- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: FHIR
Accessing Siloed EMR Systems with FHIR: Connecting to Multiple EMRs
In today’s healthcare landscape, the ability to connect to multiple EMRs (Electronic Medical Records) seamlessly has become crucial for improving patient care, reducing administrative overhead, and driving innovation. However, the diversity in EMR systems, proprietary data formats, and communication protocols has historically made integration a daunting challenge. Enter FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), the game-changing standard developed by HL7 (Health Level Seven International), which is paving the way for interoperability in healthcare.
The Problem: Siloed EMR Systems
Healthcare providers often use different EMR systems, each designed with unique data structures, interfaces, and workflows. While these systems are essential for managing patient information, they don’t “talk” to each other natively. This lack of interoperability creates data silos, leading to:
- Inefficiencies: Manual data entry and reconciliation slow down workflows.
- Fragmented Care: Providers may not have access to a complete patient history.
- Missed Opportunities: Innovations like patient-facing apps and decision-support tools struggle to integrate across multiple platforms.
The Solution: FHIR as a Universal Language
FHIR offers a standardized framework for accessing and exchanging healthcare information. By leveraging its RESTful API architecture and well-defined data models (resources), FHIR enables seamless integration across multiple EMRs. Here’s how:
- Unified Data Access via FHIR APIs Modern EMR systems like Epic, Cerner, and Allscripts have adopted FHIR APIs as part of their platforms. This standardization allows external applications to retrieve and interact with data like patient demographics, medications, and lab results without requiring custom integration for each EMR.
- Standardized Resources FHIR resources—such as Patient, Observation, Encounter, and Medication—act as reusable data models. These resources provide a consistent structure across systems, making it easier for developers to query and update data in a predictable way, regardless of the underlying EMR.
- SMART on FHIR for Authentication The SMART on FHIR framework adds an additional layer by standardizing the way apps authenticate and gain authorized access to EMR data using OAuth 2.0. This ensures secure, scalable integration while respecting patient privacy and data security regulations like HIPAA.
Benefits of Connecting to Multiple EMRs
- Streamlined Care Coordination FHIR enables providers to access and share patient data across different healthcare systems. A specialist in one hospital can view relevant records from another provider’s EMR, ensuring continuity of care.
- Simplified Integration for Developers Developers can create third-party applications, such as telehealth platforms or chronic disease management tools, that work with multiple EMRs out of the box. Instead of writing custom connectors for each system, developers interact with a single FHIR-based API.
- Empowering Patients Patient-facing apps can use FHIR to aggregate data from multiple EMRs, giving individuals a unified view of their health records. This transparency improves patient engagement and health outcomes.
- Faster Innovation The reduced complexity of integrating with EMRs allows startups and innovators to focus on building features that directly improve care delivery rather than wrestling with legacy integration challenges.
Challenges to Consider
While FHIR greatly simplifies the process of connecting to multiple EMRs, it’s not without challenges:
- Vendor Variability: Not all EMRs implement FHIR in the same way. Developers may encounter slight differences in API behavior across systems.
- Data Gaps: Older EMRs or smaller providers might not support FHIR, requiring fallback mechanisms.
- Access Control: Even with FHIR, gaining authorized access to data involves navigating organizational policies and regulatory requirements.
The Future of EMR Connectivity
As FHIR adoption continues to grow, the dream of a truly interoperable healthcare ecosystem is becoming a reality. Initiatives like the 21st Century Cures Act in the United States mandate that EMR vendors provide FHIR APIs to improve data access and patient empowerment. This regulatory push, combined with advancements in technology, means that healthcare organizations can now leverage FHIR to unlock the full potential of their data.
Conclusion
Connecting to multiple EMRs is no longer an insurmountable challenge. With FHIR as the universal standard, healthcare providers, developers, and patients can break down data silos, enabling seamless information exchange and fostering innovation. Whether you’re building a new application or improving workflows in your organization, FHIR offers the tools to bridge the gaps between EMRs and create a more connected healthcare future.
Pillars of Excellence: Key Standards in the Healthcare Industry
Introduction
The healthcare industry is marked by its unwavering commitment to patient care, safety, and the pursuit of excellence. To maintain the highest standards in patient treatment, healthcare professionals adhere to a set of well-defined guidelines and standards. In this article, we explore the key standards in the healthcare industry that serve as the foundation for quality care and patient safety.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA, which we discussed in a previous article, is a cornerstone of healthcare standards. Its Privacy and Security Rules ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information. HIPAA also facilitates secure electronic data exchange, safeguarding patient privacy.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care focuses on the individual’s needs, preferences, and values. It encourages active patient involvement in healthcare decisions, considering their physical and emotional well-being. Effective communication and shared decision-making are key components of this standard.
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Clinical practice guidelines are evidence-based recommendations for healthcare professionals to provide high-quality care for specific medical conditions. These guidelines are continually updated to reflect the latest research, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Infection Control
Infection control standards are crucial for maintaining patient safety. Healthcare facilities strictly adhere to practices designed to prevent the spread of infections. Hand hygiene, sterilization, and sanitation procedures are key components of infection control.
Accreditation and Certification
Healthcare institutions often seek accreditation and certification from organizations like The Joint Commission, which set high standards for patient care and safety. Compliance with these standards demonstrates an organization’s commitment to quality healthcare delivery.
EHR (Electronic Health Record) Standards
With the transition to electronic health records, interoperability and data standards are essential. These standards ensure that patient information can be accurately and securely exchanged between healthcare systems, promoting continuity of care.
Patient Safety Goals
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) establish patient safety goals that healthcare providers worldwide must strive to meet. These goals include improving medication safety, reducing healthcare-associated infections, and preventing patient falls.
Nursing Standards
Nursing practice is guided by standards set by organizations like the American Nurses Association (ANA). These standards define the responsibilities and expectations for nursing practice, ensuring the delivery of safe and effective care.
Mental Health Standards
Mental health standards ensure that patients with mental health conditions receive appropriate and compassionate care. These standards include the provision of crisis intervention and psychosocial support.
Ethical Standards
Ethical standards in healthcare encompass a wide range of principles, including patient confidentiality, informed consent, and truth-telling. These standards guide the behavior and decision-making of healthcare professionals, ensuring the highest ethical standards in patient care.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry’s commitment to excellence and patient well-being is evident in the multitude of standards and guidelines that govern its practice. These standards touch on various aspects of healthcare, from privacy and data security to patient safety and ethical conduct. Adherence to these standards is not just a requirement but a reflection of the industry’s dedication to providing the best possible care to patients, ensuring their safety, and upholding the highest standards of professionalism and ethics. In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, these standards remain the pillars of excellence that drive the industry forward.
Using Python to Parse HL7 and CCD Documents in Healthcare
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Python is a powerful programming language that can be used to parse and manipulate healthcare data in the HL7 and CCD formats. In this article, we will explore how to use Python to extract and process data from HL7 and CCD documents.
First, let’s start by understanding the structure of HL7 and CCD documents. HL7 messages are comprised of segments, which contain fields and subfields that represent different types of data. CCD documents, on the other hand, are based on the HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) standard and use XML to represent the data.
To parse HL7 messages in Python, we can use the hl7apy library, which is an open-source Python library for working with HL7 messages. Here’s an example of how to use hl7apy to extract patient demographic information from an HL7 message:
from hl7apy.parser import parse_message
# Parse the HL7 message
msg = parse_message(‘MSH|^~\&|HIS|BLG|LIS|BLG|20200528163415||ADT^A04|MSG0001|P|2.3||||||UNICODE’)
# Get the patient name
patient_name = msg.pid[5][0].value
# Get the patient date of birth
dob = msg.pid[7].value
# Get the patient sex
sex = msg.pid[8].value
# Print the patient information
print(“Patient Name: ” + patient_name)
print(“Date of Birth: ” + dob)
print(“Sex: ” + sex)
##########
In this example, we’re using the parse_message() method from the hl7apy library to parse the HL7 message. We then use the message object to extract the patient name, date of birth, and sex from the PID segment.
To parse CCD documents in Python, we can use the ElementTree library, which is included in the Python standard library. Here’s an example of how to use ElementTree to extract medication information from a CCD document:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Parse the CCD document
tree = ET.parse(‘ccd.xml’)
# Get the medication section
medications = tree.findall(‘.//{urn:hl7-org:v3}section[@code=”10160-0″]/{urn:hl7-org:v3}entry/{urn:hl7-org:v3}substanceAdministration’)
# Print the medication information
for med in medications:
drug_name = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}consumable/{urn:hl7-org:v3}manufacturedProduct/{urn:hl7-org:v3}manufacturedMaterial/{urn:hl7-org:v3}name/{urn:hl7-org:v3}part’).text
dosage = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}doseQuantity/{urn:hl7-org:v3}value’).text
start_date = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}effectiveTime/{urn:hl7-org:v3}low’).attrib[‘value’]
end_date = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}effectiveTime/{urn:hl7-org:v3}high’).attrib[‘value’]
print(“Drug Name: ” + drug_name)
print(“Dosage: ” + dosage)
print(“Start Date: ” + start_date)
print(“End Date: ” + end_date)
##########
In this example, we’re using the findall() method from the ElementTree library to find all the medication sections in the CCD document. We then use the find() method to extract the drug name, dosage, start and end date for each medication and print out the results.
Using Python to parse HL7 and CCD documents can be very useful in healthcare applications. For example, we can use these techniques to extract and analyze data from electronic health records (EHRs) to identify patterns and trends in patient care and outcomes. This can help healthcare providers to improve the quality of care, reduce costs, and enhance patient safety.
In conclusion, Python is a powerful tool for parsing and manipulating healthcare data in the HL7 and CCD formats. By using Python to extract and process data from these documents, we can gain valuable insights into patient care and outcomes, which can help to improve healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
HL7: The Technicalities and Use Cases in Healthcare
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
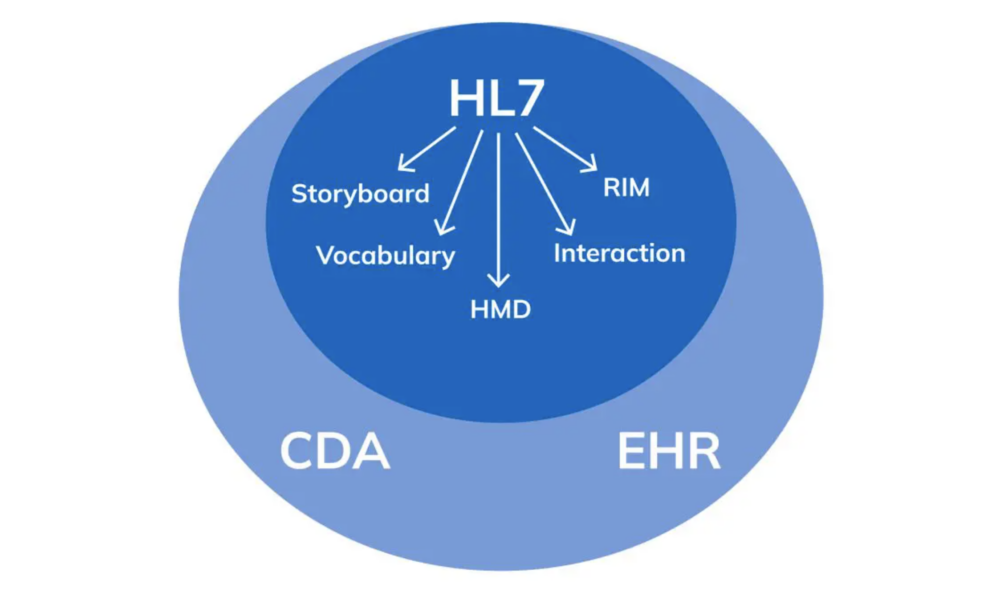
HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a widely adopted standard in healthcare for exchanging information between various healthcare applications, such as electronic health record systems, laboratory information systems, and radiology information systems. The standard defines a set of rules and formats for the exchange of clinical and administrative data. In this article, we will explore the technicalities of HL7 and provide examples of how it can be used in healthcare.
HL7 is composed of several messages, each containing one or more segments. Segments are made up of fields, and fields can contain subfields. Each segment contains information about a specific aspect of a patient’s clinical or administrative data. The most common message types in HL7 are the ADT (Admit, Discharge, Transfer), ORM (Order), and ORU (Observation Result) messages.
For example, an ADT message might contain information about a patient’s admission to the hospital, including their demographic information, admission date and time, and the admitting physician’s name. An ORM message might contain information about a laboratory test order, including the test name, patient’s name, and date and time the test was ordered. An ORU message might contain information about the results of a laboratory test, including the test name, patient’s name, and the actual test results.
HL7 can be used in a variety of ways to exchange data between healthcare applications. For example, a laboratory information system might send an ORU message to an electronic health record system when the results of a laboratory test are ready. The electronic health record system can then display the results to the provider, allowing them to make informed decisions about the patient’s care.
Another example is the use of HL7 in medical billing. A hospital’s billing system might receive ADT messages from an electronic health record system when a patient is admitted, transferred, or discharged. The billing system can then use this information to generate a claim for payment from the patient’s insurance company.
In addition to facilitating data exchange between healthcare applications, HL7 can also be used to integrate clinical decision support systems (CDSS) into electronic health record systems. CDSS systems can analyze patient data and provide recommendations to providers, such as suggesting alternative medications or highlighting potential drug interactions. By integrating CDSS systems with electronic health record systems using HL7, providers can make more informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, HL7 is a widely adopted standard in healthcare for exchanging clinical and administrative data between various healthcare applications. HL7 messages contain segments and fields that contain patient data, and there are several message types used for different purposes. HL7 can be used to exchange data between applications, integrate CDSS systems into electronic health record systems, and facilitate medical billing. By adopting HL7, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and streamline administrative processes.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/