- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Coding Evidence-Based Medicine into Web-Based Applications
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
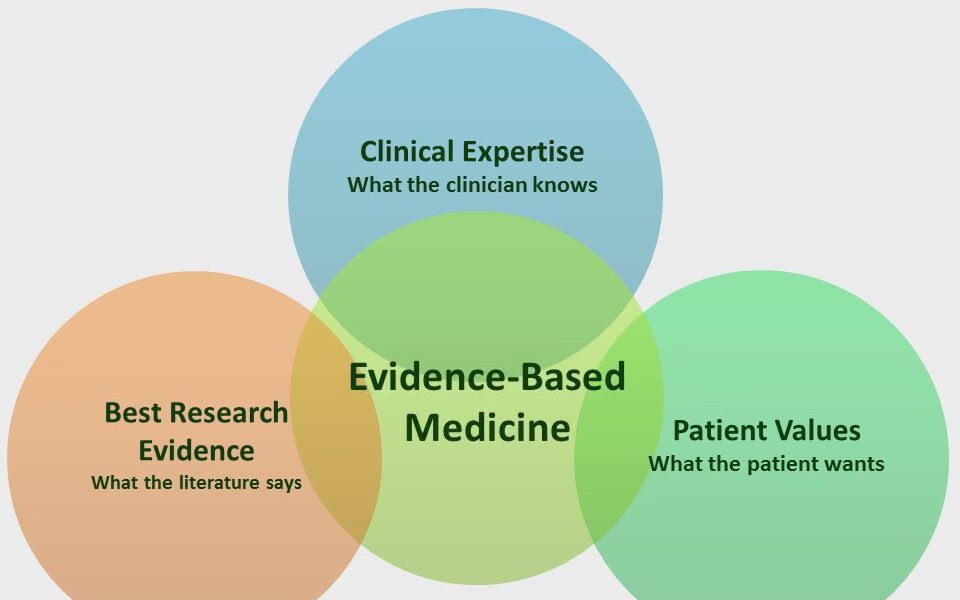
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is a medical approach that involves using the best available evidence to make informed clinical decisions. The goal of EBM is to improve the quality of patient care by integrating research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient preferences into clinical decision making. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using technology to support EBM and help clinicians make evidence-based decisions. Web-based applications are a popular way to accomplish this goal.
Web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence, as well as clinical practice guidelines and other relevant resources. These applications can help clinicians make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of a wide range of medical conditions.
The process of building a web-based EBM application involves several steps. The first step is to identify the target audience and determine the specific clinical needs that the application will address. This may involve conducting a needs assessment and identifying gaps in current clinical practice.
The second step is to identify relevant EBM resources and integrate them into the application. This may involve using electronic databases, such as PubMed or Cochrane Library, to search for the latest research evidence. It may also involve incorporating clinical practice guidelines, systematic reviews, and other evidence-based resources into the application.
Once the relevant EBM resources have been identified, the next step is to design the application’s user interface. The application should be easy to navigate, intuitive to use, and provide users with relevant information at the appropriate time. The design of the application should be based on user-centered design principles, which involve actively involving users in the design process and incorporating their feedback into the final product.
After the application has been designed, the next step is to develop the application using web development languages and frameworks such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React. The application may also incorporate server-side programming languages such as PHP or Python, and databases such as MongoDB or MySQL to store and retrieve data.
Finally, the application should be tested and validated to ensure that it is functioning as intended and providing accurate and reliable information to users. This may involve user testing, where the application is tested by actual users, as well as usability testing, where the application is tested for ease of use and effectiveness.
In conclusion, web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence and clinical practice guidelines, helping them make informed decisions about patient care. The development of these applications involves identifying the target audience and their clinical needs, integrating relevant EBM resources, designing an intuitive user interface, developing the application using web development languages and frameworks, and testing and validating the application to ensure that it is effective and reliable. By following these steps, developers can build web-based EBM applications that improve patient care and support evidence-based decision making in clinical practice.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/