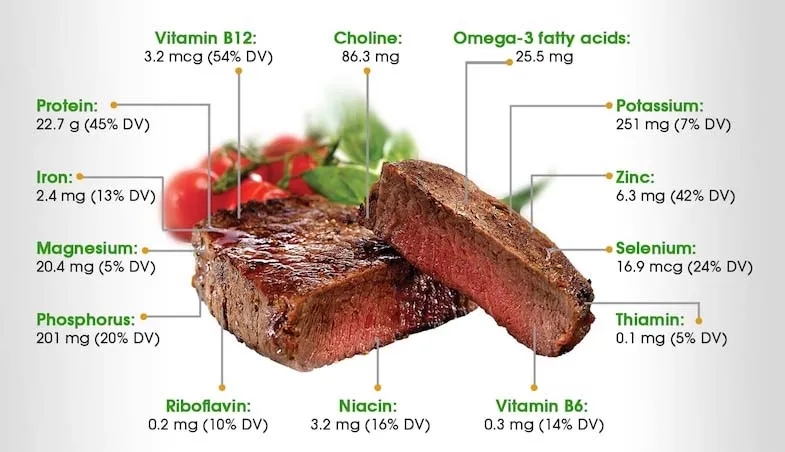
Essential Fat and Protein Sources for Vegans and Vegetarians on a Keto Diet
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: Following a ketogenic diet as a vegan or vegetarian can be challenging, as the focus on high fat and low carb intake requires careful consideration of food choices. However, with a wide range of nutrient-dense options available, it is possible to meet your fat and protein needs while adhering to a plant-based keto lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the best sources of fat and protein for vegans and vegetarians, with a special emphasis on keto-friendly choices.
Avocado: Nature’s Creamy Powerhouse (Keto-friendly) Avocado, the beloved green fruit, is not only a keto-friendly option but also a nutritional powerhouse. Packed with healthy monounsaturated fats, avocados provide a rich and creamy texture to dishes. They are also a source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent addition to a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet.
Nuts and Seeds: Crunchy Delights (Keto-friendly) Nuts and seeds are versatile and satisfying options for obtaining both healthy fats and protein. Almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds are all keto-friendly choices. These crunchy delights are not only great for snacking but can also be incorporated into recipes, such as nut butters or as toppings for salads and smoothies.
Nut and Seed Butters: Spreads of Goodness (Keto-friendly) Nut and seed butters, such as peanut butter, almond butter, and tahini, are delectable spreads that offer a generous dose of healthy fats and protein. They can be enjoyed on their own, added to smoothies, used as a dip for vegetables, or incorporated into keto-friendly baking recipes.
Coconut and Coconut Oil: Tropical Treasures (Keto-friendly) Coconut and its derivatives are keto-friendly options that bring a tropical twist to your meals. Coconut meat, coconut oil, and coconut milk are rich in healthy fats and can be used in various keto recipes, from curries to smoothies. Coconut milk, with its creamy texture, can be a great base for vegan ketogenic dishes.
Olive Oil: Liquid Gold (Keto-friendly) Olive oil, a staple in the Mediterranean diet, is a source of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. It is ideal for cooking or as a dressing for salads and vegetables, adding flavor and healthy fats to your meals.
Plant-Based Oils: A Flavorful Spectrum (Keto-friendly) Other plant-based oils, such as avocado oil, flaxseed oil, and sesame oil, offer a diverse range of flavors and are excellent sources of healthy fats for a vegan or vegetarian keto diet. These oils can be used for sautéing, roasting, and dressing to enhance the taste and nutritional profile of your dishes.
Legumes: Protein Powerhouses While not strictly keto-friendly due to their higher carb content, legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are still valuable sources of plant-based protein for vegans and vegetarians. They can be included in moderation, considering individual carb limits and dietary preferences.
Tofu and Tempeh: Plant-Based Protein Staples Tofu and tempeh, derived from soybeans, are versatile plant-based protein sources. They can be used in a variety of dishes, including stir-fries, salads, and curries. These options provide protein while keeping carbohydrate intake relatively low, making them suitable for a vegan or vegetarian keto diet.
Seitan: Meaty Texture, Plant-Based Protein Seitan, made from wheat gluten, is a high-protein option for those following a vegan or vegetarian keto diet. With its meaty texture and ability to absorb flavors, seitan is a versatile ingredient that can be used to create delicious and satisfying plant-based dishes.
Quinoa: The Complete Protein Grain Quinoa, though higher in carbs compared to other options, is a complete protein source that contains all essential amino acids. While it should be consumed in moderation on a ketogenic diet, quinoa can be a nutritious addition to a vegan or vegetarian keto meal plan when carefully portioned.
Conclusion: Maintaining a well-rounded vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet requires careful consideration of fat and protein sources. Fortunately, there is a wide array of options available that cater to these needs. Avocado, nuts, seeds, coconut, olive oil, plant-based oils, legumes in moderation, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and quinoa (in limited amounts) offer a range of essential fats and protein for individuals following a plant-based keto lifestyle.
Remember to personalize your food choices according to your specific dietary goals and preferences. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that your nutrient intake aligns with your needs and to optimize your health while following a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet. Embrace the diversity of these plant-based options, and enjoy the benefits of a well-balanced and nourishing diet.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
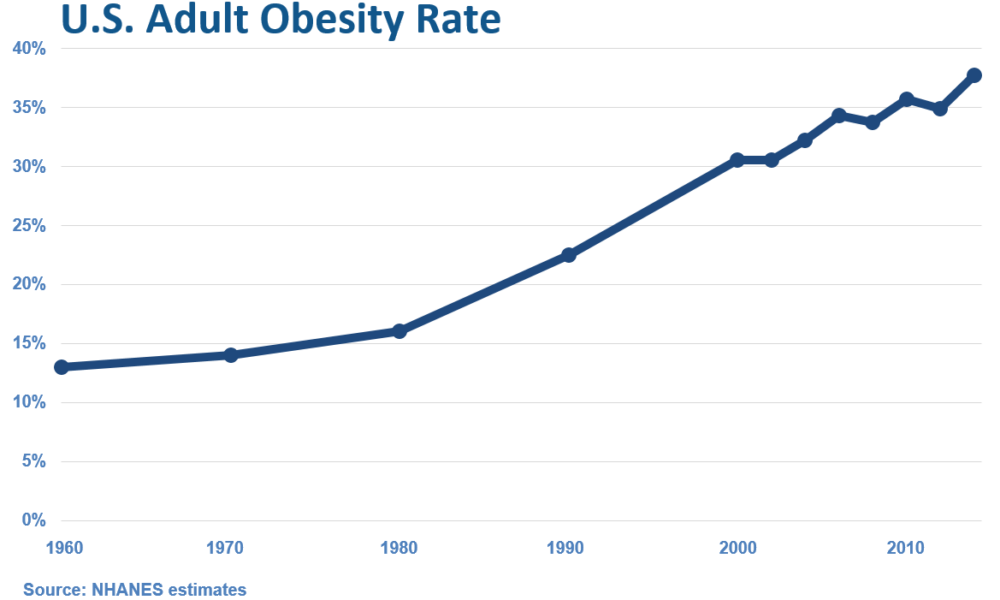
The Rise of Overweight/Obesity in the U.S.: Examining the Influence of Dietary Guidelines, the Food Pyramid, and Ancel Keys
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The United States has experienced a significant increase in overweight and obesity rates over the past few decades, leading to serious health concerns. It is intriguing to examine the correlation between the rise in overweight/obesity and the transformation of the American diet, particularly with the introduction of dietary guidelines and the prominent role played by Ansel Keys. In this article, we delve into the historical context and explore how the shift away from fresh whole foods, influenced by Keys’ research, may have inadvertently contributed to the obesity epidemic in the United States.
The Era of Fresh Whole Foods: Before the introduction of dietary guidelines in the 1980s, the American diet primarily consisted of fresh, whole foods. Meals were often prepared from scratch, using ingredients sourced directly from farms and local markets. Fresh fruits and vegetables, meats, and unprocessed grains were the foundation of everyday eating, providing a nutrient-dense and balanced approach to nutrition.
Ansel Keys and Dietary Fat: Ansel Keys, a prominent scientist, conducted influential research in the mid-20th century that examined the relationship between dietary fat and heart disease. His work, known as the “Seven Countries Study,” suggested a correlation between high-fat diets and increased risk of cardiovascular issues. However, Keys’ study focused on selected countries, disregarding nations with contrasting dietary patterns that contradicted his findings.
The Impact of Keys’ Findings: Keys’ research gained significant attention and led to a shift in nutritional thinking. Dietary fat, particularly saturated fat, became vilified, and the notion that a low-fat diet was crucial for maintaining heart health took root. As a result, dietary guidelines and recommendations began emphasizing the reduction of fat intake, leading to the promotion of low-fat and fat-free products in the market.
The Emergence of Processed Foods: The low-fat movement led to a surge in processed food products marketed as healthy alternatives. With the focus on reducing fat, manufacturers started formulating products with reduced fat content but compensated by adding excessive amounts of sugar, artificial additives, and refined carbohydrates. This shift in the food industry coincided with the introduction of dietary guidelines, further driving the consumption of processed foods among Americans.
Unintended Consequences: The shift away from fresh whole foods towards processed, low-fat alternatives had unintended consequences. These processed foods were often calorie-dense, nutrient-poor, and contributed to overconsumption. The replacement of dietary fats with refined carbohydrates and added sugars not only affected overall calorie intake but also disrupted metabolic processes, leading to weight gain and related health issues.
Reevaluating Dietary Choices: In recent years, there has been a growing realization that the previous low-fat paradigm may have played a role in the obesity epidemic. Many experts advocate for a return to a more balanced approach, focusing on the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods and reevaluating the role of dietary fats. This includes embracing healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, olive oil, fatty meats, eggs, butter, and cheeses.
Empowering Individuals through Education: To combat the rise of overweight/obesity, it is essential to empower individuals with knowledge and encourage them to make informed dietary choices. By educating ourselves about the benefits of fresh whole foods, understanding the potential pitfalls of processed foods, and reevaluating the role of dietary fats, we can make strides towards improving our overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: The rise of overweight and obesity in the United States coincides with the transformation of the American diet, influenced by the introduction of dietary guidelines and the impact of Ansel Keys’ research. While Keys’ findings had noble intentions, the emphasis on low-fat diets and the
proliferation of processed, low-fat alternatives may have inadvertently contributed to the obesity epidemic. It is important to acknowledge the historical context and the role played by fresh whole foods in the American diet before the era of dietary guidelines. By revisiting and embracing a diet centered around whole, unprocessed foods, we can reclaim a healthier approach to nutrition.
Moving forward, it is crucial to continue educating individuals about the importance of a balanced diet that includes nutrient-dense foods and minimizes reliance on processed and refined options. By fostering a culture of mindful eating and promoting the consumption of fresh, whole foods, we can work towards reversing the alarming trends of overweight and obesity and promoting a healthier future for all.
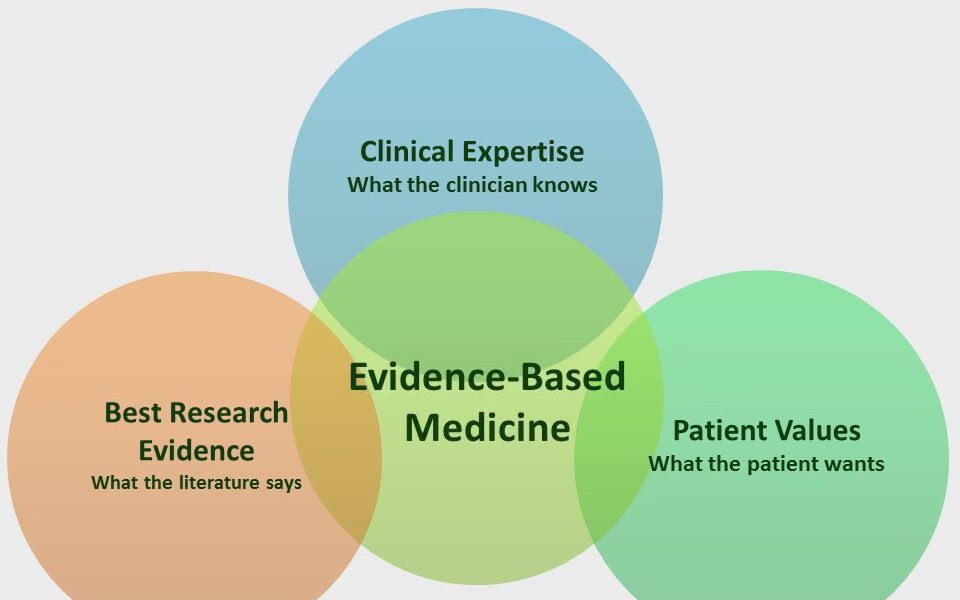
Coding Evidence-Based Medicine into Web-Based Applications
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is a medical approach that involves using the best available evidence to make informed clinical decisions. The goal of EBM is to improve the quality of patient care by integrating research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient preferences into clinical decision making. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using technology to support EBM and help clinicians make evidence-based decisions. Web-based applications are a popular way to accomplish this goal.
Web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence, as well as clinical practice guidelines and other relevant resources. These applications can help clinicians make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of a wide range of medical conditions.
The process of building a web-based EBM application involves several steps. The first step is to identify the target audience and determine the specific clinical needs that the application will address. This may involve conducting a needs assessment and identifying gaps in current clinical practice.
The second step is to identify relevant EBM resources and integrate them into the application. This may involve using electronic databases, such as PubMed or Cochrane Library, to search for the latest research evidence. It may also involve incorporating clinical practice guidelines, systematic reviews, and other evidence-based resources into the application.
Once the relevant EBM resources have been identified, the next step is to design the application’s user interface. The application should be easy to navigate, intuitive to use, and provide users with relevant information at the appropriate time. The design of the application should be based on user-centered design principles, which involve actively involving users in the design process and incorporating their feedback into the final product.
After the application has been designed, the next step is to develop the application using web development languages and frameworks such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React. The application may also incorporate server-side programming languages such as PHP or Python, and databases such as MongoDB or MySQL to store and retrieve data.
Finally, the application should be tested and validated to ensure that it is functioning as intended and providing accurate and reliable information to users. This may involve user testing, where the application is tested by actual users, as well as usability testing, where the application is tested for ease of use and effectiveness.
In conclusion, web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence and clinical practice guidelines, helping them make informed decisions about patient care. The development of these applications involves identifying the target audience and their clinical needs, integrating relevant EBM resources, designing an intuitive user interface, developing the application using web development languages and frameworks, and testing and validating the application to ensure that it is effective and reliable. By following these steps, developers can build web-based EBM applications that improve patient care and support evidence-based decision making in clinical practice.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
A Step-by-Step Guide to Coding a Personal Health Record
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
A personal health record (PHR) is a digital tool that allows individuals to maintain and manage their health information in a secure and accessible way. PHRs can be created by healthcare providers or individuals themselves. In this article, we will discuss the steps to coding a PHR.
Step 1: Define the data model
The first step in coding a PHR is to define the data model. This involves identifying the different types of health information that will be stored in the PHR. The data model should include the patient’s demographic information, medical history, medications, allergies, immunizations, laboratory results, and other relevant health information. The data model should also define the relationships between different types of information.
Step 2: Choose a programming language
The next step is to choose a programming language for coding the PHR. There are many programming languages to choose from, including Java, Python, Ruby, and PHP. The choice of programming language will depend on the developer’s expertise, the features required, and the platform on which the PHR will be deployed.
Step 3: Design the user interface
The user interface (UI) is the part of the PHR that patients will interact with. The UI should be intuitive and easy to use. It should allow patients to input and view their health information, as well as update and share it with healthcare providers. The design of the UI should be based on best practices for user experience (UX) and accessibility.
Step 4: Develop the back-end
The back-end of the PHR is the part of the application that handles the storage and retrieval of data. The back-end should be designed to ensure the security and confidentiality of patient health information. It should also be scalable and efficient, to handle large volumes of data and support future expansion.
Step 5: Integrate with other systems
PHRs need to integrate with other healthcare systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), health information exchanges (HIEs), and patient portals. Integration with these systems will allow patients to access their health information from different sources, and share it with healthcare providers as needed.
Step 6: Test and deploy
Before deploying the PHR, it is essential to test it thoroughly to ensure that it works as expected and meets the needs of patients and healthcare providers. Testing should include functionality testing, performance testing, security testing, and user acceptance testing. Once testing is complete, the PHR can be deployed on a secure platform, such as a cloud-based server or a local server.
Conclusion
Coding a PHR requires careful planning and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this article, developers can create a PHR that is secure, scalable, and user-friendly. A well-designed PHR can empower patients to take control of their health information, improve healthcare outcomes, and support the delivery of personalized and coordinated healthcare services.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Building Prototypes for Healthcare Using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Building prototypes is an essential step in the healthcare software development process. It allows developers to test and refine their ideas, improve user experience, and identify potential issues before investing significant time and resources into building a fully functional application. In this article, we will discuss how to build prototypes for healthcare using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL.
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the three fundamental technologies used to build prototypes for web applications. HTML is used to define the structure and content of web pages, CSS is used to style and format the pages, and JavaScript is used to add interactivity and functionality. These technologies are used to create the front-end of a web application, which is the part of the application that users interact with.
PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting language that is used to build dynamic web applications. It is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that interact with databases and other server-side components. PHP is used to create the back-end of a web application, which is the part of the application that is responsible for processing user input, interacting with databases, and generating dynamic content.
React
React is a popular front-end JavaScript library that is used to build user interfaces. It is used to create interactive and responsive user interfaces that can be easily updated and modified. React is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that provide a modern and user-friendly interface.
Python
Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in healthcare software development. It is used to build server-side components, machine learning models, data analysis tools, and more. Python is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that perform complex data analysis and provide advanced features such as natural language processing and machine learning.
MongoDB and MySQL
MongoDB and MySQL are two popular database management systems used in healthcare software development. MongoDB is a document-based NoSQL database that is used to store and retrieve large amounts of unstructured data. MySQL is a relational database management system that is used to store and retrieve structured data. Both databases are commonly used in healthcare software development to store patient data, medical records, and other healthcare-related information.
Conclusion
Building prototypes for healthcare using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL is an effective way to test and refine healthcare software ideas before investing significant time and resources into building a fully functional application. By using these technologies, healthcare software developers can create modern and user-friendly web applications that provide advanced features such as data analysis, machine learning, and natural language processing. With the right tools and skills, healthcare software developers can build prototypes that provide value to patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare organizations.