- Home
- About
- Portfolio
- Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
- Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
- HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
- Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
- MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
- Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
- Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
- SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
- Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
- Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
- VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: Clinical Informatics
Unlocking the Power of Health Informatics: Why It Matters
Introduction
Health informatics is a rapidly growing field that combines healthcare, information technology, and data science to transform the way we manage and utilize health-related information. In the digital age, health informatics plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient care, improving healthcare processes, and driving medical research. In this article, we delve into the importance of health informatics and the manifold ways in which it positively impacts the healthcare industry.
Enhanced Patient Care
Health informatics improves patient care by providing healthcare professionals with instant access to accurate and up-to-date patient information. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) store patient histories, test results, medications, and treatment plans, reducing the risk of medical errors and ensuring that the right treatment is delivered to the right patient.
Efficient Healthcare Processes
Health informatics streamlines administrative and clinical processes in healthcare. It reduces paperwork, automates scheduling and billing, and facilitates communication among healthcare providers. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces costs, making healthcare more accessible.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Health informatics leverages data analysis to inform healthcare decisions. By analyzing trends and patterns, healthcare providers can make more informed choices about patient care and resource allocation, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
The integration of health informatics in telemedicine enables remote consultations and monitoring of patients. This is particularly crucial in reaching patients in underserved or remote areas, providing access to quality healthcare that might otherwise be unattainable.
Public Health Surveillance
Health informatics supports public health initiatives by monitoring the spread of diseases and identifying potential outbreaks. Surveillance systems can help health agencies respond swiftly to emerging health threats.
Medical Research and Innovation
Health informatics aids medical research by facilitating access to vast pools of patient data. Researchers can analyze this data to discover new treatments, study disease trends, and develop innovative medical technologies.
Patient Engagement and Empowerment
Health informatics encourages patients to take an active role in their health. Patient portals allow individuals to access their own health records, communicate with healthcare providers, and make informed decisions about their care.
Interoperability and Data Sharing
Standardized data formats and interoperability among healthcare systems enable seamless sharing of patient information across different healthcare providers. This ensures continuity of care and prevents duplication of tests and procedures.
Healthcare Quality Improvement
Health informatics enables healthcare providers to assess and enhance the quality of care they deliver. By tracking outcomes, patient satisfaction, and compliance with best practices, providers can make data-driven improvements.
Cost Reduction and Resource Management
Health informatics helps healthcare institutions optimize resource allocation and reduce costs. By identifying inefficiencies and areas of improvement, healthcare organizations can direct their resources more effectively.
Conclusion
In an era where data is often referred to as the “new oil,” health informatics is the vehicle through which the healthcare industry taps into the vast potential of health-related information. It empowers healthcare professionals with tools and insights to provide more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centric care. With the ability to save lives, reduce healthcare costs, and drive medical innovations, health informatics is more than a trend; it is the future of healthcare. Its importance continues to grow as technology evolves and as the healthcare industry strives to provide the best possible care to patients around the world.
Pillars of Excellence: Key Standards in the Healthcare Industry
Introduction
The healthcare industry is marked by its unwavering commitment to patient care, safety, and the pursuit of excellence. To maintain the highest standards in patient treatment, healthcare professionals adhere to a set of well-defined guidelines and standards. In this article, we explore the key standards in the healthcare industry that serve as the foundation for quality care and patient safety.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA, which we discussed in a previous article, is a cornerstone of healthcare standards. Its Privacy and Security Rules ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information. HIPAA also facilitates secure electronic data exchange, safeguarding patient privacy.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care focuses on the individual’s needs, preferences, and values. It encourages active patient involvement in healthcare decisions, considering their physical and emotional well-being. Effective communication and shared decision-making are key components of this standard.
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Clinical practice guidelines are evidence-based recommendations for healthcare professionals to provide high-quality care for specific medical conditions. These guidelines are continually updated to reflect the latest research, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Infection Control
Infection control standards are crucial for maintaining patient safety. Healthcare facilities strictly adhere to practices designed to prevent the spread of infections. Hand hygiene, sterilization, and sanitation procedures are key components of infection control.
Accreditation and Certification
Healthcare institutions often seek accreditation and certification from organizations like The Joint Commission, which set high standards for patient care and safety. Compliance with these standards demonstrates an organization’s commitment to quality healthcare delivery.
EHR (Electronic Health Record) Standards
With the transition to electronic health records, interoperability and data standards are essential. These standards ensure that patient information can be accurately and securely exchanged between healthcare systems, promoting continuity of care.
Patient Safety Goals
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) establish patient safety goals that healthcare providers worldwide must strive to meet. These goals include improving medication safety, reducing healthcare-associated infections, and preventing patient falls.
Nursing Standards
Nursing practice is guided by standards set by organizations like the American Nurses Association (ANA). These standards define the responsibilities and expectations for nursing practice, ensuring the delivery of safe and effective care.
Mental Health Standards
Mental health standards ensure that patients with mental health conditions receive appropriate and compassionate care. These standards include the provision of crisis intervention and psychosocial support.
Ethical Standards
Ethical standards in healthcare encompass a wide range of principles, including patient confidentiality, informed consent, and truth-telling. These standards guide the behavior and decision-making of healthcare professionals, ensuring the highest ethical standards in patient care.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry’s commitment to excellence and patient well-being is evident in the multitude of standards and guidelines that govern its practice. These standards touch on various aspects of healthcare, from privacy and data security to patient safety and ethical conduct. Adherence to these standards is not just a requirement but a reflection of the industry’s dedication to providing the best possible care to patients, ensuring their safety, and upholding the highest standards of professionalism and ethics. In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, these standards remain the pillars of excellence that drive the industry forward.
Revolutionizing Patient Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-Generated Smart Forms
By Sharon Lojun, M.D., M.S. and Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The repetitive nature of filling out the same forms during each visit to a healthcare provider can be a time-consuming and tedious process for patients. However, Warp Core Health, an innovative healthcare technology company, is leading the charge in transforming the patient form experience. Through their groundbreaking AI-powered solutions, Warp Core Health is developing an AI-generated form that patients fill out once, and subsequently, only relevant information is presented for review and update based on the reason for the visit. This revolution in patient forms aims to streamline the healthcare experience, save time, and improve the overall efficiency of medical visits.
- The Current Challenge: Traditionally, patients are required to provide a comprehensive range of information during each visit, regardless of the reason for their appointment. This results in repetitive and time-consuming form filling, often causing frustration for patients who feel that the process is unnecessary and inefficient. Furthermore, healthcare providers must sift through extensive paperwork to locate the specific details relevant to the visit, creating an additional administrative burden.
- AI-Generated Smart Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms represent a significant advancement in the patient form process. With the power of artificial intelligence, these forms are designed to be dynamic and tailored to each patient’s specific needs. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, the smart forms intelligently analyze the reason for the visit and present only the relevant sections and questions for review and update.
- Personalized and Streamlined Experience: By eliminating the need to repeat previously provided information, patients can experience a more streamlined and personalized visit. With AI-generated smart forms, patients can focus on updating crucial details related to their current health condition, symptoms, or concerns. This targeted approach ensures that patients’ valuable time is maximized during their appointments, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering the most appropriate care.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Warp Core Health’s AI algorithms continually learn from patient data, allowing for improved accuracy and efficiency over time. As patients update their information during subsequent visits, the smart forms intelligently adapt and present new questions or prompts based on previous responses and the reason for the current visit. This iterative process ensures that patient information remains up-to-date and relevant, while minimizing redundant or unnecessary data entry.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems, creating a powerful synergy between patient information and form customization. As new data is added to the EHR, such as diagnoses, treatments, or test results, it further enhances the customization of smart forms for future visits. The AI algorithms analyze the updated EHR data and dynamically adjust the smart forms to ensure that patients are presented with the most relevant sections and questions specific to their follow-up or next visit. This dynamic customization optimizes the patient form experience, allowing for efficient updates and reviews of pertinent information while eliminating the need to navigate through irrelevant sections. By harnessing the power of EHR integration, Warp Core Health’s smart forms adapt to each patient’s evolving healthcare journey, ensuring a personalized and tailored experience throughout their medical visits.
- Data Security and Privacy: Warp Core Health places a high priority on maintaining the security and privacy of patient data. Their AI-generated smart forms are designed to adhere to stringent data protection regulations, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential. Robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards are implemented to safeguard patient privacy throughout the form-filling and data storage processes.
Conclusion: Warp Core Health’s pioneering efforts in developing AI-generated smart forms are set to revolutionize the patient form experience in healthcare. By leveraging artificial intelligence, these forms minimize repetitive data entry, present only relevant information for review and update, and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical visits. With seamless integration into electronic health record systems, Warp Core Health ensures that patient information remains up-to-date, contributing to improved continuity of care. As the healthcare industry embraces the power of AI technology, Warp Core Health’s innovative approach to patient forms promises to transform the patient experience, saving time, and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Author: Sharon Lojun, M.D., M.S.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Understanding the Distinctions: Biomedical Informatics, Clinical Informatics, and Health Informatics
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
In today’s digital age, the field of informatics plays a crucial role in transforming healthcare by harnessing the power of technology and data. Within this expansive field, three distinct disciplines often come into play: biomedical informatics, clinical informatics, and health informatics. While these terms may seem interchangeable at first glance, they each encompass unique areas of focus and expertise. Let’s delve into the differences between these three disciplines to gain a clearer understanding.
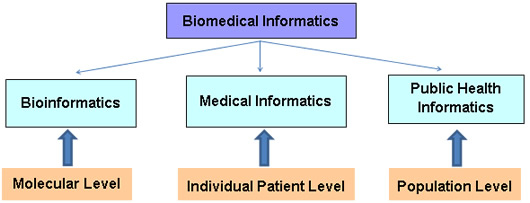
Biomedical Informatics:
Biomedical informatics, sometimes referred to as bioinformatics, revolves around the intersection of biology, medicine, and computational sciences. It focuses on leveraging technology, data analysis, and information systems to advance biomedical research, discovery, and understanding. Biomedical informatics professionals work on developing tools and methodologies to store, manage, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of biological and clinical data.
The scope of biomedical informatics spans genomics, proteomics, imaging data, clinical trials, and more. By employing computational and analytical approaches, experts in this field can identify patterns, discover new insights, and enhance our understanding of complex biological processes. Biomedical informatics plays a vital role in areas such as personalized medicine, drug discovery, and precision healthcare.
Clinical Informatics:
Clinical informatics centers on the effective use of information and communication technologies in healthcare settings, with a primary focus on improving patient care and outcomes. It encompasses the application of informatics principles and methods to facilitate clinical decision-making, enhance workflow efficiencies, and optimize healthcare delivery.
Clinical informatics professionals bridge the gap between healthcare providers and technology. They ensure the successful implementation and utilization of electronic health records (EHRs), clinical decision support systems, computerized physician order entry (CPOE), and other healthcare information systems. They work to streamline data capture, facilitate interoperability between systems, and promote data-driven approaches to patient care.
Health Informatics:
Health informatics takes a broader perspective, encompassing both biomedical and clinical informatics while extending its reach to population health, public health, and healthcare management. Health informatics focuses on the collection, management, and analysis of health-related data to improve healthcare delivery, policy-making, and population health outcomes.
Professionals in health informatics leverage technology and information systems to monitor and assess population health trends, support public health initiatives, and facilitate data-driven decision-making. They play a crucial role in developing and implementing health information exchanges, health analytics, telemedicine, and health data standards to ensure seamless data exchange and enhance healthcare delivery on a larger scale.
In essence, while biomedical informatics concentrates on advancing scientific research through data analysis, clinical informatics focuses on optimizing clinical workflows and patient care delivery. Health informatics takes a broader perspective, incorporating both biomedical and clinical informatics while extending its scope to population health and healthcare management.
By understanding the distinctions between biomedical informatics, clinical informatics, and health informatics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the specialized roles each discipline plays in shaping the future of healthcare. Together, they contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge, optimization of clinical processes, and improvement of overall healthcare outcomes for individuals and populations alike.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/