- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: Public Health
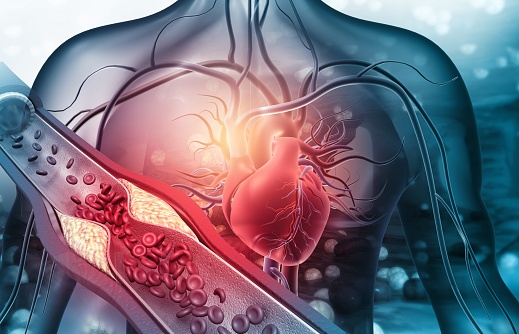
CAC: The Ultimate Test for Assessing Health and Why You Need One Now!
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, staying proactive and prioritizing preventive measures is key to maintaining optimal health. The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test has recently emerged as a groundbreaking tool in health assessment, providing invaluable insights into cardiovascular health. This article highlights the significance of CAC as the ultimate test for assessing health and emphasizes why individuals should consider getting one now to safeguard their well-being. Additionally, we’ll explore how patients can easily obtain a CAC scan for themselves.
Understanding CAC Scoring
The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test employs non-invasive computed tomography (CT) scans to detect the presence and extent of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. By quantifying the amount of calcium present, it calculates a CAC score, effectively gauging the overall burden of atherosclerosis in the arteries. This score serves as a crucial predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD), empowering individuals to take preventive action.
The Urgency of CAC as a Health Indicator
- Early Detection of Silent Risks: CAC scoring enables early detection of potential cardiovascular issues, even before symptoms manifest. By identifying calcified plaque deposits, healthcare professionals can determine an individual’s risk of experiencing a heart attack or developing coronary artery disease (CAD). Seeking a CAC test now can help unveil hidden risks and prompt timely interventions to prevent disease progression.
- Personalized Risk Assessment: Unlike traditional risk assessment tools, CAC scoring provides a precise evaluation of atherosclerosis. Through quantitative analysis, it offers a more accurate estimation of an individual’s risk of developing CVD. Obtaining a CAC score now empowers healthcare providers to devise personalized treatment plans tailored to an individual’s level of risk, enabling timely interventions and better health outcomes.
- Empowerment for Lifestyle Changes: CAC scoring serves as a powerful motivator for individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles. Witnessing the presence and extent of calcified plaque acts as a visual reminder of the importance of positive changes in diet, exercise, and stress management. By getting a CAC test now, you can proactively take charge of your health, making informed decisions and fostering long-term adherence to beneficial lifestyle modifications.
- Preventive Measures for Long-Term Health: CAC scoring facilitates proactive preventive measures by categorizing individuals into different risk groups based on their CAC scores. This allows healthcare providers to implement appropriate treatments and interventions to reduce the risk of CVD. Taking action now, based on your CAC score, can significantly improve your long-term cardiovascular health and well-being.
How to Obtain a CAC Scan
To obtain a CAC scan, you can follow these steps:
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your interest in getting a CAC scan. They will evaluate your medical history, risk factors, and overall health to determine if a CAC scan is appropriate for you.
- Referral and Imaging Facility: If your healthcare provider determines that a CAC scan is necessary, they will provide you with a referral to an imaging facility or radiology center equipped to perform the scan.
- Schedule the Scan: Contact the recommended imaging facility and schedule your CAC scan appointment. They will provide you with any necessary instructions, such as fasting requirements or medication restrictions before the test.
- The CAC Scan Procedure: During the CAC scan, you will lie on a table that moves through a CT scanner. The scan is quick and painless, typically taking only a few minutes to complete.
- Results and Follow-up: Once the scan is complete, the radiologist will analyze the images and calculate your CAC score. Your healthcare provider will then review the results with you. They will explain the implications of your CAC score, discuss any necessary lifestyle modifications or medical interventions, and develop a personalized plan to mitigate your cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion
The Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scoring test is a powerful tool for assessing cardiovascular health and preventing future complications. By identifying silent risks, providing personalized risk assessment, motivating lifestyle changes, and enabling proactive preventive measures, CAC scoring empowers individuals to take control of their well-being. To obtain a CAC scan, consult your healthcare provider, obtain a referral to an imaging facility, schedule the scan, and discuss the results and follow-up plan with your healthcare provider. Take the proactive step towards optimizing your health and consider getting a CAC scan now. Your heart and overall well-being will thank you for it.
CAC Score
After undergoing a CAC scan, you will receive a CAC score that falls within a specific range. Here are the general ranges and their corresponding meanings:
- CAC Score of 0: A CAC score of 0 indicates the absence of detectable calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This suggests a very low risk of cardiovascular events, and individuals in this range often have a favorable prognosis.
- CAC Score of 1-99: A CAC score between 1 and 99 indicates the presence of mild calcification in the coronary arteries. This range signifies a low to moderate risk of cardiovascular disease, and it is an opportunity for individuals to implement preventive measures to reduce the progression of plaque formation.
- CAC Score of 100-399: A CAC score between 100 and 399 represents the presence of moderate calcification in the coronary arteries. This range suggests a significant risk of cardiovascular disease, and it necessitates more aggressive preventive strategies and medical interventions to reduce the risk of future complications.
- CAC Score of 400 or Higher: A CAC score of 400 or higher indicates extensive calcification in the coronary arteries. This range represents a high risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. It necessitates immediate and intensive medical interventions, including lifestyle modifications and potential medication therapies, to mitigate the risk and prevent further progression.
By understanding the range of CAC scores and their implications, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that addresses their specific risk level.
To obtain a CAC scan, consult your healthcare provider, obtain a referral to an imaging facility, schedule the scan, and discuss the results and follow-up plan with your healthcare provider. Take the proactive step towards optimizing your health and consider getting a CAC scan now. Your heart and overall well-being will thank you for it.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
From Cholera to COVID-19: The Role of Epidemiology in Disease Outbreaks
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
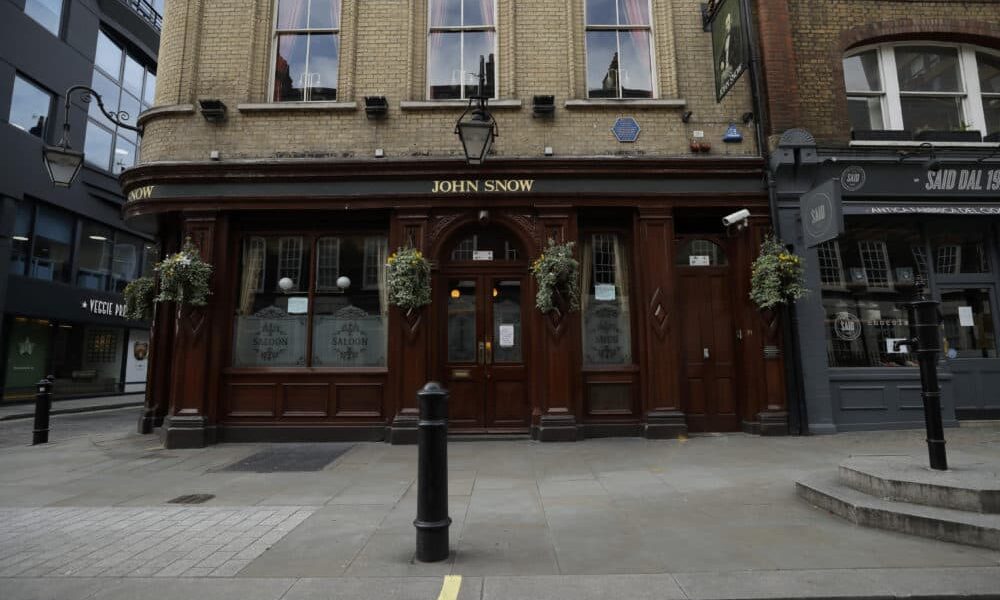
The cholera outbreak in 1854 in London, and the work of John Snow, is considered a turning point in the field of epidemiology. The outbreak caused thousands of deaths and was traced back to contaminated water from the Broad Street pump. Snow’s investigation led him to identify the source of the outbreak, and he subsequently recommended measures to prevent the spread of cholera.
Fast forward to modern times, and we are facing a new epidemic – COVID-19. The similarities between the two outbreaks are striking, and so are the differences. Like cholera, COVID-19 is a highly contagious disease that spreads through contact with infected individuals or surfaces. However, unlike cholera, COVID-19 is caused by a novel virus that is still not fully understood.
Epidemiology played a crucial role in both outbreaks. In the case of cholera, Snow used epidemiological methods to map the spread of the disease and identify the source of the outbreak. He collected data on the location of cases and the source of water for the affected individuals, and used this data to create a map that showed a clear association between the cases and the Broad Street pump. This data-driven approach was a key factor in his successful intervention.
Similarly, epidemiology has played a critical role in the management of COVID-19. Epidemiologists have been tracking the spread of the disease, identifying risk factors and patterns of transmission, and providing guidance on how to mitigate the spread of the virus. Epidemiological models have been used to predict the course of the pandemic, and to inform public health policies and interventions.
However, there are also significant differences between the two outbreaks. COVID-19 is a much more complex disease than cholera, with a wide range of symptoms and outcomes. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread by asymptomatic carriers, making it much more challenging to control. The development of effective vaccines and treatments has been a major focus of the public health response to COVID-19, and epidemiology has played a critical role in evaluating the effectiveness of these interventions.
In conclusion, the cholera outbreak and the work of John Snow laid the foundation for modern epidemiology, and the lessons learned from that outbreak have helped us manage and control many subsequent disease outbreaks. The COVID-19 pandemic has presented a new set of challenges, but the principles of epidemiology remain essential to understanding and controlling the spread of the virus. By continuing to apply these principles, we can hope to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and prepare for future outbreaks.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
What is Health Information Technology? Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of HIT
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Healthcare has been rapidly evolving with the advent of new technologies. Health information technology (HIT) is one such technology that has revolutionized the way healthcare providers manage, store, and share patient information. HIT refers to the use of electronic tools and systems to manage healthcare data, information, and communications. It has the potential to transform healthcare by improving patient care, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency.
The benefits of HIT are numerous. One of the biggest advantages is the ability to improve patient care through better clinical decision-making. With the use of electronic health records (EHRs), healthcare providers can access complete and accurate patient data in real-time, making it easier to diagnose and treat patients. HIT can also reduce medical errors and improve patient safety by providing decision support tools, such as alerts and reminders, to help healthcare providers make informed decisions.
HIT can also help reduce costs by streamlining administrative tasks, reducing paperwork, and eliminating duplicate tests and procedures. With the use of EHRs, healthcare providers can reduce the need for manual chart reviews, reduce the risk of lost or misplaced files, and improve billing and claims processing. Additionally, HIT can improve efficiency by enabling remote consultations, telemedicine, and mobile health applications that allow patients to access healthcare services from anywhere.
However, there are also challenges associated with HIT. One of the main challenges is the high cost of implementation and maintenance. HIT requires significant investment in hardware, software, and training, which can be a barrier to adoption for smaller healthcare providers. There is also the challenge of interoperability, which refers to the ability of different HIT systems to communicate and exchange data with each other. Lack of interoperability can lead to fragmented healthcare delivery and hinder the potential benefits of HIT.
Another challenge is the issue of data security and privacy. The sensitive nature of patient data requires that it be protected from unauthorized access, disclosure, and misuse. HIT systems must comply with various data privacy and security regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), to ensure that patient information is kept confidential and secure.
In conclusion, health information technology has the potential to transform healthcare by improving patient care, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency. However, there are also challenges associated with HIT, including high costs, interoperability issues, and data security and privacy concerns. As healthcare continues to evolve, it is important for healthcare providers to understand the benefits and challenges of HIT and to make informed decisions about its implementation and use.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
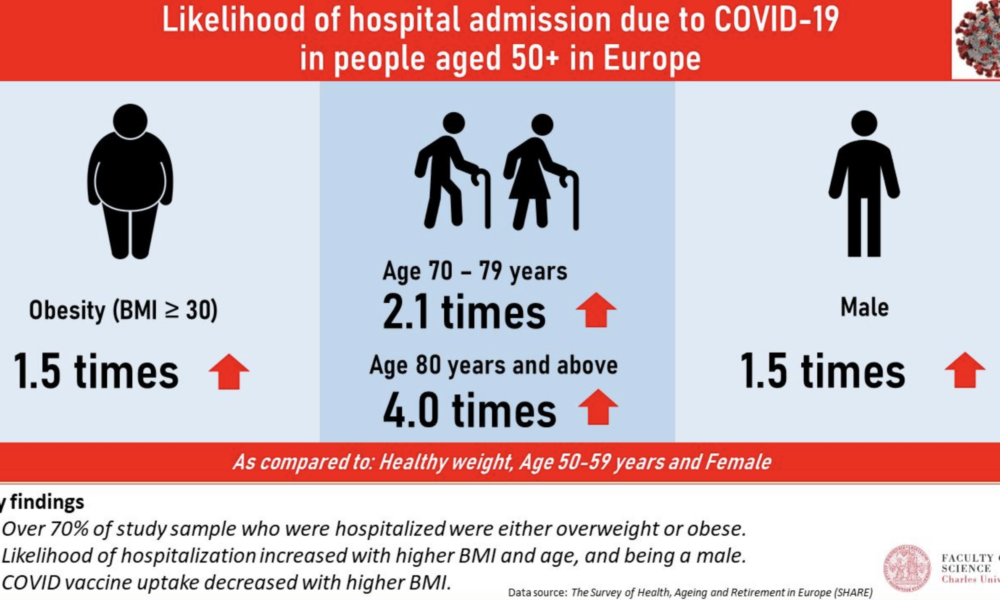
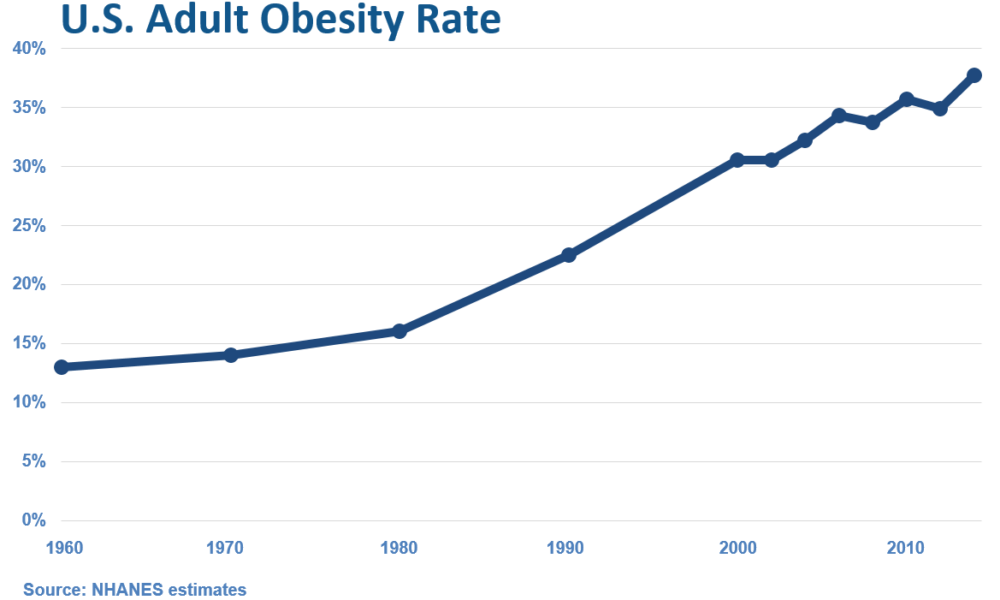
The Main Risk Factors for Mortality from COVID-19: Advanced Age, Comorbidities, and Obesity
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant morbidity and mortality globally, with over 5 million deaths reported as of October 2021. It is essential to understand the factors that increase the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 to prioritize prevention and management strategies. In this article, we will review the literature on the main risk factors for mortality from COVID-19, including advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity.
Methods:
A literature search was conducted using PubMed to identify studies that investigated the risk factors for mortality from COVID-19. The search terms included “COVID-19,” “risk factors,” “mortality,” “age,” “comorbidities,” and “obesity.” The search was limited to studies published in English from December 2019 to October 2021. A total of 15 studies were included in the review.
Results:
Advanced age has consistently been identified as a significant risk factor for mortality from COVID-19. Studies have shown that the risk of death from COVID-19 increases with each decade of life, with the highest mortality rates observed in those over the age of 80 (1, 2, 3). Additionally, comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and respiratory disease, have been shown to increase the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 (4, 5, 6, 7, 8). Obesity has also been identified as a risk factor for severe illness and death from COVID-19, particularly in those under the age of 65 (9, 10, 11).
Other risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 include male sex (12, 13), socioeconomic status (14, 15), and ethnicity (16, 17). Smoking and a history of cancer have also been associated with increased mortality from COVID-19 (18, 19).
Discussion:
The primary risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 are advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity. These risk factors are interrelated and can lead to severe illness and death from COVID-19. It is essential to prioritize prevention and management strategies for those at highest risk, such as older adults and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Vaccination, social distancing, and mask-wearing are effective preventative measures that can reduce the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the main risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 are advanced age, comorbidities, and obesity. Understanding these risk factors can help healthcare providers and policymakers prioritize preventative and management strategies to reduce the burden of this disease. Vaccination, social distancing, and mask-wearing are essential preventative measures that can reduce the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19. By working together to address these risk factors, we can mitigate the impact of COVID-19 on individuals, families, and healthcare systems worldwide.
References:
1. Li Y, Wang W, Lei Y, et al. Age-dependent risks of incidence and mortality of COVID-19 in Hubei Province and other parts of China. Front Med. 2021;8:617937.
2. Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(24):2372-2374.
3. Huang L, Zhao P, Tang D, et al. Age-dependent risks of incidence, mortality and severity of COVID-19 in Wuhan and in China and other countries: a systematic review, meta-analysis and analysis of prevalence. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(8):1759-1768. doi:10.1111/jgs.16650
4. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054-1062. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
5. Docherty AB, Harrison EM, Green CA, et al. Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1985. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1985
6. Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91-95. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017
7. Lippi G, South AM, Henry BM. Obesity and COVID-19: a tale of two pandemics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(7):383-384. doi:10.1038/s41574-020-0364-6
8. Zheng Z, Peng F, Xu B, et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020;81(2):e16-e25. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
9. Zhang JJ, Dong X, Cao YY, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;75(7):1730-1741. doi:10.1111/all.14238
10. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475-481. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
11. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061-1069. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
12. Shi Y, Yu X, Zhao H, Wang H, Zhao R, Sheng J. Host susceptibility to severe COVID-19 and establishment of a host risk score: findings of 487 cases outside Wuhan. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):108. doi:10.1186/s13054-020-2833-7
13. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054-1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
14. Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, et al. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966
15. Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1574-1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
From Keto to Carnivore: Decoding Low Carb Diets for Ultimate Health and Vitality
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
In the quest for improved health and weight management, numerous dietary approaches have gained popularity. Among the most well-known are the low carb diets, including the ketogenic diet (keto) and the carnivore diet. However, it is important to understand the subtle nuances and benefits of each variation, as well as other popular low carb diets such as the Paleo, Mediterranean, and Standard American Diet (S.A.D.). In this article, we will explore the differences and benefits of these dietary choices, shedding light on the variables that make each one unique.
The Ketogenic Diet (Keto):
The ketogenic diet is a low carb, high fat diet that encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body shifts from using glucose as its primary fuel source to using ketones. This metabolic state has been associated with several benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased mental clarity. Additionally, keto has shown promise in managing epilepsy and certain neurological disorders.
The Carnivore Diet:
At the other end of the spectrum lies the carnivore diet, which emphasizes exclusively animal products and eliminates plant-based foods entirely. This ultra-low carb, high fat, and high protein approach aims to mimic the dietary patterns of our ancestors. Advocates claim that eliminating plant foods can reduce inflammation, promote weight loss, and improve digestion. However, it is important to note that the carnivore diet is highly restrictive and lacks the diversity of nutrients found in a balanced diet.
The Paleo Diet:
The Paleo diet seeks to emulate the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. It promotes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding grains, legumes, dairy products, and processed foods. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and eliminating potential allergens, the Paleo diet aims to support weight loss, improve digestion, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
The Mediterranean Diet:
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while incorporating moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products. This approach is rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber, which have been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, improved brain function, and overall longevity.
The Standard American Diet (S.A.D.):
The Standard American Diet, unfortunately, is characterized by a high intake of processed foods, refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and a low consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This diet is associated with a variety of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. It lacks the nutrient density and balance necessary for optimal health.
Benefits of Each Approach:
Keto: Weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, increased mental clarity, potential therapeutic benefits for epilepsy and neurological disorders.
Carnivore: Potential for reduced inflammation, weight loss, and improved digestion. However, it may lack essential nutrients and long-term sustainability.
Paleo: Improved weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases, increased nutrient intake, elimination of potential allergens.
Mediterranean: Heart health, improved brain function, longevity, reduced risk of chronic diseases, balanced nutrient intake.
S.A.D.: No significant benefits compared to the other diets mentioned. Associated with various health issues.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right low carb diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health considerations. While the ketogenic and carnivore diets offer unique metabolic effects, it is important to consider the
long-term sustainability and potential nutrient deficiencies. The Paleo and Mediterranean diets provide a balanced approach by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods and diverse nutrient profiles. In contrast, the Standard American Diet (S.A.D.) is associated with numerous health problems due to its reliance on processed and unhealthy foods.
It is essential to note that individual responses to different diets may vary. What works for one person may not yield the same results for another. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
Ultimately, the key to a successful and sustainable low carb diet lies in finding a balance that aligns with your health goals and preferences. Incorporating whole, nutrient-dense foods while reducing processed carbohydrates can have a positive impact on weight management, overall health, and disease prevention. By understanding the variables and benefits of different low carb diets, you can make an informed decision and embark on a journey towards improved well-being.
Comparison chart highlighting the macronutrient composition of each diet:
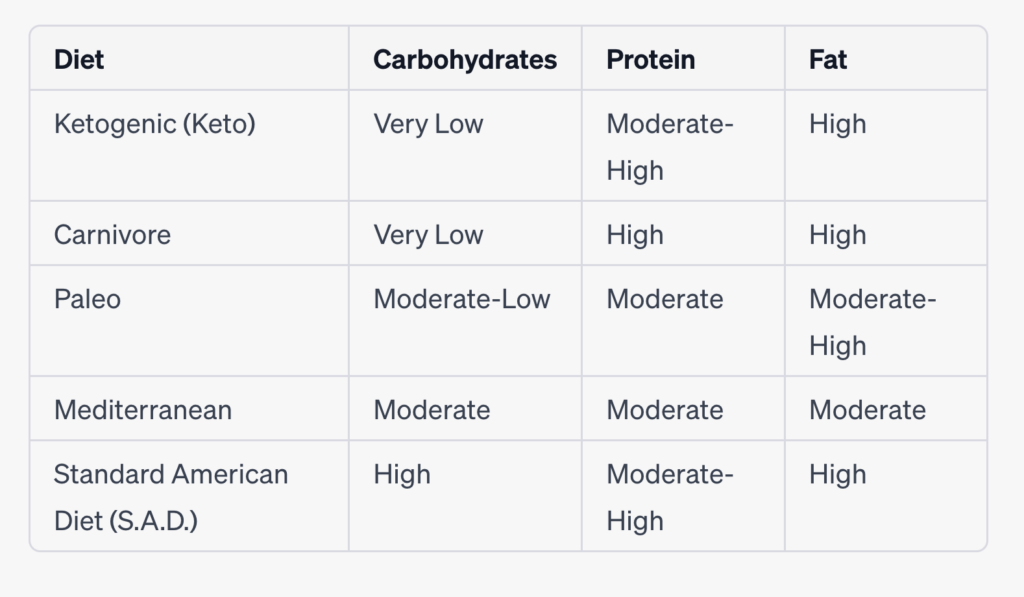
Please note that the macronutrient ratios mentioned above can vary based on individual preferences and specific interpretations of each diet. Additionally, the “Moderate” category indicates a more balanced distribution rather than being excessively high or low.
It’s important to keep in mind that macronutrient ratios can be adjusted within each diet based on individual needs, health goals, and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for determining the ideal macronutrient breakdown for your specific circumstances.
Remember that while macronutrients play a significant role in dietary choices, the quality of food, micronutrient content, and overall balance of the diet are also crucial factors to consider for long-term health and well-being.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
The Rise of Overweight/Obesity in the U.S.: Examining the Influence of Dietary Guidelines, the Food Pyramid, and Ancel Keys
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The United States has experienced a significant increase in overweight and obesity rates over the past few decades, leading to serious health concerns. It is intriguing to examine the correlation between the rise in overweight/obesity and the transformation of the American diet, particularly with the introduction of dietary guidelines and the prominent role played by Ansel Keys. In this article, we delve into the historical context and explore how the shift away from fresh whole foods, influenced by Keys’ research, may have inadvertently contributed to the obesity epidemic in the United States.
The Era of Fresh Whole Foods: Before the introduction of dietary guidelines in the 1980s, the American diet primarily consisted of fresh, whole foods. Meals were often prepared from scratch, using ingredients sourced directly from farms and local markets. Fresh fruits and vegetables, meats, and unprocessed grains were the foundation of everyday eating, providing a nutrient-dense and balanced approach to nutrition.
Ansel Keys and Dietary Fat: Ansel Keys, a prominent scientist, conducted influential research in the mid-20th century that examined the relationship between dietary fat and heart disease. His work, known as the “Seven Countries Study,” suggested a correlation between high-fat diets and increased risk of cardiovascular issues. However, Keys’ study focused on selected countries, disregarding nations with contrasting dietary patterns that contradicted his findings.
The Impact of Keys’ Findings: Keys’ research gained significant attention and led to a shift in nutritional thinking. Dietary fat, particularly saturated fat, became vilified, and the notion that a low-fat diet was crucial for maintaining heart health took root. As a result, dietary guidelines and recommendations began emphasizing the reduction of fat intake, leading to the promotion of low-fat and fat-free products in the market.
The Emergence of Processed Foods: The low-fat movement led to a surge in processed food products marketed as healthy alternatives. With the focus on reducing fat, manufacturers started formulating products with reduced fat content but compensated by adding excessive amounts of sugar, artificial additives, and refined carbohydrates. This shift in the food industry coincided with the introduction of dietary guidelines, further driving the consumption of processed foods among Americans.
Unintended Consequences: The shift away from fresh whole foods towards processed, low-fat alternatives had unintended consequences. These processed foods were often calorie-dense, nutrient-poor, and contributed to overconsumption. The replacement of dietary fats with refined carbohydrates and added sugars not only affected overall calorie intake but also disrupted metabolic processes, leading to weight gain and related health issues.
Reevaluating Dietary Choices: In recent years, there has been a growing realization that the previous low-fat paradigm may have played a role in the obesity epidemic. Many experts advocate for a return to a more balanced approach, focusing on the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods and reevaluating the role of dietary fats. This includes embracing healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, olive oil, fatty meats, eggs, butter, and cheeses.
Empowering Individuals through Education: To combat the rise of overweight/obesity, it is essential to empower individuals with knowledge and encourage them to make informed dietary choices. By educating ourselves about the benefits of fresh whole foods, understanding the potential pitfalls of processed foods, and reevaluating the role of dietary fats, we can make strides towards improving our overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: The rise of overweight and obesity in the United States coincides with the transformation of the American diet, influenced by the introduction of dietary guidelines and the impact of Ansel Keys’ research. While Keys’ findings had noble intentions, the emphasis on low-fat diets and the
proliferation of processed, low-fat alternatives may have inadvertently contributed to the obesity epidemic. It is important to acknowledge the historical context and the role played by fresh whole foods in the American diet before the era of dietary guidelines. By revisiting and embracing a diet centered around whole, unprocessed foods, we can reclaim a healthier approach to nutrition.
Moving forward, it is crucial to continue educating individuals about the importance of a balanced diet that includes nutrient-dense foods and minimizes reliance on processed and refined options. By fostering a culture of mindful eating and promoting the consumption of fresh, whole foods, we can work towards reversing the alarming trends of overweight and obesity and promoting a healthier future for all.
Coding Evidence-Based Medicine into Web-Based Applications
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
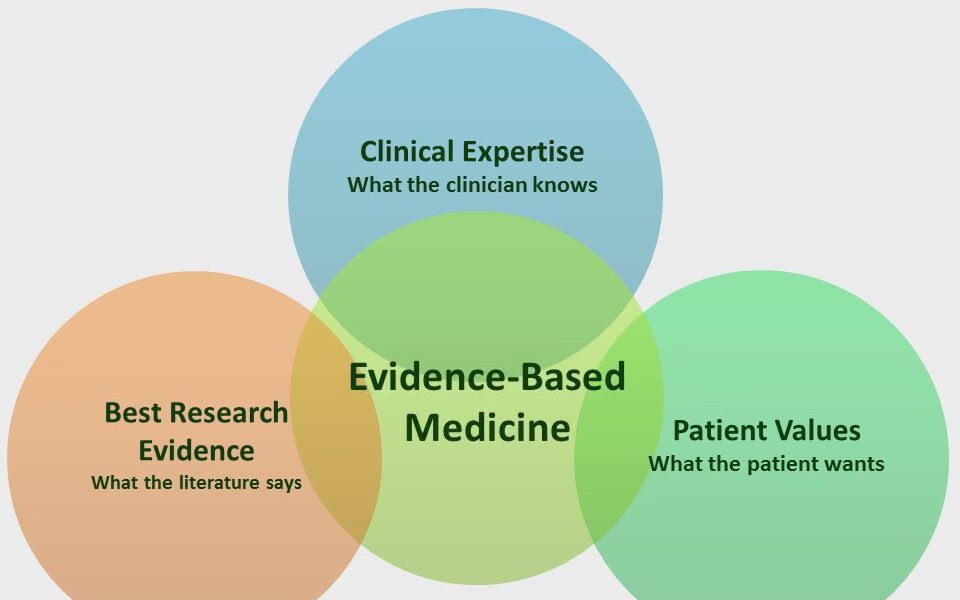
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is a medical approach that involves using the best available evidence to make informed clinical decisions. The goal of EBM is to improve the quality of patient care by integrating research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient preferences into clinical decision making. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using technology to support EBM and help clinicians make evidence-based decisions. Web-based applications are a popular way to accomplish this goal.
Web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence, as well as clinical practice guidelines and other relevant resources. These applications can help clinicians make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of a wide range of medical conditions.
The process of building a web-based EBM application involves several steps. The first step is to identify the target audience and determine the specific clinical needs that the application will address. This may involve conducting a needs assessment and identifying gaps in current clinical practice.
The second step is to identify relevant EBM resources and integrate them into the application. This may involve using electronic databases, such as PubMed or Cochrane Library, to search for the latest research evidence. It may also involve incorporating clinical practice guidelines, systematic reviews, and other evidence-based resources into the application.
Once the relevant EBM resources have been identified, the next step is to design the application’s user interface. The application should be easy to navigate, intuitive to use, and provide users with relevant information at the appropriate time. The design of the application should be based on user-centered design principles, which involve actively involving users in the design process and incorporating their feedback into the final product.
After the application has been designed, the next step is to develop the application using web development languages and frameworks such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React. The application may also incorporate server-side programming languages such as PHP or Python, and databases such as MongoDB or MySQL to store and retrieve data.
Finally, the application should be tested and validated to ensure that it is functioning as intended and providing accurate and reliable information to users. This may involve user testing, where the application is tested by actual users, as well as usability testing, where the application is tested for ease of use and effectiveness.
In conclusion, web-based applications that incorporate EBM can provide clinicians with easy access to the latest research evidence and clinical practice guidelines, helping them make informed decisions about patient care. The development of these applications involves identifying the target audience and their clinical needs, integrating relevant EBM resources, designing an intuitive user interface, developing the application using web development languages and frameworks, and testing and validating the application to ensure that it is effective and reliable. By following these steps, developers can build web-based EBM applications that improve patient care and support evidence-based decision making in clinical practice.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Building Prototypes for Healthcare Using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Building prototypes is an essential step in the healthcare software development process. It allows developers to test and refine their ideas, improve user experience, and identify potential issues before investing significant time and resources into building a fully functional application. In this article, we will discuss how to build prototypes for healthcare using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL.
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the three fundamental technologies used to build prototypes for web applications. HTML is used to define the structure and content of web pages, CSS is used to style and format the pages, and JavaScript is used to add interactivity and functionality. These technologies are used to create the front-end of a web application, which is the part of the application that users interact with.
PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting language that is used to build dynamic web applications. It is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that interact with databases and other server-side components. PHP is used to create the back-end of a web application, which is the part of the application that is responsible for processing user input, interacting with databases, and generating dynamic content.
React
React is a popular front-end JavaScript library that is used to build user interfaces. It is used to create interactive and responsive user interfaces that can be easily updated and modified. React is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that provide a modern and user-friendly interface.
Python
Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in healthcare software development. It is used to build server-side components, machine learning models, data analysis tools, and more. Python is commonly used in healthcare software development to build web applications that perform complex data analysis and provide advanced features such as natural language processing and machine learning.
MongoDB and MySQL
MongoDB and MySQL are two popular database management systems used in healthcare software development. MongoDB is a document-based NoSQL database that is used to store and retrieve large amounts of unstructured data. MySQL is a relational database management system that is used to store and retrieve structured data. Both databases are commonly used in healthcare software development to store patient data, medical records, and other healthcare-related information.
Conclusion
Building prototypes for healthcare using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, React, Python, MongoDB, and MySQL is an effective way to test and refine healthcare software ideas before investing significant time and resources into building a fully functional application. By using these technologies, healthcare software developers can create modern and user-friendly web applications that provide advanced features such as data analysis, machine learning, and natural language processing. With the right tools and skills, healthcare software developers can build prototypes that provide value to patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare organizations.