- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: Ketogenic Diet
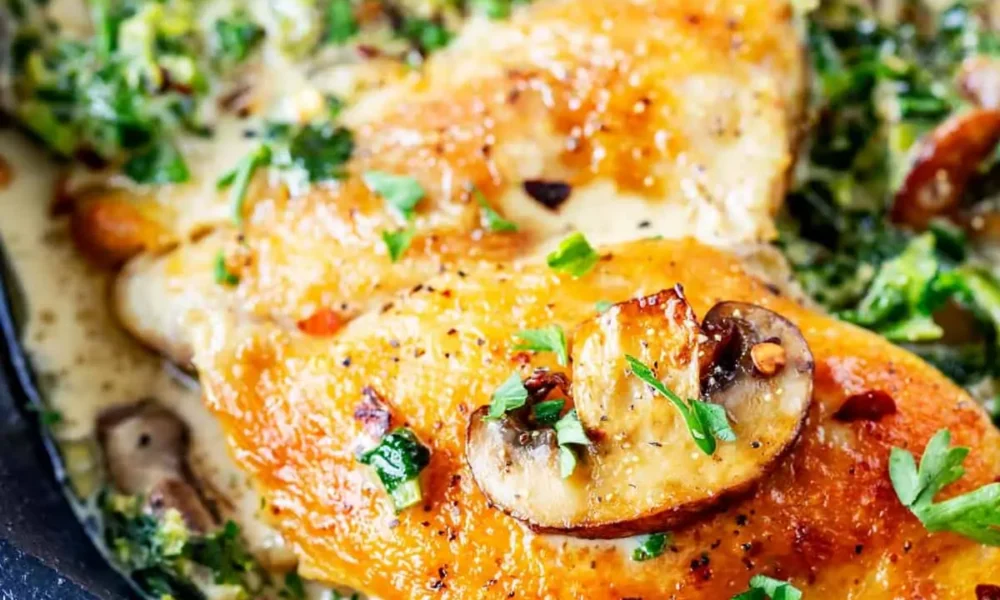
Chicken Thighs with Mushrooms and Spinach: A Flavorful Delight
By Lisa Fitzmeyer
Introduction: Chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach is a delicious and nutritious dish that combines tender chicken thighs, earthy mushrooms, and vibrant spinach. This recipe offers a harmonious blend of flavors and textures, making it a satisfying meal for any occasion. Follow this simple recipe to create a mouthwatering dish that will impress your family and friends.
Ingredients:
- 6-8 chicken thighs
- Avocado oil
- 2 tablespoons fresh rosemary, chopped
- 1 medium onion, sliced
- White button mushrooms, sliced
- 4 cloves of garlic, chopped
- Fresh spinach or kale
Instructions:
- Preheat the oven to 350°F (175°C).
- In a large skillet, heat 4 tablespoons of avocado oil over medium heat. Place the chicken thighs in the pan, skin side down, and cook until the skin is crispy and golden brown. This will take about 5-6 minutes. Flip the chicken thighs and cook for an additional 2-3 minutes. The chicken will not be fully cooked at this stage but will finish cooking in the oven.
- Transfer the chicken thighs to a baking dish, arranging them in a single layer.
- In the same skillet, add the sliced onions, chopped garlic, and fresh rosemary. Sauté them in the remaining oil until the onions become jammy and translucent. This process will take about 5 minutes.
- Add the sliced mushrooms to the skillet and sauté for an additional 3-4 minutes until they are tender and slightly browned.
- Spoon the onion, garlic, and mushroom mixture around the chicken thighs in the baking dish, distributing it evenly.
- Place the baking dish in the preheated oven and bake for 30 minutes, or until the chicken thighs are cooked through and reach an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
- Remove the baking dish from the oven and increase the oven temperature to 400°F (200°C).
- Meanwhile, coat the fresh spinach or kale with a drizzle of olive oil, ensuring that all leaves are lightly coated.
- Spread the oiled spinach or kale around the chicken and vegetables in the baking dish.
- Return the dish to the oven and bake for an additional 5 minutes, or until the spinach or kale wilts slightly.
- Carefully remove the baking dish from the oven. The chicken thighs should be juicy, and the mushrooms, onions, and spinach or kale will have melded together beautifully.
- Serve the chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach alongside your favorite keto-friendly sides, such as roasted cauliflower or zucchini noodles, or a fresh green salad dressed with olive oil and lemon juice. Enjoy the delightful flavors and wholesome goodness of this keto-friendly chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach dish!
Enjoy the delightful flavors and wholesome goodness of this chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach dish!
Note: Feel free to adjust the quantities of ingredients to suit your preferences and the number of servings desired.
From Keto to Carnivore: Decoding Low Carb Diets for Ultimate Health and Vitality
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
In the quest for improved health and weight management, numerous dietary approaches have gained popularity. Among the most well-known are the low carb diets, including the ketogenic diet (keto) and the carnivore diet. However, it is important to understand the subtle nuances and benefits of each variation, as well as other popular low carb diets such as the Paleo, Mediterranean, and Standard American Diet (S.A.D.). In this article, we will explore the differences and benefits of these dietary choices, shedding light on the variables that make each one unique.
The Ketogenic Diet (Keto):
The ketogenic diet is a low carb, high fat diet that encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body shifts from using glucose as its primary fuel source to using ketones. This metabolic state has been associated with several benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased mental clarity. Additionally, keto has shown promise in managing epilepsy and certain neurological disorders.
The Carnivore Diet:
At the other end of the spectrum lies the carnivore diet, which emphasizes exclusively animal products and eliminates plant-based foods entirely. This ultra-low carb, high fat, and high protein approach aims to mimic the dietary patterns of our ancestors. Advocates claim that eliminating plant foods can reduce inflammation, promote weight loss, and improve digestion. However, it is important to note that the carnivore diet is highly restrictive and lacks the diversity of nutrients found in a balanced diet.
The Paleo Diet:
The Paleo diet seeks to emulate the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. It promotes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding grains, legumes, dairy products, and processed foods. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and eliminating potential allergens, the Paleo diet aims to support weight loss, improve digestion, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
The Mediterranean Diet:
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while incorporating moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products. This approach is rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber, which have been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, improved brain function, and overall longevity.
The Standard American Diet (S.A.D.):
The Standard American Diet, unfortunately, is characterized by a high intake of processed foods, refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and a low consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This diet is associated with a variety of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. It lacks the nutrient density and balance necessary for optimal health.
Benefits of Each Approach:
Keto: Weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, increased mental clarity, potential therapeutic benefits for epilepsy and neurological disorders.
Carnivore: Potential for reduced inflammation, weight loss, and improved digestion. However, it may lack essential nutrients and long-term sustainability.
Paleo: Improved weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases, increased nutrient intake, elimination of potential allergens.
Mediterranean: Heart health, improved brain function, longevity, reduced risk of chronic diseases, balanced nutrient intake.
S.A.D.: No significant benefits compared to the other diets mentioned. Associated with various health issues.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right low carb diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health considerations. While the ketogenic and carnivore diets offer unique metabolic effects, it is important to consider the
long-term sustainability and potential nutrient deficiencies. The Paleo and Mediterranean diets provide a balanced approach by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods and diverse nutrient profiles. In contrast, the Standard American Diet (S.A.D.) is associated with numerous health problems due to its reliance on processed and unhealthy foods.
It is essential to note that individual responses to different diets may vary. What works for one person may not yield the same results for another. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
Ultimately, the key to a successful and sustainable low carb diet lies in finding a balance that aligns with your health goals and preferences. Incorporating whole, nutrient-dense foods while reducing processed carbohydrates can have a positive impact on weight management, overall health, and disease prevention. By understanding the variables and benefits of different low carb diets, you can make an informed decision and embark on a journey towards improved well-being.
Comparison chart highlighting the macronutrient composition of each diet:
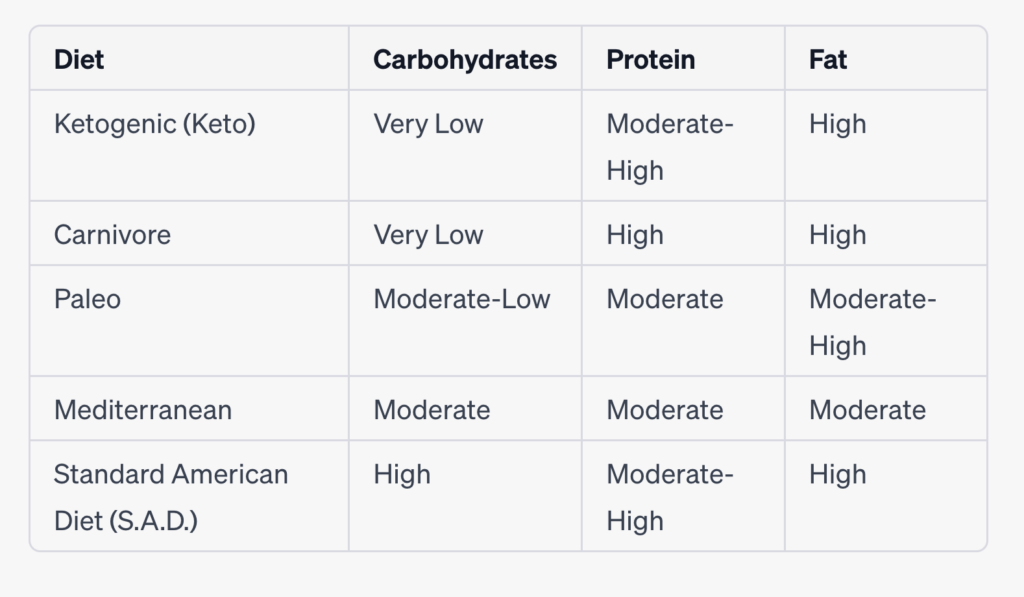
Please note that the macronutrient ratios mentioned above can vary based on individual preferences and specific interpretations of each diet. Additionally, the “Moderate” category indicates a more balanced distribution rather than being excessively high or low.
It’s important to keep in mind that macronutrient ratios can be adjusted within each diet based on individual needs, health goals, and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for determining the ideal macronutrient breakdown for your specific circumstances.
Remember that while macronutrients play a significant role in dietary choices, the quality of food, micronutrient content, and overall balance of the diet are also crucial factors to consider for long-term health and well-being.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
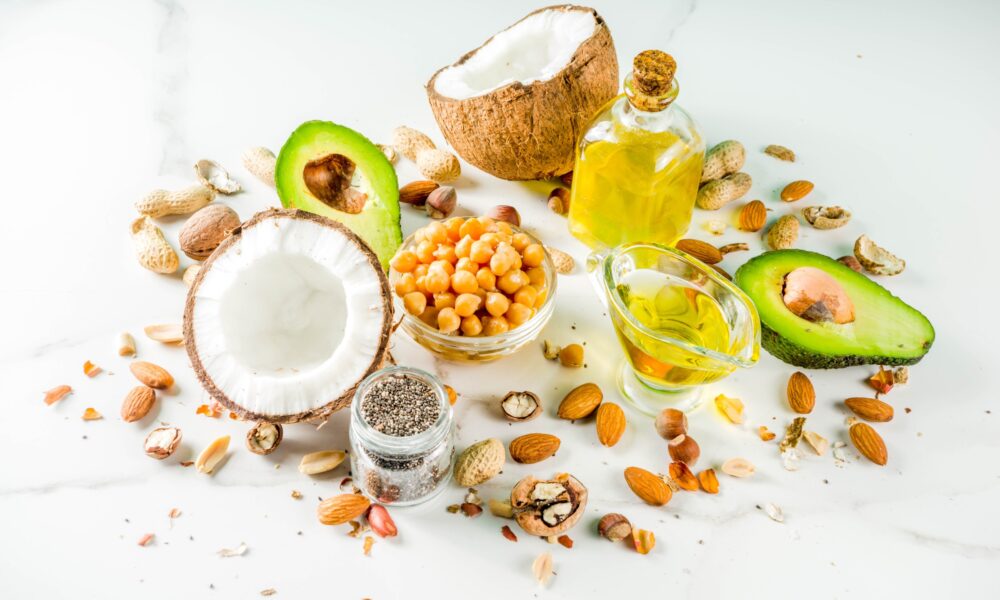
Essential Fat and Protein Sources for Vegans and Vegetarians on a Keto Diet
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: Following a ketogenic diet as a vegan or vegetarian can be challenging, as the focus on high fat and low carb intake requires careful consideration of food choices. However, with a wide range of nutrient-dense options available, it is possible to meet your fat and protein needs while adhering to a plant-based keto lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the best sources of fat and protein for vegans and vegetarians, with a special emphasis on keto-friendly choices.
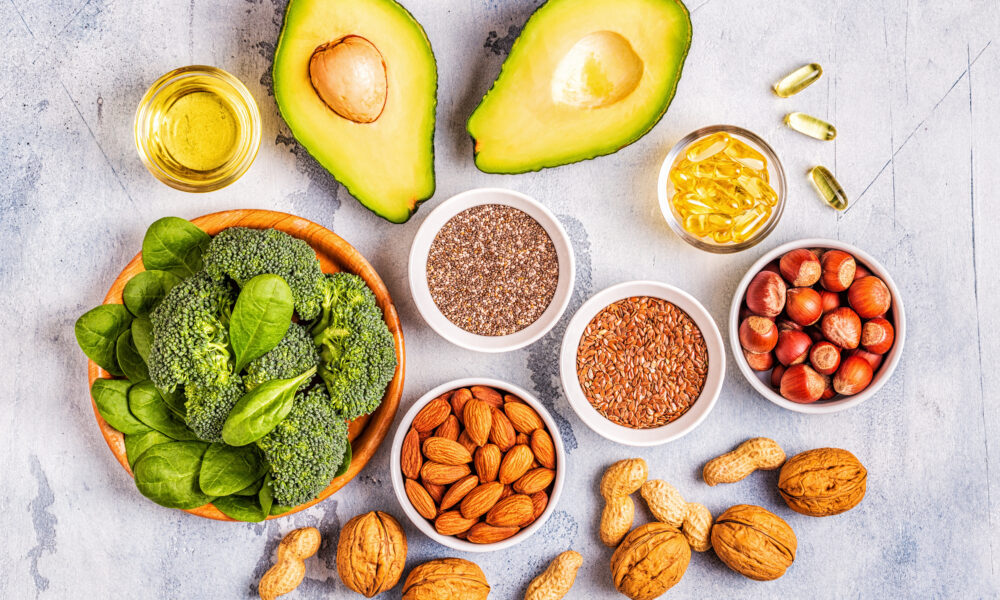
Avocado: Nature’s Creamy Powerhouse (Keto-friendly) Avocado, the beloved green fruit, is not only a keto-friendly option but also a nutritional powerhouse. Packed with healthy monounsaturated fats, avocados provide a rich and creamy texture to dishes. They are also a source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent addition to a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet.
Nuts and Seeds: Crunchy Delights (Keto-friendly) Nuts and seeds are versatile and satisfying options for obtaining both healthy fats and protein. Almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds are all keto-friendly choices. These crunchy delights are not only great for snacking but can also be incorporated into recipes, such as nut butters or as toppings for salads and smoothies.
Nut and Seed Butters: Spreads of Goodness (Keto-friendly) Nut and seed butters, such as peanut butter, almond butter, and tahini, are delectable spreads that offer a generous dose of healthy fats and protein. They can be enjoyed on their own, added to smoothies, used as a dip for vegetables, or incorporated into keto-friendly baking recipes.
Coconut and Coconut Oil: Tropical Treasures (Keto-friendly) Coconut and its derivatives are keto-friendly options that bring a tropical twist to your meals. Coconut meat, coconut oil, and coconut milk are rich in healthy fats and can be used in various keto recipes, from curries to smoothies. Coconut milk, with its creamy texture, can be a great base for vegan ketogenic dishes.
Olive Oil: Liquid Gold (Keto-friendly) Olive oil, a staple in the Mediterranean diet, is a source of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. It is ideal for cooking or as a dressing for salads and vegetables, adding flavor and healthy fats to your meals.
Plant-Based Oils: A Flavorful Spectrum (Keto-friendly) Other plant-based oils, such as avocado oil, flaxseed oil, and sesame oil, offer a diverse range of flavors and are excellent sources of healthy fats for a vegan or vegetarian keto diet. These oils can be used for sautéing, roasting, and dressing to enhance the taste and nutritional profile of your dishes.
Legumes: Protein Powerhouses While not strictly keto-friendly due to their higher carb content, legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are still valuable sources of plant-based protein for vegans and vegetarians. They can be included in moderation, considering individual carb limits and dietary preferences.
Tofu and Tempeh: Plant-Based Protein Staples Tofu and tempeh, derived from soybeans, are versatile plant-based protein sources. They can be used in a variety of dishes, including stir-fries, salads, and curries. These options provide protein while keeping carbohydrate intake relatively low, making them suitable for a vegan or vegetarian keto diet.
Seitan: Meaty Texture, Plant-Based Protein Seitan, made from wheat gluten, is a high-protein option for those following a vegan or vegetarian keto diet. With its meaty texture and ability to absorb flavors, seitan is a versatile ingredient that can be used to create delicious and satisfying plant-based dishes.
Quinoa: The Complete Protein Grain Quinoa, though higher in carbs compared to other options, is a complete protein source that contains all essential amino acids. While it should be consumed in moderation on a ketogenic diet, quinoa can be a nutritious addition to a vegan or vegetarian keto meal plan when carefully portioned.
Conclusion: Maintaining a well-rounded vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet requires careful consideration of fat and protein sources. Fortunately, there is a wide array of options available that cater to these needs. Avocado, nuts, seeds, coconut, olive oil, plant-based oils, legumes in moderation, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and quinoa (in limited amounts) offer a range of essential fats and protein for individuals following a plant-based keto lifestyle.
Remember to personalize your food choices according to your specific dietary goals and preferences. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that your nutrient intake aligns with your needs and to optimize your health while following a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet. Embrace the diversity of these plant-based options, and enjoy the benefits of a well-balanced and nourishing diet.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›