- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: CAC
Unlocking the Benefits of Vitamin K2: Clearing Arterial Calcium and Achieving a CAC Score of Zero
by Stephen Fitzmeyer
Introduction: Maintaining cardiovascular health is a top priority for many individuals seeking to lead a long and vibrant life. While regular exercise, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are crucial elements, recent research has shed light on the potential benefits of vitamin K2 in promoting arterial health. In this article, we delve into the role of vitamin K2 in clearing calcium from arteries, leading to the desirable achievement of a coronary artery calcium (CAC) score of zero.
Understanding the Role of Calcium in Arteries: Calcium is an essential mineral for our body, contributing to the formation and strength of bones and teeth. However, when calcium starts accumulating in arterial walls, it can lead to the formation of plaque, narrowing the arteries and hindering blood flow. This process, known as arterial calcification, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes.
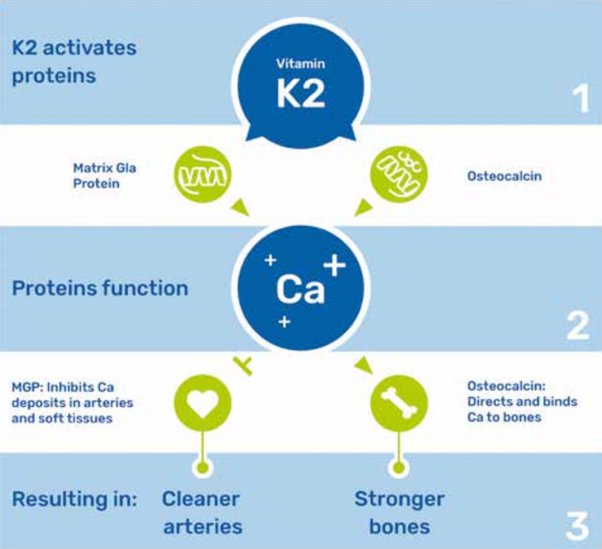
Vitamin K2: A Key Player in Arterial Health: Emerging research suggests that vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in maintaining arterial health by effectively managing calcium levels in the body. Vitamin K2 activates proteins that shuttle calcium away from arteries and deposit it in bones, where it is needed. By doing so, vitamin K2 helps to prevent and even reverse arterial calcification.
Clearing Arterial Calcium with Vitamin K2: One of the most remarkable aspects of vitamin K2 is its potential to clear existing arterial calcium deposits. Studies have shown that by ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin K2, individuals with arterial calcification may experience a reduction in the severity of plaque buildup over time. This can lead to improved arterial flexibility and reduced cardiovascular risks.
Achieving a CAC Score of Zero: A coronary artery calcium (CAC) score is a measure of the amount of calcium buildup in the coronary arteries. A score of zero indicates no detectable calcium, which is considered an optimal outcome. While multiple factors contribute to achieving a CAC score of zero, including lifestyle choices and genetics, incorporating vitamin K2 into your routine may play a significant role in promoting arterial health and minimizing calcium deposits.
How to Incorporate Vitamin K2 into Your Routine: To maximize the potential benefits of vitamin K2, it is important to ensure an adequate intake of this nutrient. Vitamin K2 can be found in certain foods, including fermented dairy products, organ meats, and certain cheeses. However, for those who may have limited access to these sources or have dietary restrictions, vitamin K2 supplements are widely available and offer a convenient way to meet the recommended daily intake.
Consult with a Healthcare Professional: As with any dietary change or supplement regimen, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating vitamin K2 into your routine. They can assess your individual health needs, provide guidance on appropriate dosages, and help monitor the progress of arterial health through regular check-ups and assessments.
Conclusion: Achieving optimal arterial health and aiming for a CAC score of zero is a significant goal for cardiovascular well-being. While there are multiple factors at play, emerging research highlights the potential of vitamin K2 in promoting arterial health and clearing arterial calcium. By incorporating vitamin K2 into your routine and consulting with a healthcare professional, you can take proactive steps towards supporting your cardiovascular health and enjoying a life free from the burden of arterial calcification.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
CAC: The Ultimate Test for Assessing Health and Why You Need One Now!
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, staying proactive and prioritizing preventive measures is key to maintaining optimal health. The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test has recently emerged as a groundbreaking tool in health assessment, providing invaluable insights into cardiovascular health. This article highlights the significance of CAC as the ultimate test for assessing health and emphasizes why individuals should consider getting one now to safeguard their well-being. Additionally, we’ll explore how patients can easily obtain a CAC scan for themselves.
Understanding CAC Scoring
The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test employs non-invasive computed tomography (CT) scans to detect the presence and extent of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. By quantifying the amount of calcium present, it calculates a CAC score, effectively gauging the overall burden of atherosclerosis in the arteries. This score serves as a crucial predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD), empowering individuals to take preventive action.
The Urgency of CAC as a Health Indicator
- Early Detection of Silent Risks: CAC scoring enables early detection of potential cardiovascular issues, even before symptoms manifest. By identifying calcified plaque deposits, healthcare professionals can determine an individual’s risk of experiencing a heart attack or developing coronary artery disease (CAD). Seeking a CAC test now can help unveil hidden risks and prompt timely interventions to prevent disease progression.
- Personalized Risk Assessment: Unlike traditional risk assessment tools, CAC scoring provides a precise evaluation of atherosclerosis. Through quantitative analysis, it offers a more accurate estimation of an individual’s risk of developing CVD. Obtaining a CAC score now empowers healthcare providers to devise personalized treatment plans tailored to an individual’s level of risk, enabling timely interventions and better health outcomes.
- Empowerment for Lifestyle Changes: CAC scoring serves as a powerful motivator for individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles. Witnessing the presence and extent of calcified plaque acts as a visual reminder of the importance of positive changes in diet, exercise, and stress management. By getting a CAC test now, you can proactively take charge of your health, making informed decisions and fostering long-term adherence to beneficial lifestyle modifications.
- Preventive Measures for Long-Term Health: CAC scoring facilitates proactive preventive measures by categorizing individuals into different risk groups based on their CAC scores. This allows healthcare providers to implement appropriate treatments and interventions to reduce the risk of CVD. Taking action now, based on your CAC score, can significantly improve your long-term cardiovascular health and well-being.
How to Obtain a CAC Scan
To obtain a CAC scan, you can follow these steps:
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your interest in getting a CAC scan. They will evaluate your medical history, risk factors, and overall health to determine if a CAC scan is appropriate for you.
- Referral and Imaging Facility: If your healthcare provider determines that a CAC scan is necessary, they will provide you with a referral to an imaging facility or radiology center equipped to perform the scan.
- Schedule the Scan: Contact the recommended imaging facility and schedule your CAC scan appointment. They will provide you with any necessary instructions, such as fasting requirements or medication restrictions before the test.
- The CAC Scan Procedure: During the CAC scan, you will lie on a table that moves through a CT scanner. The scan is quick and painless, typically taking only a few minutes to complete.
- Results and Follow-up: Once the scan is complete, the radiologist will analyze the images and calculate your CAC score. Your healthcare provider will then review the results with you. They will explain the implications of your CAC score, discuss any necessary lifestyle modifications or medical interventions, and develop a personalized plan to mitigate your cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion
The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test is a powerful tool for assessing cardiovascular health and preventing future complications. By identifying silent risks, providing personalized risk assessment, motivating lifestyle changes, and enabling proactive preventive measures, CAC scoring empowers individuals to take control of their well-being. To obtain a CAC scan, consult your healthcare provider, obtain a referral to an imaging facility, schedule the scan, and discuss the results and follow-up plan with your healthcare provider. Take the proactive step towards optimizing your health and consider getting a CAC scan now. Your heart and overall well-being will thank you for it.
CAC Score
After undergoing a CAC scan, you will receive a CAC score that falls within a specific range. Here are the general ranges and their corresponding meanings:
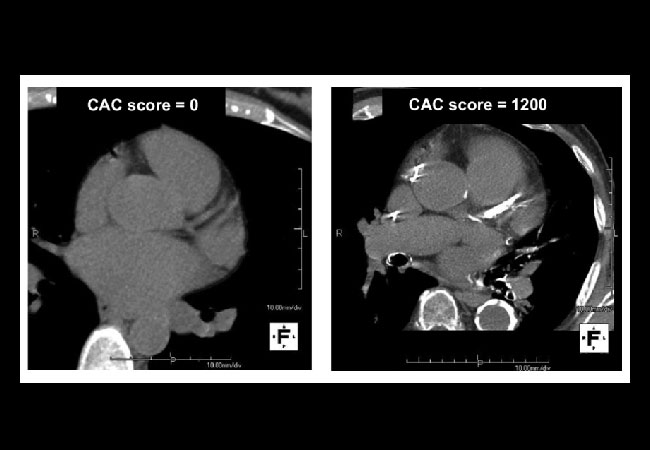
- CAC Score of 0: A CAC score of 0 indicates the absence of detectable calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This suggests a very low risk of cardiovascular events, and individuals in this range often have a favorable prognosis.
- CAC Score of 1-99: A CAC score between 1 and 99 indicates the presence of mild calcification in the coronary arteries. This range signifies a low to moderate risk of cardiovascular disease, and it is an opportunity for individuals to implement preventive measures to reduce the progression of plaque formation.
- CAC Score of 100-399: A CAC score between 100 and 399 represents the presence of moderate calcification in the coronary arteries. This range suggests a significant risk of cardiovascular disease, and it necessitates more aggressive preventive strategies and medical interventions to reduce the risk of future complications.
- CAC Score of 400 or Higher: A CAC score of 400 or higher indicates extensive calcification in the coronary arteries. This range represents a high risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. It necessitates immediate and intensive medical interventions, including lifestyle modifications and potential medication therapies, to mitigate the risk and prevent further progression.
By understanding the range of CAC scores and their implications, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that addresses their specific risk level.
To obtain a CAC scan, consult your healthcare provider, obtain a referral to an imaging facility, schedule the scan, and discuss the results and follow-up plan with your healthcare provider. Take the proactive step towards optimizing your health and consider getting a CAC scan now. Your heart and overall well-being will thank you for it.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/