- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: Intermittent Fasting
Rejuvenate Your Body: Harnessing the Power of Intermittent Fasting for Autophagy
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction
Intermittent fasting has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. One of the key aspects of intermittent fasting is its ability to stimulate a process called autophagy. Autophagy, which translates to “self-eating” in Greek, is a natural cellular process that plays a vital role in maintaining cellular health and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the importance of intermittent fasting for autophagy and how it can positively impact our health.
Understanding Autophagy
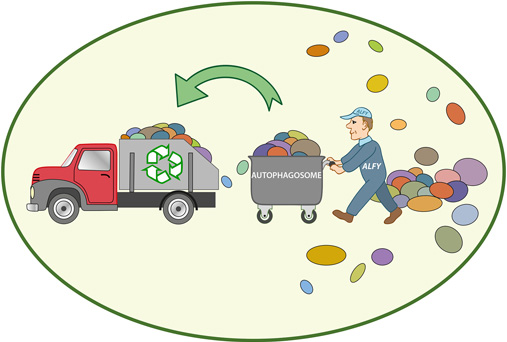
Autophagy is an intricate process by which cells remove and recycle damaged, dysfunctional, or unnecessary components, such as proteins and organelles. It acts as a cellular cleansing mechanism, promoting cellular renewal and enhancing the overall efficiency of our cells. This process is crucial for maintaining cellular health, preventing the accumulation of toxic substances, and reducing the risk of various diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
Autophagy and Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of fasting and eating. It doesn’t focus on what you eat but rather when you eat. Commonly, individuals adopt one of the popular intermittent fasting methods, such as the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) or the 5:2 diet (eating normally for five days and significantly reducing calorie intake for two non-consecutive days).
Studies have suggested that intermittent fasting can stimulate autophagy, thereby enhancing cellular health. When we fast, our body experiences a drop in insulin levels, leading to a state of increased autophagy. During this fasting period, the body shifts from utilizing glucose as a primary source of energy to utilizing stored fats through a process called ketosis. Ketosis has been shown to induce autophagy and promote cellular rejuvenation.
Benefits of Autophagy
- Cellular Regeneration: Autophagy allows for the removal of damaged or malfunctioning cellular components, promoting cellular regeneration and rejuvenation. This process helps to maintain cellular health and prevent the accumulation of toxic substances that can lead to various diseases.
- Anti-Aging Effects: Autophagy has been linked to anti-aging effects. By eliminating damaged cellular components and proteins, autophagy can help slow down the aging process and delay age-related diseases.
- Disease Prevention: Autophagy plays a crucial role in protecting against various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. By eliminating dysfunctional cells and reducing oxidative stress, autophagy helps to mitigate the risk of these diseases.
- Metabolic Health: Intermittent fasting and autophagy can have positive effects on metabolic health. It has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote healthy weight management.
- Clearance of Protein Aggregates: Intermittent fasting triggers autophagy, enabling cells to remove protein aggregates, including amyloid, tau, alpha-synuclein, and Lewy bodies. These aggregates are associated with neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other conditions. By effectively clearing these toxic substances, intermittent fasting helps decrease neuroinflammation and supports brain health.
- Reduction of Primed Glial Cells: Primed glial cells, when overactive, contribute to neuroinflammation. Intermittent fasting helps clear these primed glial cells, further decreasing neuroinflammation and offering neuroprotective effects. This reduction in neuroinflammation is key in preserving brain function and mitigating the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusion
Autophagy is a vital cellular process that promotes cellular health, rejuvenation, and disease prevention. Intermittent fasting serves as an effective tool to stimulate autophagy and reap its numerous benefits. By adopting intermittent fasting, individuals can harness the power of autophagy, enhancing their overall well-being and reducing the risk of various age-related diseases.
However, it is important to note that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with specific medical conditions or nutritional needs. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before implementing any significant dietary changes.
Incorporating intermittent fasting into one’s lifestyle, along with a balanced diet and regular exercise, can pave the way for improved cellular health and a healthier, more vibrant life.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Navigating the Ketogenic Diet with Intermittent Fasting for Type 1 Diabetics: A Safe Approach to Managing Blood Sugar with Modern Technology
Introduction: Embracing a ketogenic diet, characterized by low carbohydrate intake and high fat consumption, along with intermittent fasting (IF), holds potential health benefits. But what about individuals with Type 1 Diabetes who rely on insulin for blood sugar management? Can they safely adopt a ketogenic lifestyle? In this article, we will explore how individuals with Type 1 Diabetes can safely navigate a ketogenic diet with the inclusion of intermittent fasting, ensuring stable blood sugar control and optimized health outcomes. With modern technology, such as the t:slim X2 Insulin Pump, monitoring blood sugars has become easier than ever.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes and the Ketogenic Diet: Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Traditionally, carbohydrate counting and insulin dosing have been vital for managing blood sugar. However, the ketogenic diet offers an alternative approach by minimizing carbohydrate intake, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the need for large insulin doses.
Safely Adopting the Ketogenic Diet:
- Consult with Healthcare Professionals: Seek guidance from your healthcare team, including a registered dietitian and endocrinologist, to ensure a safe and effective transition to a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting. They can provide personalized advice and help adjust insulin doses accordingly.
- Utilize Modern Technology: Take advantage of modern technology, such as the t:slim X2 Insulin Pump, which makes monitoring blood sugars easier than ever. This pump offers advanced features like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) integration, insulin delivery adjustments, and data tracking, allowing for better management of blood sugar levels.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels, especially during the initial stages of transitioning to a ketogenic diet. Frequent testing, combined with the convenience of devices like the t:slim X2 Insulin Pump, helps identify trends, make necessary insulin dose adjustments, and modify your diet accordingly.
- Individualized Carbohydrate Intake: Work with a registered dietitian experienced in managing diabetes to determine the appropriate carbohydrate limit for your specific needs, considering factors such as insulin sensitivity, activity levels, and overall health.
- Timing of Meals and Insulin: Intermittent fasting can be incorporated into the ketogenic diet, but it requires careful planning. Collaborate closely with your healthcare team to determine the best fasting and eating windows while considering insulin requirements and blood sugar control.
Benefits of Ketogenic Diet with IF for Type 1 Diabetics:
- Blood Sugar Stability: By reducing carbohydrate intake, individuals with Type 1 Diabetes may experience more stable blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of extreme highs and lows.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: The combination of a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting may improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels and potentially reducing the need for high insulin doses.
- Weight Management: The ketogenic diet, coupled with intermittent fasting, may aid in weight management, which is beneficial for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes who may be at a higher risk of weight fluctuations.
- Potential for Fewer Complications: Maintaining stable blood sugar levels and reducing the need for high insulin doses may lower the risk of long-term complications associated with Type 1 Diabetes.
Conclusion: While the ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting hold potential benefits for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes, it is crucial to approach them with caution and under the guidance of healthcare professionals. With modern technology, such as the t:slim X2 Insulin Pump, monitoring blood sugars has become easier than ever, allowing for better control and management. Working closely with your healthcare team, including a registered dietitian and endocrinologist, will ensure a safe and effective transition to a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting. Together, you can develop an individualized plan that considers your insulin requirements, blood sugar levels, and overall health goals. With the right support and modern tools at your disposal, it is possible for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes to safely embrace a ketogenic lifestyle and experience the potential benefits it offers in blood sugar management and overall well-being.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2