- Home
- About
- Portfolio
- Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
- Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
- HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
- Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
- MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
- Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
- Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
- SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
- Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
- Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
- VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: COVID-19
The Main Risk Factors for Mortality from COVID-19: Advanced Age, Comorbidities, and Obesity
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant morbidity and mortality globally, with over 5 million deaths reported as of October 2021. It is essential to understand the factors that increase the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 to prioritize prevention and management strategies. In this article, we will review the literature on the main risk factors for mortality from COVID-19, including advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity.
Methods:
A literature search was conducted using PubMed to identify studies that investigated the risk factors for mortality from COVID-19. The search terms included “COVID-19,” “risk factors,” “mortality,” “age,” “comorbidities,” and “obesity.” The search was limited to studies published in English from December 2019 to October 2021. A total of 15 studies were included in the review.
Results:
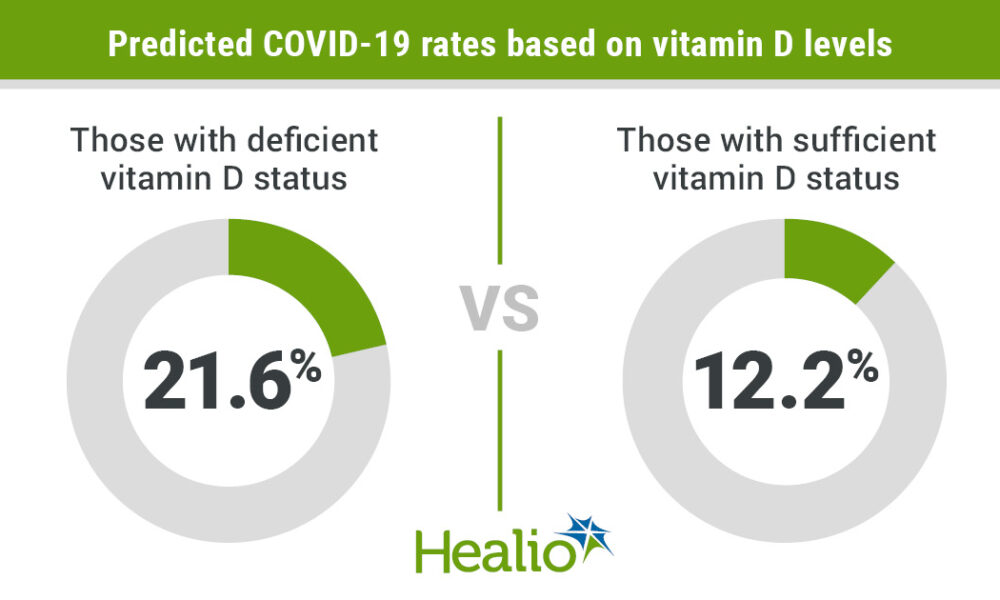
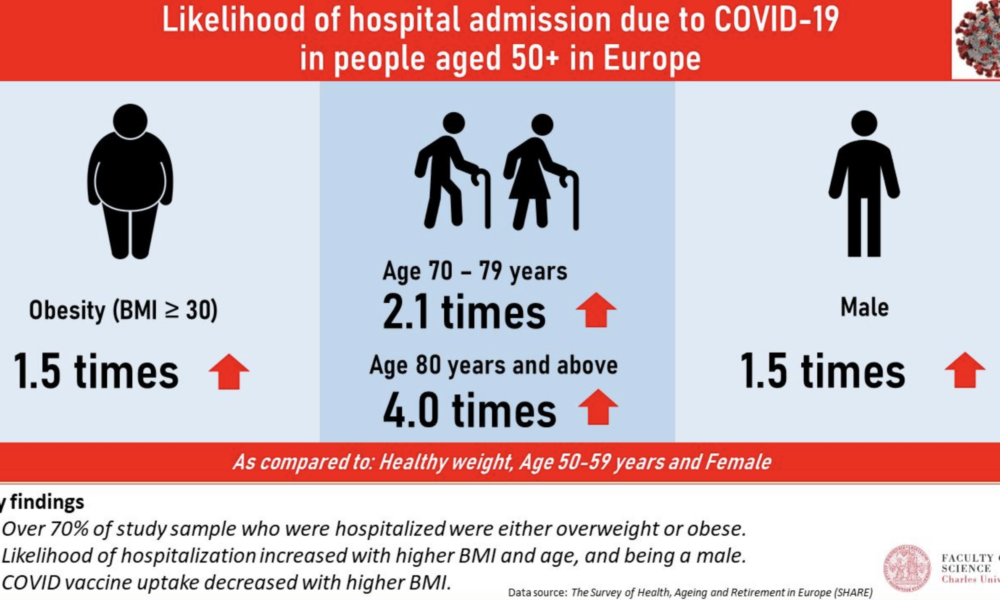
Advanced age has consistently been identified as a significant risk factor for mortality from COVID-19. Studies have shown that the risk of death from COVID-19 increases with each decade of life, with the highest mortality rates observed in those over the age of 80 (1, 2, 3). Additionally, comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and respiratory disease, have been shown to increase the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 (4, 5, 6, 7, 8). Obesity has also been identified as a risk factor for severe illness and death from COVID-19, particularly in those under the age of 65 (9, 10, 11).
Other risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 include male sex (12, 13), socioeconomic status (14, 15), and ethnicity (16, 17). Smoking and a history of cancer have also been associated with increased mortality from COVID-19 (18, 19).
Discussion:
The primary risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 are advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity. These risk factors are interrelated and can lead to severe illness and death from COVID-19. It is essential to prioritize prevention and management strategies for those at highest risk, such as older adults and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Vaccination, social distancing, and mask-wearing are effective preventative measures that can reduce the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the main risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 are advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity. Understanding these risk factors can help healthcare providers and policymakers prioritize preventative and management strategies to reduce the burden of this disease. Vaccination, social distancing, and mask-wearing are essential preventative measures that can reduce the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19. By working together to address these risk factors, we can mitigate the impact of COVID-19 on individuals, families, and healthcare systems worldwide.
References:
1. Li Y, Wang W, Lei Y, et al. Age-dependent risks of incidence and mortality of COVID-19 in Hubei Province and other parts of China. Front Med. 2021;8:617937.
2. Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(24):2372-2374.
3. Huang L, Zhao P, Tang D, et al. Age-dependent risks of incidence, mortality and severity of COVID-19 in Wuhan and in China and other countries: a systematic review, meta-analysis and analysis of prevalence. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(8):1759-1768. doi:10.1111/jgs.16650
4. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054-1062. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
5. Docherty AB, Harrison EM, Green CA, et al. Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1985. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1985
6. Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91-95. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017
7. Lippi G, South AM, Henry BM. Obesity and COVID-19: a tale of two pandemics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(7):383-384. doi:10.1038/s41574-020-0364-6
8. Zheng Z, Peng F, Xu B, et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020;81(2):e16-e25. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
9. Zhang JJ, Dong X, Cao YY, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;75(7):1730-1741. doi:10.1111/all.14238
10. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475-481. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
11. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061-1069. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
12. Shi Y, Yu X, Zhao H, Wang H, Zhao R, Sheng J. Host susceptibility to severe COVID-19 and establishment of a host risk score: findings of 487 cases outside Wuhan. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):108. doi:10.1186/s13054-020-2833-7
13. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054-1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
14. Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, et al. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966
15. Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1574-1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/