- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
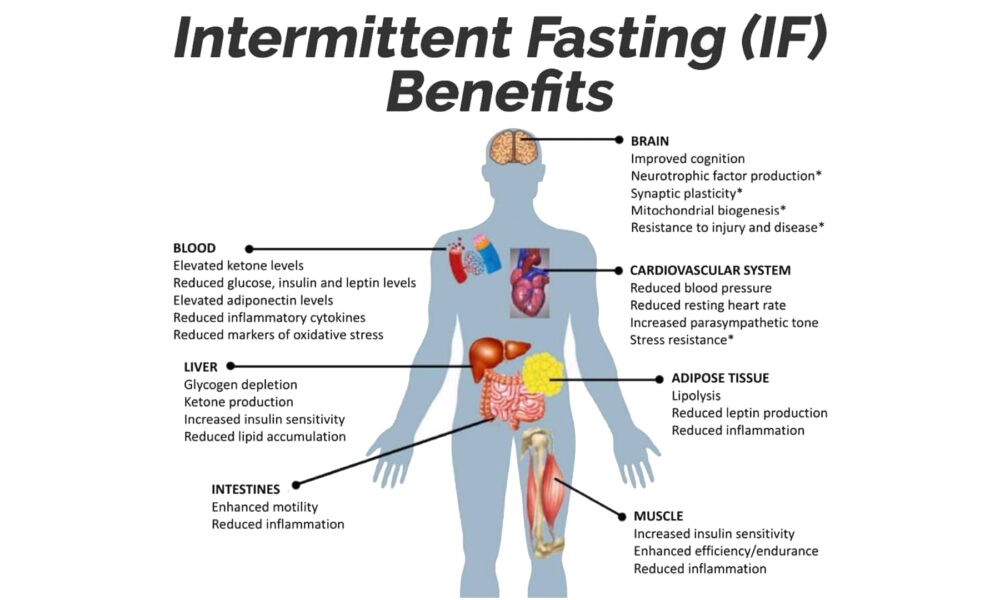
Category: Intermittent Fasting
Harnessing the Power of Nutritional Neurology: A Ketogenic Lifestyle and Intermittent Fasting Approach
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
In recent years, the field of nutritional neurology has gained significant attention as a promising approach to enhance brain health and treat various neurological disorders. By combining the principles of a ketogenic lifestyle and intermittent fasting, researchers and healthcare professionals are exploring new avenues for improving and potentially even curing certain neurological conditions. This article aims to shed light on the concept of nutritional neurology and its potential impact on ten neurological disorders.
Understanding Nutritional Neurology:
Nutritional neurology focuses on the relationship between diet and brain health. It recognizes that the food we consume can directly impact the structure and function of our nervous system. A ketogenic lifestyle involves consuming a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that induces a state of ketosis. Intermittent fasting, on the other hand, refers to periods of time when food intake is restricted, alternating with periods of regular eating.
Neurological Disorders and the Role of Nutritional Neurology:
Epilepsy: Studies have shown that a ketogenic diet can significantly reduce seizure frequency in individuals with epilepsy, particularly in children whose seizures are drug-resistant.
Alzheimer’s Disease: A ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting have shown potential in enhancing brain function and reducing cognitive decline in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Parkinson’s Disease: Nutritional neurology, particularly the ketogenic diet, may help improve motor symptoms and overall quality of life in individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Some evidence suggests that a ketogenic diet may alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of MS by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Migraine: The ketogenic diet, combined with intermittent fasting, may reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines by modulating brain energy metabolism and reducing neuroinflammation.
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): Nutritional interventions, including a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting, have shown promise in managing symptoms associated with ASD, such as behavioral issues and cognitive impairments.
Depression: Emerging research suggests that a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting may have antidepressant effects by modulating neurotransmitter activity and reducing inflammation.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Nutritional neurology approaches, such as a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting, have shown potential in promoting neuroprotection and supporting recovery following TBI.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): While further research is needed, preliminary studies indicate that a ketogenic diet may improve mitochondrial function and potentially slow the progression of ALS.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Nutritional interventions, including a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting, may help manage symptoms of ADHD by improving focus, attention, and behavior.
Conclusion:
Nutritional neurology offers a fascinating perspective on brain health and the treatment of neurological disorders. By embracing a ketogenic lifestyle and incorporating intermittent fasting, individuals may potentially experience improvements in various neurological conditions. However, it is important to note that nutritional interventions should be pursued under the guidance of healthcare professionals and tailored to each individual’s specific needs. As research continues to unfold, nutritional neurology holds the promise of transforming the way we approach neurological disorders and enhancing the lives of countless individuals.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Intermittent Fasting: The Key to Metabolic Health, Empowered by the Ketogenic Diet for Satiety, Hunger Reduction, and Craving Control
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction
In the realm of metabolic health, one strategy has risen above the rest: Intermittent Fasting (IF). When coupled with the Ketogenic (Keto) diet, IF becomes an unrivaled approach that unlocks the full potential of satiety, hunger reduction, and cravings control. By harnessing the power of fasting, IF paves the way for optimal metabolic function, while the Keto diet amplifies these benefits, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Intermittent Fasting: A Metabolic Game Changer
Intermittent Fasting has garnered widespread acclaim due to its profound impact on metabolic health. Rather than focusing solely on what you eat, IF centers on when you eat, establishing periods of fasting interspersed with designated eating windows.
At the core of IF lies its ability to promote metabolic flexibility. By depriving your body of constant food intake, it becomes adept at tapping into stored fat as an alternative energy source. This metabolic switch leads to weight loss, increased insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation.
Satiety and Hunger Reduction: The Role of IF
One of the key advantages of IF is its capacity to enhance satiety and curb hunger. During fasting periods, your body turns to its fat stores for fuel, facilitating fat burning and weight loss. However, the benefits extend far beyond shedding pounds.
IF effectively regulates hunger and fullness hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, which influence appetite. With consistent practice, these hormones rebalance, resulting in reduced hunger and decreased cravings. By allowing your body ample time between meals, IF equips you with a newfound sense of control over your eating habits.
The Power of the Ketogenic Diet
Enter the Ketogenic diet, a low-carbohydrate, high-fat approach that synergizes remarkably with IF. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing healthy fat consumption, the Keto diet promotes nutritional ketosis—a metabolic state where your body primarily relies on fat for energy.
The Keto diet is a satiety powerhouse. Healthy fats take longer to digest, keeping you feeling full and satisfied for extended periods. This phenomenon effectively curbs hunger, reduces cravings, and prevents the energy crashes associated with high-carbohydrate diets.
IF and Keto: The Dynamic Duo for Metabolic Health
When Intermittent Fasting and the Ketogenic diet join forces, a metabolic transformation occurs. IF acts as the catalyst, priming your body for efficient fat burning, while the Keto diet ensures that fat becomes the primary fuel source.
By following a Ketogenic diet within your designated eating window, you not only maintain a state of ketosis but also heighten the feeling of satiety. The combined approach effectively reduces hunger and cravings, making it easier to adhere to your dietary goals and achieve optimal metabolic health.
Conclusion
Intermittent Fasting is the key to unlocking metabolic health, and when paired with the Ketogenic diet, it becomes an unbeatable strategy for satiety, hunger reduction, and craving control. IF enhances your body’s ability to tap into stored fat for energy and regulates hunger hormones, while the Keto diet amplifies these effects through increased fat consumption.
Embrace Intermittent Fasting as your metabolic ally and leverage the Ketogenic diet as the perfect complement. Together, they offer a path to sustainable weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and enhanced overall well-being. Experience the transformative power of IF and Keto, and embrace a life of metabolic vitality.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
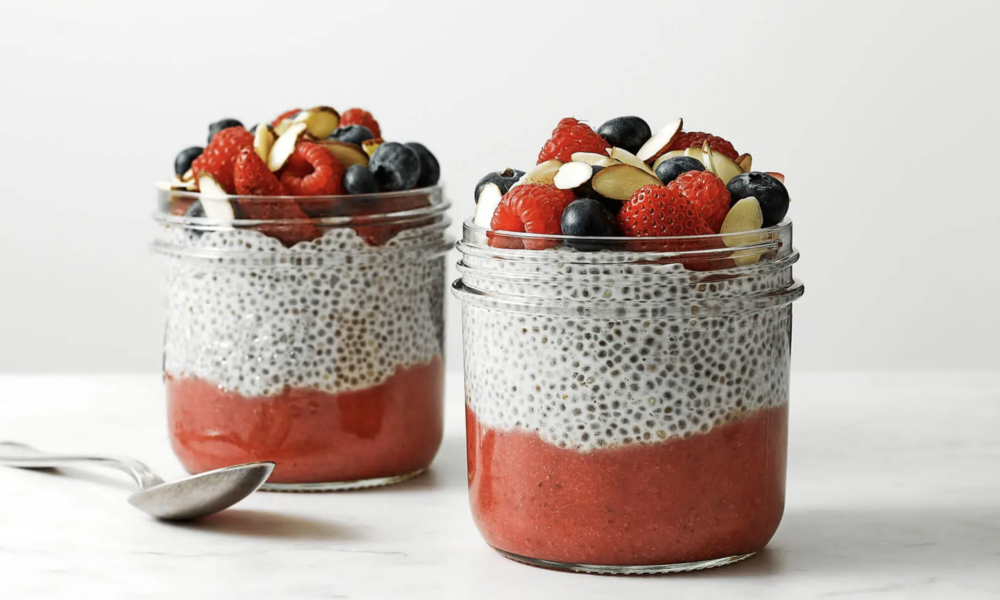
Harness the Power of Chia Seeds: Essential Fat Source for Vegans and Vegetarians on a Ketogenic Diet
By Stephen Fitzmeyer
Introduction: Following a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting can present unique challenges for vegans and vegetarians. However, there is an incredibly versatile and nutrient-dense solution that can help bridge the fat gap in their diets—chia seeds. These tiny powerhouses are abundant in healthy fats, making them an indispensable addition for individuals seeking to maintain a balanced and nourishing meal plan. Let’s explore the vital role chia seeds play in providing essential fats for vegans and vegetarians on a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting.
Rich in Healthy Fats: Chia seeds are a remarkable source of healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats are crucial for brain health, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular well-being. By incorporating chia seeds into their meals, vegans and vegetarians can ensure they are meeting their daily fat requirements, which are essential for overall health and vitality.
Promote Ketosis: In a ketogenic diet, the primary energy source shifts from carbohydrates to fats. Chia seeds, with their high fat content and low carbohydrate profile, contribute to achieving and maintaining a state of ketosis. Including chia seeds in a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet provides a reliable and convenient way to increase fat intake while minimizing carb consumption, aiding the body in transitioning to a fat-burning metabolic state.
Satiety and Appetite Control: One of the challenges of intermittent fasting is managing hunger and maintaining satiety during fasting periods. The combination of healthy fats and fiber in chia seeds helps promote a feeling of fullness, making them an effective tool for appetite control. The fats in chia seeds are digested slowly, providing sustained energy and reducing the likelihood of cravings or overeating. By incorporating chia seeds into meals or snacks, vegans and vegetarians can support their efforts in adhering to an intermittent fasting schedule.
Versatile and Easy to Include: Chia seeds offer immense versatility in meal preparation, making them an ideal addition to a vegan or vegetarian ketogenic diet. They can be added to smoothies, sprinkled on salads, used as a thickening agent in sauces, or incorporated into baked goods. Their ability to absorb liquids and form a gel-like consistency allows them to adapt to various culinary creations, enhancing both taste and texture.
Nutrient-Rich Profile: Beyond their healthy fat content, chia seeds boast an impressive nutrient profile. They are a notable source of plant-based protein, essential minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and manganese, and dietary fiber. This nutrient combination is especially valuable for vegans and vegetarians who may face challenges in meeting their daily requirements. By integrating chia seeds into their diet, individuals can enhance their overall nutritional intake and ensure they are obtaining a well-rounded range of essential nutrients.
Conclusion: For vegans and vegetarians on a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting, chia seeds are a nutritional powerhouse that plays a vital role in meeting the necessary fat intake. With their high healthy fat content, chia seeds support ketosis, enhance satiety, and provide a wide array of essential nutrients. By incorporating chia seeds into their meals, vegans and vegetarians can effectively address the challenge of obtaining adequate fats while adhering to their dietary preferences and maintaining the principles of a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting. Embrace the extraordinary potential of chia seeds and witness the transformative impact they can have on your vegan or vegetarian ketogenic journey.

—
Here are some keto-friendly examples of how to use chia seeds in your daily meals:
- Keto Chia Pudding:
- In a jar, combine 2 tablespoons of chia seeds, 1 cup of unsweetened almond milk (or any non-dairy milk with no added sugars), and a few drops of liquid stevia (or any keto-approved sweetener) to taste.
- Stir well and let it sit in the refrigerator overnight or for at least 4 hours.
- In the morning, give it a good stir and top with a sprinkle of low-carb berries (such as raspberries or blackberries), chopped nuts, or a dollop of coconut cream for added richness.
- Chia Seed Smoothie Booster:
- Add 1 tablespoon of chia seeds to your favorite keto-friendly smoothie recipe.
- Blend until smooth, and the chia seeds will provide added thickness and a boost of healthy fats to your smoothie.
- Keto Chia Seed Pudding Parfait:
- In a jar or glass, layer chia pudding (made with chia seeds, unsweetened almond milk, and keto-friendly sweetener) with a dollop of full-fat coconut yogurt or unsweetened Greek yogurt.
- Top with a sprinkle of crushed nuts, unsweetened coconut flakes, and a few low-carb berries.
- Repeat the layers and create a beautiful and satisfying chia seed pudding parfait.
- Keto Chia Seed Crackers:
- In a bowl, mix 1/4 cup of chia seeds, 1/4 cup of ground flaxseed, 2 tablespoons of coconut flour, 1/2 teaspoon of garlic powder, 1/2 teaspoon of onion powder, 1/4 teaspoon of sea salt, and 1/4 cup of water.
- Let the mixture sit for a few minutes to allow the chia seeds and flaxseed to absorb the water and form a gel-like consistency.
- Spread the mixture evenly on a parchment-lined baking sheet and bake at 350°F (175°C) for about 15-20 minutes, or until the crackers are golden and crispy.
- Allow them to cool before breaking them into crackers.
- Serve the keto chia seed crackers with your favorite low-carb dip or enjoy them on their own as a crunchy snack.
- Keto Chia Seed Breakfast Porridge:
- In a saucepan, combine 2 tablespoons of chia seeds, 2 tablespoons of unsweetened coconut flakes, 1/2 cup of unsweetened almond milk, 1/2 cup of water, and a pinch of cinnamon.
- Cook over medium heat, stirring occasionally, until the mixture thickens and reaches your desired porridge consistency.
- Remove from heat and let it cool for a few minutes.
- Top with sliced almonds, a drizzle of sugar-free syrup or melted coconut oil, and a sprinkle of ground flaxseed or hemp hearts for added crunch and healthy fats.
Remember to adjust the portion sizes and ingredients based on your specific dietary needs and goals on the keto diet. Enjoy these keto-friendly chia seed recipes and explore more possibilities to incorporate this nutritious superfood into your daily keto meal plan.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Unveiling the Role of ApoB and the Therapeutic Potential of Ketogenic Lifestyle and Intermittent Fasting in Atherosclerosis
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
Atherosclerosis, a major contributor to cardiovascular disease, arises from a complex interplay of various factors. Among them, Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) emerges as the primary driver in the development and progression of this condition. In this article, we delve into the critical role of ApoB in atherosclerosis and shed light on the influence of inflammation in enhancing its effects.
Understanding the Role of ApoB:
ApoB, a protein found in lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, serves as a key player in atherosclerosis. It acts as a carrier, facilitating the transportation of cholesterol to peripheral tissues, including the arterial walls. In the absence of ApoB, the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis are virtually non-existent.
The Significance of ApoB in Atherosclerosis:
ApoB takes center stage in atherosclerosis, as it is responsible for delivering cholesterol-rich lipoproteins, particularly LDL, to arterial walls. These lipoproteins undergo modifications and become trapped in the arterial intima, initiating the formation of fatty streaks. With time, inflammation is triggered, attracting immune cells and accelerating the transformation of fatty streaks into advanced atherosclerotic plaques.
Inflammation and its Role:
While inflammation is a key player in atherosclerosis, it acts as an enhancer rather than the primary driver. Inflammation exacerbates the process by promoting the retention and modification of ApoB-containing lipoproteins, leading to plaque progression and instability. Thus, controlling inflammation becomes crucial in managing atherosclerosis, but addressing the root cause—ApoB—remains essential.
Implications and Therapeutic Strategies:
Understanding the central role of ApoB opens up avenues for therapeutic interventions in managing atherosclerosis. Addressing ApoB levels and reducing the burden of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins is key. Here, lifestyle modifications such as adopting a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet (such as a ketogenic diet) and implementing intermittent fasting can prove beneficial. These approaches help regulate ApoB-containing lipoproteins, mitigate their retention in arterial walls, and slow down the progression of atherosclerosis.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications that target additional risk factors associated with atherosclerosis, such as hypertension and obesity, should be considered. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing other comorbidities can complement the efforts to address ApoB and reduce the overall risk of atherosclerosis.
Conclusion:
ApoB stands as the primary driver in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis, while inflammation serves to enhance and accelerate the process. Recognizing the pivotal role of ApoB provides insights into therapeutic strategies that can mitigate its effects. By adopting lifestyle modifications, such as a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet and intermittent fasting, individuals can positively influence ApoB levels and manage atherosclerosis. Combining these interventions with measures to address other risk factors offers a comprehensive approach to reducing the burden of atherosclerosis and promoting cardiovascular health.
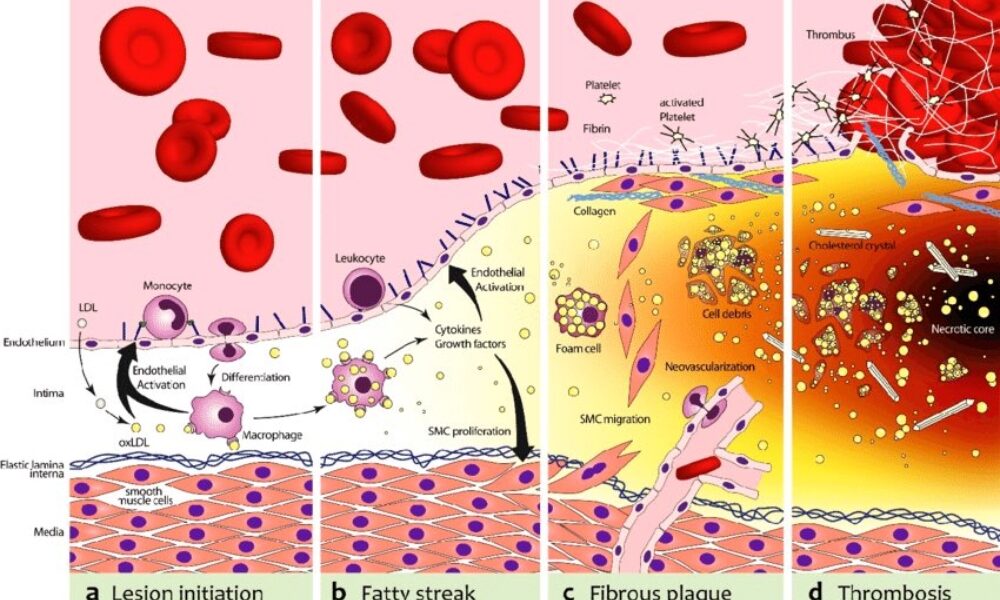
The biochemical pathway of plaque formation involving ApoB can be described as follows:
- ApoB synthesis: ApoB is a protein synthesized in the liver and intestines. It is a major component of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and LDL particles.
- Lipoprotein assembly: VLDL particles are assembled in the liver and contain ApoB-100. They transport triglycerides and cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues. During circulation, VLDL particles undergo enzymatic changes, resulting in the conversion of triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol.
- LDL formation: As VLDL particles lose triglycerides, they become smaller and denser, transforming into LDL particles. LDL contains a single molecule of ApoB-100 and is the primary carrier of cholesterol in the bloodstream.
- LDL uptake: LDL particles bind to LDL receptors on cell surfaces, allowing the cells to take up cholesterol. These receptors are present in various tissues, including the arterial walls.
- Retention and modification: In the arterial walls, LDL particles can undergo modifications, such as oxidation and glycation, making them more prone to retention. These modified LDL particles interact with extracellular matrix proteins and proteoglycans in the arterial intima, leading to their entrapment within the vessel walls.
- Inflammation and foam cell formation: The retained LDL particles, along with their cholesterol content, trigger an inflammatory response. Immune cells, particularly macrophages, migrate to the site of inflammation. They engulf the cholesterol-rich LDL particles, transforming into foam cells, which are characterized by their lipid-filled cytoplasm.
- Fatty streak formation: The accumulation of foam cells and other immune cells results in the formation of fatty streaks, which are the initial visible signs of plaque development. Fatty streaks consist of foam cells, lipids, inflammatory cells, and smooth muscle cells.
- Advanced plaque formation: Over time, the fatty streaks can progress into more advanced atherosclerotic plaques. These plaques are characterized by a fibrous cap composed of smooth muscle cells and collagen, a lipid-rich core containing foam cells and cholesterol, and a necrotic center.
Throughout this biochemical pathway, ApoB plays a crucial role in the transport of cholesterol to peripheral tissues, including the arterial walls. It facilitates the delivery of cholesterol-rich LDL particles, which, under certain conditions, contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Understanding this pathway provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets for preventing and managing plaque formation and related cardiovascular diseases.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/