- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: Ketogenic Diet
Unveiling the Role of ApoB and the Therapeutic Potential of Ketogenic Lifestyle and Intermittent Fasting in Atherosclerosis
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
Atherosclerosis, a major contributor to cardiovascular disease, arises from a complex interplay of various factors. Among them, Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) emerges as the primary driver in the development and progression of this condition. In this article, we delve into the critical role of ApoB in atherosclerosis and shed light on the influence of inflammation in enhancing its effects.
Understanding the Role of ApoB:
ApoB, a protein found in lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, serves as a key player in atherosclerosis. It acts as a carrier, facilitating the transportation of cholesterol to peripheral tissues, including the arterial walls. In the absence of ApoB, the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis are virtually non-existent.
The Significance of ApoB in Atherosclerosis:
ApoB takes center stage in atherosclerosis, as it is responsible for delivering cholesterol-rich lipoproteins, particularly LDL, to arterial walls. These lipoproteins undergo modifications and become trapped in the arterial intima, initiating the formation of fatty streaks. With time, inflammation is triggered, attracting immune cells and accelerating the transformation of fatty streaks into advanced atherosclerotic plaques.
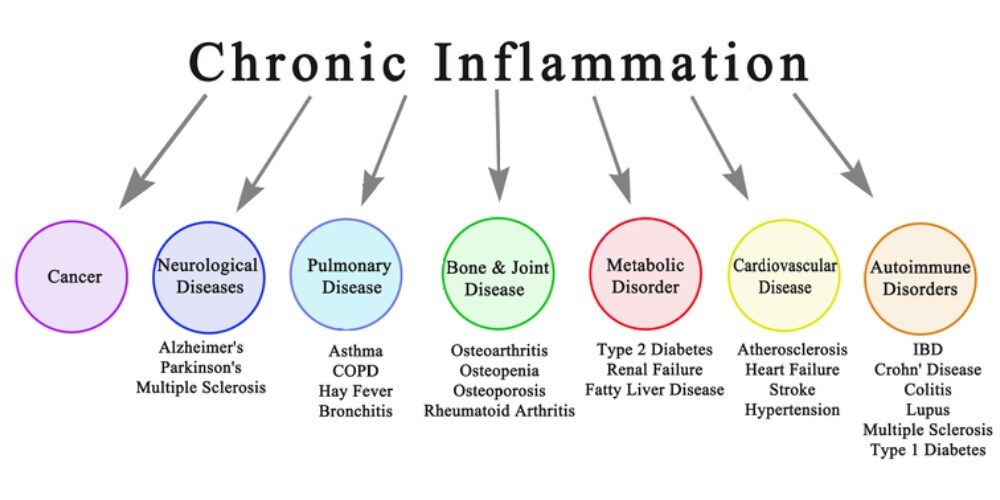
Inflammation and its Role:
While inflammation is a key player in atherosclerosis, it acts as an enhancer rather than the primary driver. Inflammation exacerbates the process by promoting the retention and modification of ApoB-containing lipoproteins, leading to plaque progression and instability. Thus, controlling inflammation becomes crucial in managing atherosclerosis, but addressing the root cause—ApoB—remains essential.
Implications and Therapeutic Strategies:
Understanding the central role of ApoB opens up avenues for therapeutic interventions in managing atherosclerosis. Addressing ApoB levels and reducing the burden of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins is key. Here, lifestyle modifications such as adopting a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet (such as a ketogenic diet) and implementing intermittent fasting can prove beneficial. These approaches help regulate ApoB-containing lipoproteins, mitigate their retention in arterial walls, and slow down the progression of atherosclerosis.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications that target additional risk factors associated with atherosclerosis, such as hypertension and obesity, should be considered. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing other comorbidities can complement the efforts to address ApoB and reduce the overall risk of atherosclerosis.
Conclusion:
ApoB stands as the primary driver in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis, while inflammation serves to enhance and accelerate the process. Recognizing the pivotal role of ApoB provides insights into therapeutic strategies that can mitigate its effects. By adopting lifestyle modifications, such as a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet and intermittent fasting, individuals can positively influence ApoB levels and manage atherosclerosis. Combining these interventions with measures to address other risk factors offers a comprehensive approach to reducing the burden of atherosclerosis and promoting cardiovascular health.
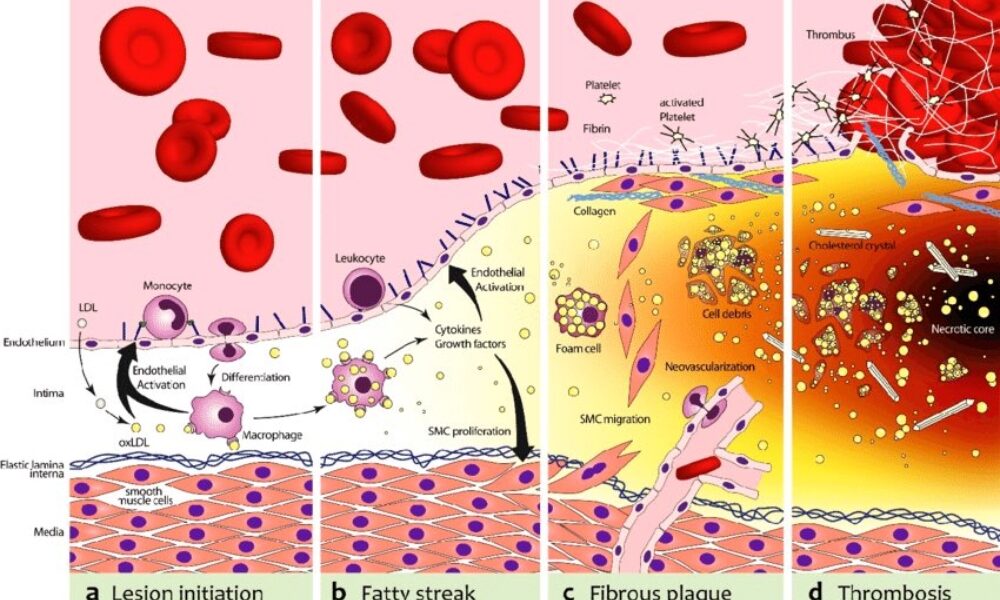
The biochemical pathway of plaque formation involving ApoB can be described as follows:
- ApoB synthesis: ApoB is a protein synthesized in the liver and intestines. It is a major component of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and LDL particles.
- Lipoprotein assembly: VLDL particles are assembled in the liver and contain ApoB-100. They transport triglycerides and cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues. During circulation, VLDL particles undergo enzymatic changes, resulting in the conversion of triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol.
- LDL formation: As VLDL particles lose triglycerides, they become smaller and denser, transforming into LDL particles. LDL contains a single molecule of ApoB-100 and is the primary carrier of cholesterol in the bloodstream.
- LDL uptake: LDL particles bind to LDL receptors on cell surfaces, allowing the cells to take up cholesterol. These receptors are present in various tissues, including the arterial walls.
- Retention and modification: In the arterial walls, LDL particles can undergo modifications, such as oxidation and glycation, making them more prone to retention. These modified LDL particles interact with extracellular matrix proteins and proteoglycans in the arterial intima, leading to their entrapment within the vessel walls.
- Inflammation and foam cell formation: The retained LDL particles, along with their cholesterol content, trigger an inflammatory response. Immune cells, particularly macrophages, migrate to the site of inflammation. They engulf the cholesterol-rich LDL particles, transforming into foam cells, which are characterized by their lipid-filled cytoplasm.
- Fatty streak formation: The accumulation of foam cells and other immune cells results in the formation of fatty streaks, which are the initial visible signs of plaque development. Fatty streaks consist of foam cells, lipids, inflammatory cells, and smooth muscle cells.
- Advanced plaque formation: Over time, the fatty streaks can progress into more advanced atherosclerotic plaques. These plaques are characterized by a fibrous cap composed of smooth muscle cells and collagen, a lipid-rich core containing foam cells and cholesterol, and a necrotic center.
Throughout this biochemical pathway, ApoB plays a crucial role in the transport of cholesterol to peripheral tissues, including the arterial walls. It facilitates the delivery of cholesterol-rich LDL particles, which, under certain conditions, contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Understanding this pathway provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets for preventing and managing plaque formation and related cardiovascular diseases.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Satiety: The Key to Success on a Ketogenic Diet
Introduction:
Embarking on a ketogenic diet can be a transformative journey towards improved health and well-being. This low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan has gained popularity due to its potential for weight loss, enhanced metabolic health, and increased mental clarity. However, one often overlooked aspect that holds the key to success on a ketogenic diet is satiety—the feeling of fullness and satisfaction after a meal. In this article, we will explore the importance of satiety and how it plays a crucial role in achieving success on a ketogenic diet.
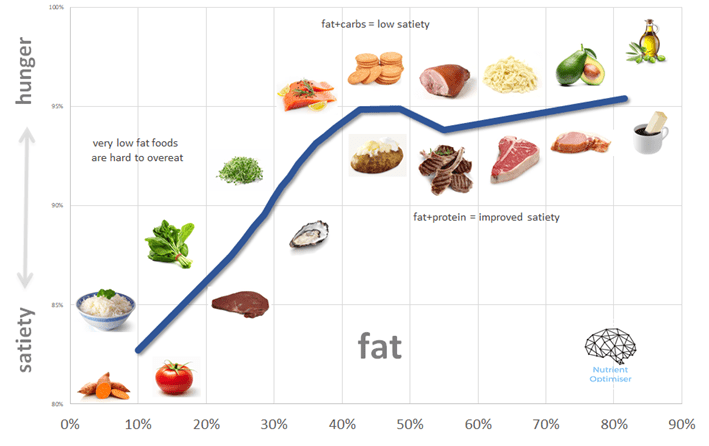
Understanding Satiety:
Satiety is more than just feeling full—it’s about feeling satisfied and nourished after a meal. Achieving satiety is essential because it helps to prevent overeating, control cravings, and maintain adherence to a ketogenic diet in the long term. When we feel satisfied after a meal, we are less likely to seek out unnecessary snacks or indulge in high-carbohydrate foods that can derail our progress.
The Role of Macronutrients:
The macronutrient composition of a ketogenic diet plays a significant role in achieving satiety. Here’s how each macronutrient contributes to the feeling of fullness:
- Healthy Fats: Fats are a cornerstone of the ketogenic diet, and they play a crucial role in promoting satiety. Consuming an adequate amount of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and coconut oil, can help slow down digestion, increase feelings of fullness, and provide sustained energy throughout the day.
- Protein Power: Protein is another important macronutrient for satiety on a ketogenic diet. It is known for its ability to promote feelings of fullness and support muscle maintenance. Including high-quality sources of protein, such as fish, poultry, eggs, and tofu, in your meals can help curb cravings and keep you satisfied for longer periods.
- Fibrous Vegetables: Non-starchy vegetables, such as leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, and zucchini, are excellent sources of dietary fiber. Fiber adds bulk to meals, promoting a feeling of fullness while providing essential nutrients. Including an abundance of fibrous vegetables in your ketogenic meals can enhance satiety and support overall gut health.
Strategies for Enhancing Satiety on a Ketogenic Diet:
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods in your ketogenic diet. These nutrient-dense options provide more satiety compared to processed and refined foods.
- Mindful Eating: Slow down and savor each bite. Mindful eating practices, such as chewing slowly and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, can help you tune into your body’s satiety signals.
- Balanced Meals: Aim to include a combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber-rich vegetables in every meal. This balanced approach provides a wide range of nutrients and helps achieve satiety more effectively.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated throughout the day. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking. Drinking enough water can help prevent this confusion and support satiety.
- Meal Planning and Preparation: Plan your meals in advance and prepare them at home whenever possible. This allows you to control the quality of ingredients and portion sizes, ensuring that your meals are satisfying and aligned with your ketogenic goals.
Conclusion:
Achieving satiety is a fundamental aspect of success on a ketogenic diet. By prioritizing healthy fats, adequate protein, and fibrous vegetables, you can create meals that not only support ketosis but also promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction. Remember to listen to your body’s signals, practice mindful eating, and make informed choices when it comes to food selection and preparation.
Satiety is not only crucial for short-term satisfaction but also for long-term adherence to a ketogenic lifestyle. By feeling consistently satiated, you can avoid the pitfalls of unnecessary snacking, mindless eating, and the temptation to stray from your dietary goals. The ability to sustain your ketogenic diet with ease increases your chances of achieving your desired health outcomes, whether it’s weight loss, improved metabolic markers, or increased mental clarity.
It’s important to note that individual preferences and needs may vary when it comes to achieving satiety on a ketogenic diet. Experiment with different food combinations, portion sizes, and eating schedules to find what works best for you. Some individuals may find that smaller, more frequent meals work well, while others prefer larger, less frequent meals. Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all approach, and customization is key.
In addition to macronutrient composition and meal planning, factors like stress management, sleep quality, and physical activity also influence satiety. Addressing these lifestyle factors alongside your ketogenic diet can further enhance the feeling of fullness and overall well-being.
Ultimately, satiety is the secret ingredient to success on a ketogenic diet. By focusing on nutrient-dense, whole foods, maintaining a balanced macronutrient profile, and listening to your body’s cues, you can create a sustainable and enjoyable way of eating that supports your health and weight management goals. Embrace the power of satiety and let it guide you on your journey to a healthier, happier you.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist and Founder of Warp Core Health
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›