- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
- Home
- Warp Core Health
- Blog
- Metabolic Syndrome
Category: Metabolic Syndrome
The Vegan/Vegetarian Guide to Following a Ketogenic Diet with Intermittent Fasting
- May 20, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: The ketogenic diet has gained popularity for its potential benefits in weight loss, improved metabolic health, and increased energy levels. However, individuals following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle might wonder if it’s possible to adopt a ketogenic diet without compromising their dietary preferences. The good news is that with careful planning and consideration, vegans and vegetarians can successfully incorporate the principles of a ketogenic diet while practicing intermittent fasting.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: A ketogenic diet is characterized by a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake and an increased consumption of healthy fats. The aim is to shift the body’s primary fuel source from carbohydrates to fat, resulting in a metabolic state known as ketosis. This switch allows the body to burn stored fat for energy instead of relying on glucose from carbohydrates.
Key Principles for Vegans and Vegetarians: While traditional ketogenic diets often rely heavily on animal-based products, vegan and vegetarian versions can be equally effective and satisfying. Here are some key principles to follow:
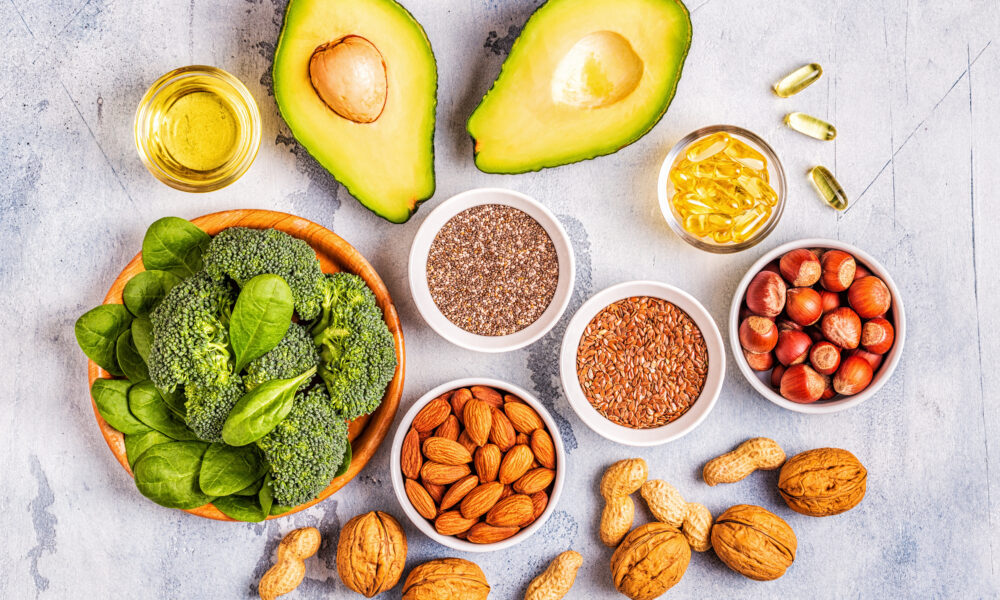
- Plant-Based Fats: Incorporate healthy fats from plant sources such as avocados, coconut oil, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. These provide essential nutrients, promote satiety, and support the ketogenic state.
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Fill your plate with a variety of low-carbohydrate, non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, zucchini, cauliflower, and bell peppers. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber while keeping carbohydrate intake low.
- Protein Alternatives: For vegetarians, include high-quality protein sources like eggs, dairy products, and plant-based protein options such as tofu, tempeh, seitan, and legumes. Vegans can rely on plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, legumes, quinoa, and hemp seeds.
- Healthy Snacks: Choose keto-friendly snacks like nuts, seeds, olives, coconut chips, or homemade energy balls using low-carb ingredients. These snacks help maintain energy levels and keep you satisfied between meals.
Incorporating Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent fasting (IF) can complement a ketogenic diet by optimizing insulin sensitivity and enhancing fat-burning processes. Here are two popular approaches:
- Time-Restricted Eating: Choose a daily eating window, such as 16/8, where you fast for 16 hours and eat all your meals within an 8-hour window. Adjust the timing to suit your lifestyle and preferences.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: This method involves fasting on alternate days, with reduced calorie intake or fasting for a full 24 hours. On non-fasting days, focus on consuming nutrient-dense, ketogenic-friendly meals.
Tips for Success:
- Plan and Prepare: Meal planning is essential for ensuring a well-balanced, ketogenic meal that meets your dietary requirements. Experiment with new recipes and explore plant-based alternatives to traditional high-carb ingredients.
- Monitor Nutrient Intake: Keep track of your macronutrient ratios, especially carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, to ensure you stay within the ketogenic range. Online food trackers or mobile apps can assist you in monitoring your nutrient intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall well-being.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional who specializes in plant-based nutrition and ketogenic diets. They can provide personalized guidance, address specific concerns, and help optimize your nutritional intake.
Conclusion: Following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle doesn’t mean you have to forgo the benefits of a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting. By carefully selecting plant-based fats, protein sources, and low-carbohydrate vegetables
and incorporating intermittent fasting, you can successfully adopt a ketogenic approach while aligning with your vegan or vegetarian values. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure your dietary choices meet your nutritional needs and to discuss any specific concerns you may have.
By following these principles and incorporating a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting, you can achieve your weight loss goals, improve metabolic health, and potentially alleviate or reverse symptoms associated with chronic diseases. Embrace the power of plant-based nutrition and the ketogenic lifestyle to support your overall well-being and pave the way for a healthier future.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
The First Step to Metabolic Health: Giving Up Seed Oils for Better Well-being
- May 18, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: In our pursuit of better health, we often focus on what we eat. We meticulously choose fresh produce, lean proteins, and whole grains. However, there’s one crucial ingredient hiding in many processed foods and restaurant meals that we need to pay attention to: seed oils. These commonly used cooking oils, such as soybean, canola, corn, and sunflower oils, have gained popularity but come at a cost to our metabolic health. Understanding their contribution to poor health and taking the first step of eliminating them from our diet can have significant benefits for our overall well-being.
The Problem with Seed Oils: Seed oils have become prevalent in the modern Western diet due to their affordability and high smoke point, making them ideal for cooking and food production. However, these oils are often highly processed and contain high levels of omega-6 fatty acids, which can disrupt the delicate balance of omega-6 to omega-3 ratio in our bodies. The overconsumption of omega-6 fatty acids, coupled with a deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids, has been linked to various health issues, including inflammation, obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular diseases.
The Processing Method: To truly grasp the negative impact of seed oils on our health, it’s essential to understand the process by which they are manufactured. Most seed oils undergo a complex process involving extraction, refining, bleaching, and deodorizing. This process strips the oils of their natural antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, leaving behind a product that is often rancid and devoid of any nutritional value. Additionally, the high heat and chemical solvents used during extraction can introduce harmful compounds, such as trans fats and free radicals, into the final product.
The First Step to Metabolic Health: Eliminating seed oils from our diet is a crucial first step towards achieving metabolic health. By replacing these unhealthy oils with healthier alternatives, such as extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, or grass-fed butter, we can positively impact our well-being in several ways:
- Reduced Inflammation: Seed oils, with their imbalanced omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, promote inflammation in the body. By switching to healthier oils, we can restore the balance and alleviate chronic inflammation, which is a key driver of many chronic diseases.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Seed oils have been associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes. Choosing healthier oils can help improve insulin sensitivity and support better blood sugar control.
- Enhanced Heart Health: Seed oils high in omega-6 fatty acids can negatively impact cardiovascular health by promoting inflammation, oxidative stress, and unhealthy cholesterol profiles. Opting for heart-healthy oils can lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular well-being.
- Nutrient-Rich Alternatives: Healthy oils like extra virgin olive oil and coconut oil offer a wealth of essential nutrients, antioxidants, and beneficial compounds that contribute to overall health. These oils can provide valuable health benefits and enhance the nutritional quality of our meals.
Conclusion: Taking the first step towards metabolic health involves eliminating seed oils from our diet. By understanding the detrimental effects of these oils on our well-being and opting for healthier alternatives, we can promote better metabolic function, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of chronic diseases. Making this dietary change is a powerful choice that sets the stage for a healthier future. Remember to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance on making healthier oil choices that align with your specific dietary needs and health goals.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Unlocking the Potential: Exploring the Benefits of Taurine in Extending Life
- May 16, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
In the pursuit of living longer, healthier lives, researchers and health enthusiasts alike are continuously exploring various strategies and supplements that may hold the key to longevity. One such compound that has captured the attention of scientists and health-conscious individuals is taurine. Widely recognized for its role in energy metabolism and overall health, taurine is an amino acid that offers a range of potential benefits, including its ability to extend life. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of taurine and its potential as a longevity-enhancing compound.
Taurine, often referred to as a “wonder molecule,” is naturally produced in the body and is found abundantly in various tissues, including the heart, brain, and muscles. It plays a crucial role in numerous physiological processes, such as regulating cell membrane stability, supporting antioxidant activity, modulating neurotransmission, and aiding in the proper functioning of vital organs. These multifaceted functions contribute to its potential in promoting longevity.
One of the key mechanisms through which taurine may extend life is its ability to combat oxidative stress and inflammation. As we age, our bodies accumulate damage from free radicals and experience increased inflammation, which contribute to the aging process and the development of age-related diseases. Taurine acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Additionally, it exerts anti-inflammatory effects, helping to mitigate chronic inflammation that can accelerate aging and increase the risk of age-related conditions.
Furthermore, taurine has been shown to support cardiovascular health, which is closely linked to longevity. It helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels, improves lipid profiles by lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and enhances the function of blood vessels. By promoting cardiovascular wellness, taurine may reduce the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications, ultimately contributing to a longer and healthier life.
The benefits of taurine extend beyond cardiovascular health. Research suggests that it may also support brain function and mental well-being, another crucial aspect of healthy aging. Taurine has been shown to enhance cognitive performance, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and improve mood and sleep quality. By supporting optimal brain health, taurine may help maintain cognitive function and overall mental vitality as we age.
Additionally, taurine’s role in energy metabolism and exercise performance is worth noting. It aids in the production of cellular energy by supporting the function of mitochondria, the powerhouse of our cells. This energy-boosting effect may contribute to maintaining an active lifestyle and promoting physical fitness, both of which are linked to longevity and overall well-being.
While taurine is naturally present in certain foods, such as meat, seafood, and dairy products, some individuals may benefit from taurine supplementation to ensure optimal levels. As with any supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting taurine supplementation, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
In conclusion, taurine holds immense promise as a compound that may contribute to extending life and promoting healthy aging. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, cognitive, and energy-enhancing properties position it as a potential longevity-enhancing supplement. However, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and establish optimal dosage recommendations.
As the quest for longevity continues, taurine presents itself as a compelling area of exploration and potential intervention. Embracing a holistic approach to health, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and informed supplementation, may help unlock the remarkable benefits of taurine and pave the way for a longer, healthier, and more vibrant life.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. It is always recommended to consult
with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet, lifestyle, or supplementation routine. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health needs and considerations.
Remember, while taurine shows promise in extending life and promoting health, it is just one piece of the puzzle in the complex journey of aging gracefully. Adopting a comprehensive approach to overall wellness, including maintaining a nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and staying socially connected, is essential for optimal health and longevity.
As the scientific community continues to delve deeper into the potential benefits of taurine and other compounds, it is an exciting time to explore the possibilities of enhancing our well-being and extending our lifespan. By staying informed, making informed choices, and working closely with healthcare professionals, we can strive to lead longer, healthier, and more fulfilling lives.
Please note that individual responses to taurine may vary, and it is important to consider your specific health status and any existing medical conditions before incorporating taurine or any other supplement into your routine.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Taking Control of Your Health: Combating Metabolic Syndrome with Keto and Intermittent Fasting
- May 12, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Metabolic syndrome has reached alarming levels in the United States, with a staggering 88% of the adult population affected. This condition not only poses immediate health risks but also increases the likelihood of developing chronic diseases in the future. However, by adopting a combination of the ketogenic diet (keto) and intermittent fasting (IF), you can take proactive steps to regain control of your health and prevent the onset of chronic diseases that have plagued previous generations.
The Metabolic Syndrome Epidemic: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of interconnected metabolic abnormalities that include abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, and abnormal lipid profiles. This dangerous combination significantly increases the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and other chronic conditions. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the U.S. highlights the urgent need for effective strategies to address this health crisis.
The Power of the Ketogenic Diet (Keto): The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan that promotes ketosis, a metabolic state in which the body primarily burns fat for fuel. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing healthy fats, the keto diet helps regulate blood sugar levels, promote weight loss, and improve insulin sensitivity, all of which are crucial in combating metabolic syndrome. Keto can also lead to a shift in the body’s fuel source, reducing reliance on carbohydrates and promoting fat burning, which can aid in weight management and reducing abdominal obesity.
Intermittent Fasting (IF) for Metabolic Health: Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. This approach not only helps control calorie intake but also promotes metabolic flexibility and enhances various health benefits. IF can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss. It also stimulates autophagy, a natural cellular cleansing process that helps remove damaged cells and supports overall cellular health. By incorporating IF alongside the ketogenic diet, you can further enhance the positive impact on metabolic syndrome and long-term health.
Breaking the Cycle: One of the most significant advantages of adopting a proactive approach to your health through keto and IF is the ability to break the cycle of chronic diseases that have affected previous generations. By making lifestyle changes now, you can prevent the onset of conditions like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity, which have plagued your parents or family members. Taking control of your health empowers you to pave a different path and avoid the struggles and limitations associated with chronic diseases.
Embracing a Healthier Future: Combating metabolic syndrome with keto and IF requires commitment and dedication, but the rewards are well worth the effort. Alongside the metabolic benefits, you may experience weight loss, increased energy levels, improved mental clarity, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to ensure your keto and IF practices are suitable for your individual health needs.
By taking control of your health now, you have the opportunity to rewrite your future. Don’t let metabolic syndrome and chronic diseases define your life. Embrace the power of keto and IF as tools to optimize your metabolic health, reclaim your vitality, and build a foundation for long-term well-being. Make a conscious choice today to break free from the statistics and create a healthier future for yourself and generations to come.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Transforming Healthcare in Rural America: The Role of Artificial Intelligence
- May 9, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Access to quality healthcare remains a significant challenge for rural communities in America. Limited resources, geographical barriers, and a shortage of healthcare professionals contribute to healthcare disparities in these areas. However, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) offers a transformative solution to address these challenges. This article explores how AI can improve healthcare in rural America, enhancing diagnosis and treatment, expanding access to specialized care, optimizing healthcare delivery, and empowering patients to take control of their health.
- Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment: AI algorithms have the potential to revolutionize the diagnostic process in rural healthcare settings. Machine learning models can analyze medical data, including patient records, lab results, and imaging scans, to assist healthcare providers in making accurate and timely diagnoses. AI can also support the identification of patterns and trends in population health data, helping healthcare professionals proactively address prevalent conditions in rural communities.
- Telemedicine and Remote Care: One of the most significant advantages of AI in rural healthcare is the ability to offer telemedicine and remote care services. Through AI-powered platforms, patients in remote areas can access virtual consultations with healthcare providers, eliminating the need for long-distance travel. This technology allows rural residents to receive timely medical advice, monitor chronic conditions, and access specialized care without the burden of geographical barriers.
- Optimization of Healthcare Delivery: AI can help optimize healthcare delivery in rural areas by streamlining processes and reducing inefficiencies. Predictive analytics can aid in resource allocation, ensuring that medical facilities have adequate staff, supplies, and equipment to meet the needs of the community. AI can also assist in predicting disease outbreaks and enabling targeted interventions, enabling rural healthcare providers to respond effectively to public health emergencies.
- Support for Rural Healthcare Professionals: AI can alleviate the burden on rural healthcare professionals by providing decision support tools and real-time access to medical information. AI-powered systems can analyze vast medical literature, recommend treatment options based on best practices, and offer guidance in complex medical scenarios. This assistance can enhance the capabilities of rural healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver high-quality care with greater confidence.
- Empowering Patients: AI technologies can empower rural patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey. Mobile health applications and wearable devices equipped with AI capabilities can help individuals monitor their vital signs, track their health conditions, and receive personalized health recommendations. By promoting self-care and providing health education, AI empowers rural residents to take control of their well-being and make informed decisions about their health.
Conclusion: Artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionize healthcare in rural America, addressing the unique challenges faced by these communities. Through enhanced diagnosis and treatment, telemedicine, optimized healthcare delivery, support for healthcare professionals, and patient empowerment, AI can bridge the gap in access to quality healthcare services. As rural areas strive for equitable healthcare, leveraging the power of AI becomes crucial. Collaborative efforts between healthcare organizations, policymakers, and technology experts are needed to ensure that AI is effectively integrated into rural healthcare systems, ultimately improving health outcomes and enhancing the well-being of rural Americans.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Harnessing the Power of Probiotics: Exploring Mitochondrial Uncoupling and its Benefits
- May 7, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Probiotics have gained considerable attention for their potential health benefits, especially in the context of gut health. However, recent studies have revealed an intriguing connection between probiotics and mitochondrial uncoupling, a process that holds promise for various health benefits. In this article, we will explore the role of probiotics in mitochondrial uncoupling and delve into the potential advantages it offers.
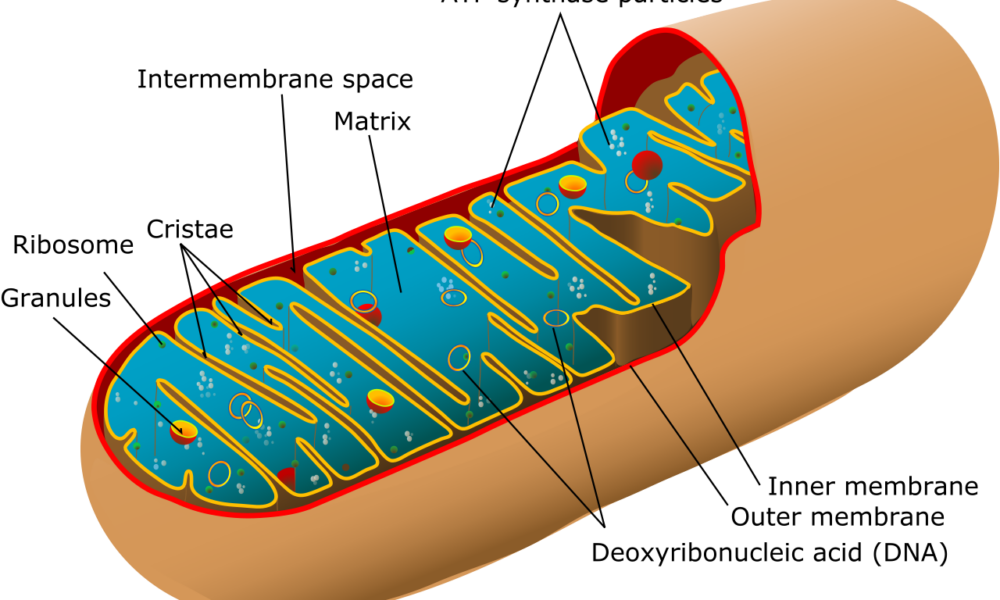
Understanding Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells, responsible for energy production. Normally, energy production occurs through a tightly regulated process called oxidative phosphorylation, where adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is generated. However, mitochondrial uncoupling refers to the disruption of this process, leading to the dissipation of energy as heat instead of ATP production. This phenomenon is facilitated by a protein called uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) and is primarily found in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and beige fat cells.
The Link Between Probiotics and Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Recent studies have demonstrated that certain probiotic strains can influence mitochondrial uncoupling and enhance the activity of UCP1. Specifically, probiotics like Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Akkermansia muciniphila have shown potential in promoting the browning of white adipose tissue, leading to increased thermogenesis and energy expenditure. These probiotics can modulate the gut microbiota composition and promote the release of specific metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), that play a role in mitochondrial uncoupling.
The Benefits of Probiotic-Induced Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Mitochondrial uncoupling, induced by probiotics, offers several potential benefits:
- Increased energy expenditure: By promoting thermogenesis and energy dissipation as heat, mitochondrial uncoupling can potentially boost overall energy expenditure, which may be beneficial for weight management and metabolic health.
- Improved glucose metabolism: Studies have suggested that probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling may improve glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, which could be particularly advantageous for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic disorders.
- Enhanced fat oxidation: Mitochondrial uncoupling can stimulate the breakdown of stored fat and enhance fat oxidation, potentially aiding in weight loss and reducing body fat.
- Regulation of inflammation: Probiotics that induce mitochondrial uncoupling have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved gut barrier function, which may have positive implications for various inflammatory conditions.
Conclusion: The emerging research on probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling highlights a fascinating link between gut health and metabolic processes. Probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Akkermansia muciniphila, show potential in promoting mitochondrial uncoupling and unlocking its associated benefits, including increased energy expenditure, improved glucose metabolism, enhanced fat oxidation, and regulation of inflammation. However, it is essential to note that further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term effects of probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling.
As our understanding of the gut-brain axis and the intricate connections within our bodies continues to grow, harnessing the power of probiotics for mitochondrial uncoupling opens up new avenues for potential health interventions. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals or specialists in the field can provide personalized advice and guidance for incorporating probiotics and optimizing their benefits in relation to mitochondrial uncoupling.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Vitamin D Supplementation: A Promising Strategy to Lower Diabetes Risk in Prediabetic Individuals
- May 1, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Vitamin D, a vital nutrient with multifaceted functions in the body, has been found to play a role in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. Observational studies have consistently shown an association between low levels of vitamin D in the blood and an increased risk of developing diabetes. Given these findings, researchers set out to investigate whether administering vitamin D to individuals at high risk for diabetes could effectively reduce that risk. In this article, we discuss the results of a comprehensive meta-analysis that examined the impact of vitamin D supplementation on diabetes prevention in adults with prediabetes.
Study Details: The study authors conducted a systematic search of three databases, encompassing research published up until December 9, 2022. Their focus was to compare the use of vitamin D versus a placebo for diabetes prevention in individuals with prediabetes. The data were subjected to a rigorous meta-analysis and reanalysis to evaluate the pooled results of multiple trials. Importantly, the trials included were deemed to have a low risk of bias, enhancing the reliability of the findings.
Results: Over a period of three years, the study revealed that individuals in the vitamin D group had a lower incidence of new-onset diabetes compared to the placebo group. Specifically, 22.7% of participants in the vitamin D group developed diabetes, while 25% of those in the placebo group experienced new-onset diabetes. This translates to a 15% reduction in the risk of developing diabetes for individuals receiving vitamin D supplementation. To prevent one case of diabetes, approximately 30 adults with prediabetes would need to be treated with vitamin D.
Risk Reduction by Blood Levels: Furthermore, the study analyzed the effect of different blood levels of vitamin D on diabetes risk. Among participants who maintained a mean serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level of at least 125 nmol/L (≥50 ng/mL), cholecalciferol reduced the risk of diabetes by an impressive 76%, with a 3-year absolute risk reduction of 18.1%. In contrast, individuals with lower vitamin D levels (50 to 74 nmol/L or 20 to 29 ng/mL) still experienced a reduction in risk, albeit to a lesser extent.
Doses Used: The vitamin D supplementation regimens in the trials included 20,000 units of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) administered weekly, 4000 units of cholecalciferol daily, or 0.75 micrograms of eldecalcitol (a synthetic analogue of vitamin D) daily.
Adverse Events: While rare, the study did not provide definitive conclusions regarding the safety of vitamin D supplementation. Adverse events such as kidney stones, hypercalcemia, and hypercalciuria were not significantly different between the vitamin D and placebo groups.
Implications: The results of this study suggest that vitamin D supplementation can be an effective strategy for reducing the risk of developing diabetes in adults with prediabetes. These findings highlight the potential of a simple and accessible intervention that may have a significant impact on public health. However, further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, long-term effects, and safety profile of vitamin D supplementation in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion: Vitamin D supplementation has emerged as a promising avenue for lowering the risk of diabetes in individuals with prediabetes. The meta-analysis demonstrated a notable reduction in the incidence of new-onset diabetes among those receiving vitamin D supplementation compared to the placebo group. While the study sheds light on the efficacy of vitamin D, ongoing research is necessary to fully elucidate its role and establish specific guidelines for implementation. Nonetheless, these findings contribute to our understanding of diabetes prevention and underscore the potential benefits of incorporating an inexpensive and readily available solution like vitamin D supplementation in the overall approach to diabetes prevention. By considering the role of vitamin D in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism, individuals at high risk for diabetes, particularly those with prediabetes, may have an additional tool at their disposal to mitigate their risk.
As further research is conducted and more evidence accumulates, healthcare professionals can better inform their patients about the potential benefits and appropriate dosages of vitamin D supplementation. Implementing routine screening for vitamin D levels and providing personalized recommendations may become an integral part of preventive healthcare strategies aimed at reducing the burden of type 2 diabetes.
In conclusion, the meta-analysis and reanalysis of pooled data revealed that vitamin D supplementation was effective in lowering the risk of developing diabetes in adults with prediabetes. While additional studies are needed to confirm these findings and establish safety guidelines, the potential of an affordable and accessible intervention like vitamin D offers hope in the fight against type 2 diabetes. By addressing the role of vitamin D in diabetes prevention, healthcare providers can empower individuals with prediabetes to take proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Energy Showdown: Unleashing the ATP Powerhouses – Fat’s Astonishing 129 ATP vs. Sugar’s Modest 30-32 ATP
- April 28, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Understanding the energy production capabilities of different macronutrients is essential for comprehending the body’s preference for a high-fat diet. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of ATP production and compare the energy yield from fat and sugar metabolism. By unraveling the secrets of ATP, we can gain insights into why the body finds fat metabolism particularly advantageous.
The ATP Comparison: Fat vs. Sugar Metabolism To understand the body’s preference for a high-fat diet, let’s examine the ATP yield from fat and sugar metabolism more accurately.
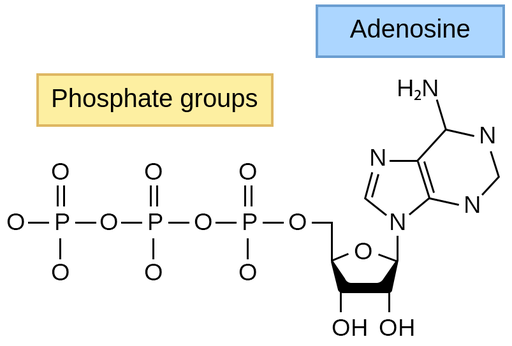
Sugar Metabolism: During the process of glycolysis, one molecule of glucose produces a net gain of approximately 2 ATP molecules. Through subsequent processes like the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, each molecule of pyruvate derived from glucose generates an additional 28-30 ATP molecules. Therefore, the total ATP yield from one molecule of glucose is typically around 30-32 ATP molecules.
Fat Metabolism: When it comes to fat metabolism, the oxidation of one molecule of a typical fatty acid, such as palmitic acid, can produce a remarkable number of ATP molecules. The complete oxidation of one molecule of palmitic acid, a common 16-carbon fatty acid, generates approximately 129 ATP molecules.
The Significance of ATP Yield: The substantial difference in ATP yield between fat and sugar metabolism holds great significance in understanding the body’s preference for a high-fat diet. Here’s why:
- Enhanced Energy Production: Fat metabolism provides a significantly higher ATP yield compared to sugar metabolism. With around 129 ATP molecules generated from one molecule of palmitic acid, the body gains a substantial energy advantage. This abundant supply of ATP allows for sustained and long-lasting energy production, supporting endurance activities and reducing the need for frequent refueling.
- Metabolic Adaptability: A high-fat diet encourages the body to become metabolically adaptable, efficiently utilizing fats as the primary fuel source. This metabolic flexibility enables improved fat oxidation and decreased reliance on carbohydrates, which can be advantageous for weight management and overall metabolic health.
- Stable Blood Sugar Control: Unlike carbohydrates, which can lead to rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, fats provide a more stable and sustained release of energy. By reducing the reliance on carbohydrates and minimizing blood sugar spikes, a high-fat diet promotes stable blood sugar control, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and supporting metabolic health.
- Cognitive Benefits: The brain, a highly energy-demanding organ, can benefit from a high-fat diet. Ketones, produced during fat metabolism, can serve as an alternative fuel source for the brain. This utilization of ketones provides a steady supply of energy, promoting improved cognitive function, mental clarity, and focus.
Conclusion: The ATP comparison between fat and sugar metabolism reveals the energy powerhouse that fat metabolism represents. With a significantly higher ATP yield compared to sugar metabolism, a high-fat diet provides enhanced energy production, metabolic
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist and Founder of Warp Core Health
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Understanding the CAC Test and Achieving a Score of 0 with Ketogenic Diet and Intermittent Fasting
- April 10, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
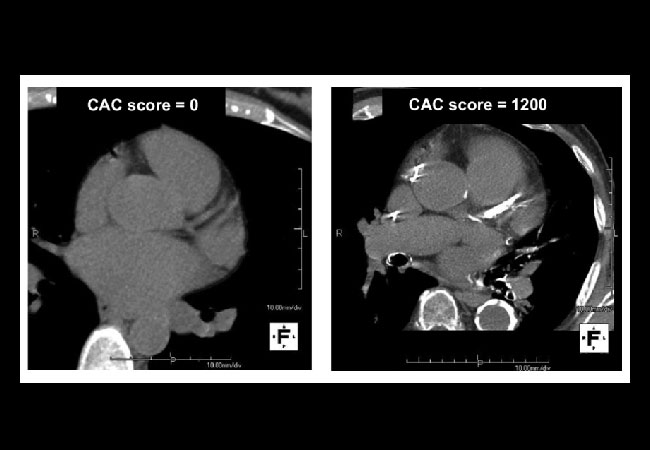
Coronary artery calcification (CAC) test is a non-invasive test that measures the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries. The test uses a CT scanner to detect calcium deposits in the coronary arteries, which is an indication of the presence of plaque that can cause heart disease. A high score on the CAC test is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other related conditions. However, research has shown that a combination of a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting can help achieve a CAC score of 0, indicating optimal heart health.
CAC Test and Its Importance:
The CAC test measures the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries and is used to assess an individual’s risk of developing heart disease. The test uses a CT scanner to detect calcium deposits in the walls of the coronary arteries. These deposits are a sign of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries that can lead to heart disease. The CAC score is a measure of the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries, and a high score indicates an increased risk of heart disease.
Achieving a CAC Score of 0 with a Ketogenic Diet and Intermittent Fasting:
Research has shown that a combination of a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting can help achieve a CAC score of 0, indicating optimal heart health. A ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that promotes the use of fat as the primary source of energy. This diet has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering triglycerides and increasing HDL cholesterol levels.
Intermittent fasting is a pattern of eating that involves periods of fasting and periods of eating. This eating pattern has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure, all of which can contribute to optimal heart health.
Studies have shown that a combination of a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting can help reduce the risk of heart disease and achieve a CAC score of 0. One study found that a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting for six months resulted in a significant reduction in the CAC score in participants with high initial scores. Another study showed that a low-carbohydrate diet combined with intermittent fasting for eight weeks resulted in a significant reduction in triglycerides and an increase in HDL cholesterol levels.
Conclusion:
The CAC test is an important tool for assessing an individual’s risk of developing heart disease. However, a combination of a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting can help achieve a CAC score of 0, indicating optimal heart health. These lifestyle changes have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure. Therefore, incorporating a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting into your lifestyle can lead to optimal heart health.
References:
1. Lu DY, Lu TR, Jackson NC, et al. Effects of a ketogenic diet combined with exercise on the CAC score and atherogenic index of plasma in adults with overweight and obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:3105-3116. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S326587
2. Ganesan K, Habboush Y, Sultan S. Intermittent fasting: the choice for a healthier lifestyle. Cureus. 2018;10(7):e2947. doi:10.7759/cureus.2947
3. Yokoyama Y, Takachi R, Ishihara J, et al. Association between a low-carbohydrate diet and coronary artery calcification in Japanese men and women: a cross-sectional study
——
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Achieving Optimal Metabolic Health: Criteria and Strategies
- April 6, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Metabolic health is an essential component of overall health, and it is crucial to understand the criteria necessary to achieve optimal metabolic health. An individual is considered to have optimal metabolic health if their markers meet the following levels: A1C less than 5.7%, blood pressure lower than 120/80 mmHg, waist circumference of 0.5 or less, triglycerides less than 150 mg/dL, and HDL cholesterol 60 mg/dL (1.6 mmol/L) or above.
On the other hand, an individual may be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome if they fail to meet three of the above criteria. Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of developing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. It is estimated that over one-third of American adults have metabolic syndrome, emphasizing the need to address this issue.
To achieve optimal metabolic health, a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions is necessary. The strategies to improve metabolic health include regular physical activity, healthy dietary choices, maintaining a healthy weight, smoking cessation, and managing stress. Additionally, medical interventions such as medication management of blood pressure and blood glucose levels may be necessary for some individuals.
Incorporating these strategies into daily life can significantly improve metabolic health and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. It is essential to work with healthcare providers to establish personalized goals and develop a plan to achieve them. Regular monitoring of metabolic markers is also crucial to ensure that the interventions are effective.
In conclusion, achieving optimal metabolic health requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. By meeting the criteria outlined above and incorporating strategies to improve metabolic health, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases and improve their overall health and well-being.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›
Recent Posts
- Protected: Warp Core Health: Building a Custom AI Model for Transforming Healthcare
- The Intersection of Healthcare, AI, Clinical Informatics, and Machine Learning
- Accessing Siloed EMR Systems with FHIR: Connecting to Multiple EMRs
- How AI and Informatics Are Transforming Healthcare
- How AI Can Transform Healthcare Applications
Categories
- ApoB
- Artificial Intelligence
- Autophagy
- Biochemistry
- Biomedical Informatics
- Biostatistics
- Blood Glucose
- CAC
- Carbs
- CCD
- CDA
- Clinical Informatics
- Coding Bootcamp
- Coronary Artery Disease
- COVID-19
- Cybersecurity
- Data Science
- Diabetes
- Diet
- EHS
- EMR
- Epidemiology
- Evidence Based Medicine
- Fats
- FHIR
- Fiber
- Generative AI
- Global Health
- Health Administration
- Health Informatics
- Health IT
- HIPAA
- HL7
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- ICD 10
- Intermittent Fasting
- Ketogenic Diet
- Machine Learning
- Macronutrients
- MCT Oil
- Metabolic Health
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Minerals
- Mitochondria
- MySQL
- Neurology
- Nutritional Ketosis
- Nutritional Neurology
- Nutritional Psychiatry
- PHP
- PHR
- Programming
- Prompt Engineering
- Proteins
- Prototypes
- Public Health
- Python
- Recipes
- Sleep Health
- Stroke
- Uric Acid
- Vegan and Vegetarians
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K2
- Vitamins