- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Category: HL7
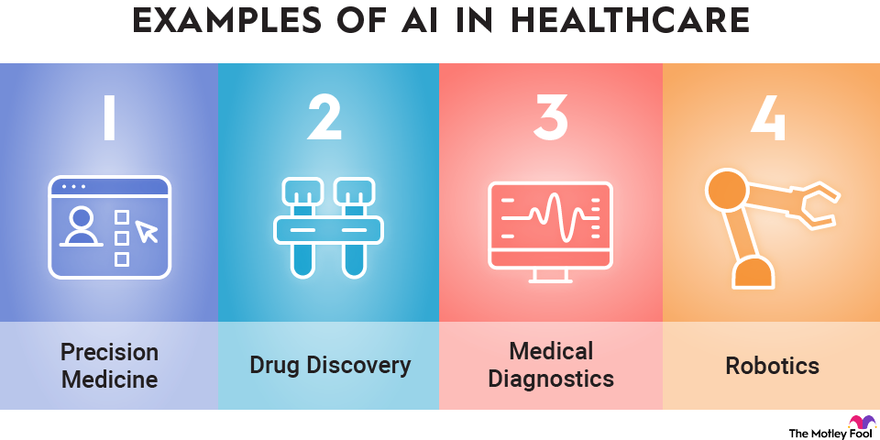
How AI Can Transform Healthcare Applications
How AI Can Transform Healthcare Applications
As a developer of healthcare applications, you’re constantly looking for ways to improve functionality, efficiency, and user experience. Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a transformative opportunity to enhance healthcare apps, making them smarter, more user-friendly, and impactful. Here’s how AI can elevate your healthcare applications to the next level.
1. Enhancing Patient Care and Management
- Personalized Treatment Recommendations: AI algorithms analyze patient data like lab results, genetic information, and medical history to suggest tailored treatment plans.
- Virtual Assistants: Chatbots powered by natural language processing (NLP) can answer common patient questions, help schedule appointments, and remind patients about medications.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models predict potential health issues, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, allowing for early intervention and better patient outcomes.
2. Supporting Clinical Decision-Making
- AI Diagnosis Tools: Machine learning can analyze medical images, lab tests, or patient-reported symptoms to help identify conditions quickly and accurately.
- Drug Interaction Alerts: AI systems can flag potential drug interactions or contraindications based on a patient’s medication history.
- Risk Assessment Models: Predictive models assess patient risks for conditions like stroke or sepsis, enabling proactive care.
3. Optimizing Workflow
- Automated Documentation: NLP tools transcribe and summarize doctor-patient conversations, reducing administrative burdens.
- Intelligent Scheduling: AI-powered tools optimize staff and appointment scheduling, minimizing wait times and maximizing resource utilization.
- Claims Automation: Automate insurance claim reviews with AI, reducing errors and speeding up reimbursement processes.
4. Enhancing Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
- AI Diagnostics: Enhance telehealth platforms with tools that analyze patient-reported data or uploaded images during virtual consultations.
- Wearable Data Integration: Develop AI algorithms to process data from wearables, offering actionable insights into patient health.
- Symptom Checkers: AI-driven tools allow patients to input symptoms and receive preliminary assessments, streamlining triage.
5. Delivering Data Insights and Analytics
- Patient Cohort Analysis: AI identifies patterns in patient populations, improving treatment strategies and research.
- Health Trend Forecasting: Analyze big data to predict public health trends or disease outbreaks.
- Operational Efficiency: Use AI to optimize inventory, staffing, and resource allocation in clinical settings.
6. Improving Patient Engagement
- Conversational Interfaces: Enable patients to interact with your app through natural language queries, making healthcare more accessible.
- Gamification: Use AI to personalize gamified elements, encouraging adherence to treatment plans or healthy behaviors.
- Educational Content: Deliver tailored educational materials based on a patient’s condition or interests.
7. Ensuring Compliance and Security
- Data Anonymization: AI can de-identify sensitive patient data for compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Fraud Detection: AI detects anomalies in billing or prescriptions that may indicate fraud.
- Secure Data Sharing: Facilitate secure and efficient sharing of patient records among healthcare providers.
8. Facilitating Research and Development
- Clinical Trial Matching: Match eligible patients to clinical trials using AI-driven analysis of their medical profiles.
- Drug Discovery: Use AI models to simulate and analyze potential drug compounds.
- Real-World Evidence: Generate insights from patient data to support post-market surveillance and drug efficacy studies.
9. Expanding Accessibility
- Language Translation: Offer multilingual support for diverse patient populations with AI translation tools.
- Accessibility Features: Build AI-driven speech-to-text and text-to-speech features for patients with disabilities.
10. Elevating User Experience
- Predictive Navigation: Anticipate user actions to streamline navigation and improve usability.
- Behavioral Nudges: Deliver proactive reminders or nudges, such as medication adherence prompts, based on user behavior.
- Dynamic Interfaces: Personalize app interfaces based on user preferences and engagement patterns.
Example: Implementing an AI-Powered Symptom Checker
Here’s an example of how you might structure an app to include a symptom checker using AI:
- Input Collection: The app asks users to input symptoms via text or voice.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI processes the input to extract relevant medical terms and symptoms.
- Symptom Analysis: The app uses a machine learning model trained on a medical dataset to compare the user’s symptoms with known patterns of illnesses.
- Recommendation Engine: Based on the analysis, the app provides possible conditions and suggests whether the user should seek immediate care, consult a doctor, or try home remedies.
- Continuous Learning: The app collects anonymized feedback from user interactions to improve the accuracy of the model over time.
Example Code for NLP Symptom Processing:
from transformers import pipeline
# Load a pre-trained NLP model for healthcare applications
nlp_model = pipeline("text-classification", model="bert-base-healthcare")
# Example user input
user_input = "I have a persistent cough and shortness of breath."
# Process the input
analysis = nlp_model(user_input)
# Output AI-generated insights
print("Potential conditions:", analysis)
This code snippet demonstrates how to use a pre-trained NLP (Natural Language Processing) model from the Hugging Face transformers library to classify text related to healthcare applications. Here’s a breakdown of what each part of the code does:
1. Importing pipeline from the transformers library
from transformers import pipelineThe pipeline function provides an easy interface to use pre-trained models for various NLP tasks like text classification, question answering, translation, etc.
2. Loading a Pre-trained NLP Model
nlp_model = pipeline("text-classification", model="bert-base-healthcare")pipeline("text-classification"): This specifies that the task is text classification, where input text will be categorized into predefined classes or labels.model="bert-base-healthcare": Refers to a pre-trained BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model fine-tuned for healthcare-related text classification. This specific model would likely be trained to understand healthcare vocabulary and contexts.
3. Processing User Input
user_input = "I have a persistent cough and shortness of breath."
analysis = nlp_model(user_input)The pipeline processes the input text using the loaded model to predict potential conditions or categories related to the input.
4. Outputting Results
print("Potential conditions:", analysis)The analysis variable contains the model’s predictions, such as potential health conditions or relevant categories for the provided symptoms.
Example Output
Potential conditions: [{'label': 'Respiratory Issue', 'score': 0.95}]- label: The predicted category (e.g., “Respiratory Issue”).
- score: The confidence score for this prediction (e.g., 0.95, indicating 95% confidence).
Use Case
This code can be part of a healthcare chatbot, clinical decision support system, or any application designed to provide preliminary insights based on patient symptoms. However, these AI-generated insights should not replace professional medical advice.
Getting Started with AI Integration
To start incorporating AI into your healthcare applications:
- Start Small: Begin with a single AI feature, such as a chatbot or predictive analytics, to test feasibility and user acceptance.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure clean, accurate data to power your AI models effectively.
- Focus on Ethics: Build trust by maintaining transparency, privacy, and fairness in AI algorithms.
- Iterate and Scale: Use feedback to refine AI functionalities and expand capabilities over time.
AI is reshaping healthcare, offering exciting opportunities to create more impactful applications. By leveraging AI, you can provide better care, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in healthcare technology.
Pillars of Excellence: Key Standards in the Healthcare Industry
Introduction
The healthcare industry is marked by its unwavering commitment to patient care, safety, and the pursuit of excellence. To maintain the highest standards in patient treatment, healthcare professionals adhere to a set of well-defined guidelines and standards. In this article, we explore the key standards in the healthcare industry that serve as the foundation for quality care and patient safety.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA, which we discussed in a previous article, is a cornerstone of healthcare standards. Its Privacy and Security Rules ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information. HIPAA also facilitates secure electronic data exchange, safeguarding patient privacy.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care focuses on the individual’s needs, preferences, and values. It encourages active patient involvement in healthcare decisions, considering their physical and emotional well-being. Effective communication and shared decision-making are key components of this standard.
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Clinical practice guidelines are evidence-based recommendations for healthcare professionals to provide high-quality care for specific medical conditions. These guidelines are continually updated to reflect the latest research, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Infection Control
Infection control standards are crucial for maintaining patient safety. Healthcare facilities strictly adhere to practices designed to prevent the spread of infections. Hand hygiene, sterilization, and sanitation procedures are key components of infection control.
Accreditation and Certification
Healthcare institutions often seek accreditation and certification from organizations like The Joint Commission, which set high standards for patient care and safety. Compliance with these standards demonstrates an organization’s commitment to quality healthcare delivery.
EHR (Electronic Health Record) Standards
With the transition to electronic health records, interoperability and data standards are essential. These standards ensure that patient information can be accurately and securely exchanged between healthcare systems, promoting continuity of care.
Patient Safety Goals
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) establish patient safety goals that healthcare providers worldwide must strive to meet. These goals include improving medication safety, reducing healthcare-associated infections, and preventing patient falls.
Nursing Standards
Nursing practice is guided by standards set by organizations like the American Nurses Association (ANA). These standards define the responsibilities and expectations for nursing practice, ensuring the delivery of safe and effective care.
Mental Health Standards
Mental health standards ensure that patients with mental health conditions receive appropriate and compassionate care. These standards include the provision of crisis intervention and psychosocial support.
Ethical Standards
Ethical standards in healthcare encompass a wide range of principles, including patient confidentiality, informed consent, and truth-telling. These standards guide the behavior and decision-making of healthcare professionals, ensuring the highest ethical standards in patient care.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry’s commitment to excellence and patient well-being is evident in the multitude of standards and guidelines that govern its practice. These standards touch on various aspects of healthcare, from privacy and data security to patient safety and ethical conduct. Adherence to these standards is not just a requirement but a reflection of the industry’s dedication to providing the best possible care to patients, ensuring their safety, and upholding the highest standards of professionalism and ethics. In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, these standards remain the pillars of excellence that drive the industry forward.
Using Python to Parse HL7 and CCD Documents in Healthcare
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Python is a powerful programming language that can be used to parse and manipulate healthcare data in the HL7 and CCD formats. In this article, we will explore how to use Python to extract and process data from HL7 and CCD documents.
First, let’s start by understanding the structure of HL7 and CCD documents. HL7 messages are comprised of segments, which contain fields and subfields that represent different types of data. CCD documents, on the other hand, are based on the HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) standard and use XML to represent the data.
To parse HL7 messages in Python, we can use the hl7apy library, which is an open-source Python library for working with HL7 messages. Here’s an example of how to use hl7apy to extract patient demographic information from an HL7 message:
from hl7apy.parser import parse_message
# Parse the HL7 message
msg = parse_message(‘MSH|^~\&|HIS|BLG|LIS|BLG|20200528163415||ADT^A04|MSG0001|P|2.3||||||UNICODE’)
# Get the patient name
patient_name = msg.pid[5][0].value
# Get the patient date of birth
dob = msg.pid[7].value
# Get the patient sex
sex = msg.pid[8].value
# Print the patient information
print(“Patient Name: ” + patient_name)
print(“Date of Birth: ” + dob)
print(“Sex: ” + sex)
##########
In this example, we’re using the parse_message() method from the hl7apy library to parse the HL7 message. We then use the message object to extract the patient name, date of birth, and sex from the PID segment.
To parse CCD documents in Python, we can use the ElementTree library, which is included in the Python standard library. Here’s an example of how to use ElementTree to extract medication information from a CCD document:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Parse the CCD document
tree = ET.parse(‘ccd.xml’)
# Get the medication section
medications = tree.findall(‘.//{urn:hl7-org:v3}section[@code=”10160-0″]/{urn:hl7-org:v3}entry/{urn:hl7-org:v3}substanceAdministration’)
# Print the medication information
for med in medications:
drug_name = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}consumable/{urn:hl7-org:v3}manufacturedProduct/{urn:hl7-org:v3}manufacturedMaterial/{urn:hl7-org:v3}name/{urn:hl7-org:v3}part’).text
dosage = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}doseQuantity/{urn:hl7-org:v3}value’).text
start_date = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}effectiveTime/{urn:hl7-org:v3}low’).attrib[‘value’]
end_date = med.find(‘{urn:hl7-org:v3}effectiveTime/{urn:hl7-org:v3}high’).attrib[‘value’]
print(“Drug Name: ” + drug_name)
print(“Dosage: ” + dosage)
print(“Start Date: ” + start_date)
print(“End Date: ” + end_date)
##########
In this example, we’re using the findall() method from the ElementTree library to find all the medication sections in the CCD document. We then use the find() method to extract the drug name, dosage, start and end date for each medication and print out the results.
Using Python to parse HL7 and CCD documents can be very useful in healthcare applications. For example, we can use these techniques to extract and analyze data from electronic health records (EHRs) to identify patterns and trends in patient care and outcomes. This can help healthcare providers to improve the quality of care, reduce costs, and enhance patient safety.
In conclusion, Python is a powerful tool for parsing and manipulating healthcare data in the HL7 and CCD formats. By using Python to extract and process data from these documents, we can gain valuable insights into patient care and outcomes, which can help to improve healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Understanding the Continuity of Care Document (CCD) in Healthcare
Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
In healthcare, it is crucial to have an accurate and complete medical history for patients in order to provide the best possible care. The Continuity of Care Document (CCD) is a standard format for summarizing a patient’s medical history and care plan. It contains a concise summary of the patient’s health status, including medical conditions, medications, allergies, and other relevant information. In this article, we will explore the CCD in more detail, including its structure and use cases.
The CCD is based on the HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) standard, which provides a framework for structuring clinical documents. The CCD is designed to be a concise, easy-to-read summary of a patient’s health status that can be shared among healthcare providers. It includes information about the patient’s medical conditions, medications, allergies, immunizations, procedures, and laboratory results. The CCD also includes information about the patient’s care plan, such as goals, instructions, and recommended follow-up visits.
The CCD can be used in a variety of settings to improve care coordination and continuity. For example, a patient might be referred from a primary care physician to a specialist. By sharing the CCD, the specialist can quickly get up to speed on the patient’s medical history and current care plan, which can improve the quality of care and reduce the risk of medical errors. The CCD can also be used in emergency situations, where a patient might not be able to provide a complete medical history.
Here are some examples of how the CCD can be used:
Referrals: When a patient is referred from one healthcare provider to another, the referring provider can send a CCD to the receiving provider. This ensures that the receiving provider has all the necessary information to provide appropriate care.
Transitions of Care: When a patient is discharged from a hospital or other healthcare facility, a CCD can be sent to the patient’s primary care provider. This ensures that the primary care provider has all the necessary information to manage the patient’s care after discharge.
Emergency Situations: When a patient is brought to an emergency department, a CCD can be used to provide important medical information to the emergency department staff. This can help ensure that the patient receives appropriate care and treatment.
Patient Portals: Some healthcare organizations offer patient portals that allow patients to access their medical records online. The CCD can be used to provide a summary of the patient’s medical history and care plan in a format that is easy for patients to understand.
In conclusion, the CCD is a standard format for summarizing a patient’s medical history and care plan. It includes information about the patient’s medical conditions, medications, allergies, immunizations, procedures, and laboratory results. The CCD can be used in a variety of settings to improve care coordination and continuity, including referrals, transitions of care, emergency situations, and patient portals. By using the CCD, healthcare providers can improve the quality of care and reduce the risk of medical errors.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
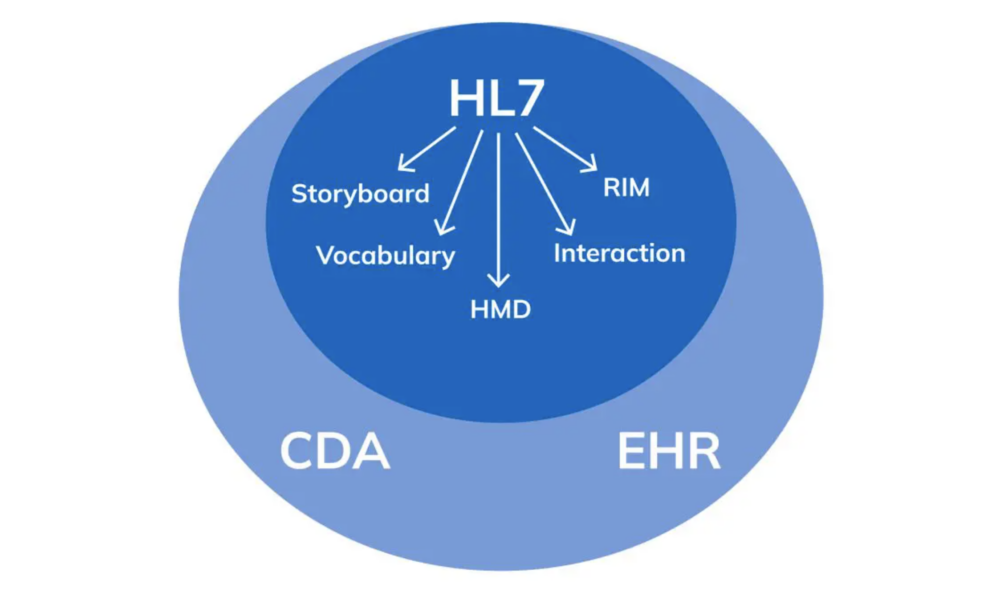
HL7: The Technicalities and Use Cases in Healthcare
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a widely adopted standard in healthcare for exchanging information between various healthcare applications, such as electronic health record systems, laboratory information systems, and radiology information systems. The standard defines a set of rules and formats for the exchange of clinical and administrative data. In this article, we will explore the technicalities of HL7 and provide examples of how it can be used in healthcare.
HL7 is composed of several messages, each containing one or more segments. Segments are made up of fields, and fields can contain subfields. Each segment contains information about a specific aspect of a patient’s clinical or administrative data. The most common message types in HL7 are the ADT (Admit, Discharge, Transfer), ORM (Order), and ORU (Observation Result) messages.
For example, an ADT message might contain information about a patient’s admission to the hospital, including their demographic information, admission date and time, and the admitting physician’s name. An ORM message might contain information about a laboratory test order, including the test name, patient’s name, and date and time the test was ordered. An ORU message might contain information about the results of a laboratory test, including the test name, patient’s name, and the actual test results.
HL7 can be used in a variety of ways to exchange data between healthcare applications. For example, a laboratory information system might send an ORU message to an electronic health record system when the results of a laboratory test are ready. The electronic health record system can then display the results to the provider, allowing them to make informed decisions about the patient’s care.
Another example is the use of HL7 in medical billing. A hospital’s billing system might receive ADT messages from an electronic health record system when a patient is admitted, transferred, or discharged. The billing system can then use this information to generate a claim for payment from the patient’s insurance company.
In addition to facilitating data exchange between healthcare applications, HL7 can also be used to integrate clinical decision support systems (CDSS) into electronic health record systems. CDSS systems can analyze patient data and provide recommendations to providers, such as suggesting alternative medications or highlighting potential drug interactions. By integrating CDSS systems with electronic health record systems using HL7, providers can make more informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, HL7 is a widely adopted standard in healthcare for exchanging clinical and administrative data between various healthcare applications. HL7 messages contain segments and fields that contain patient data, and there are several message types used for different purposes. HL7 can be used to exchange data between applications, integrate CDSS systems into electronic health record systems, and facilitate medical billing. By adopting HL7, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and streamline administrative processes.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Revolutionizing Patient Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-Generated Smart Forms
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The repetitive nature of filling out the same forms during each visit to a healthcare provider can be a time-consuming and tedious process for patients. However, Warp Core Health, an innovative healthcare technology company, is leading the charge in transforming the patient form experience. Through their groundbreaking AI-powered solutions, Warp Core Health is developing an AI-generated form that patients fill out once, and subsequently, only relevant information is presented for review and update based on the reason for the visit. This revolution in patient forms aims to streamline the healthcare experience, save time, and improve the overall efficiency of medical visits.
- The Current Challenge: Traditionally, patients are required to provide a comprehensive range of information during each visit, regardless of the reason for their appointment. This results in repetitive and time-consuming form filling, often causing frustration for patients who feel that the process is unnecessary and inefficient. Furthermore, healthcare providers must sift through extensive paperwork to locate the specific details relevant to the visit, creating an additional administrative burden.
- AI-Generated Smart Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms represent a significant advancement in the patient form process. With the power of artificial intelligence, these forms are designed to be dynamic and tailored to each patient’s specific needs. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, the smart forms intelligently analyze the reason for the visit and present only the relevant sections and questions for review and update.
- Personalized and Streamlined Experience: By eliminating the need to repeat previously provided information, patients can experience a more streamlined and personalized visit. With AI-generated smart forms, patients can focus on updating crucial details related to their current health condition, symptoms, or concerns. This targeted approach ensures that patients’ valuable time is maximized during their appointments, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering the most appropriate care.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Warp Core Health’s AI algorithms continually learn from patient data, allowing for improved accuracy and efficiency over time. As patients update their information during subsequent visits, the smart forms intelligently adapt and present new questions or prompts based on previous responses and the reason for the current visit. This iterative process ensures that patient information remains up-to-date and relevant, while minimizing redundant or unnecessary data entry.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems, creating a powerful synergy between patient information and form customization. As new data is added to the EHR, such as diagnoses, treatments, or test results, it further enhances the customization of smart forms for future visits. The AI algorithms analyze the updated EHR data and dynamically adjust the smart forms to ensure that patients are presented with the most relevant sections and questions specific to their follow-up or next visit. This dynamic customization optimizes the patient form experience, allowing for efficient updates and reviews of pertinent information while eliminating the need to navigate through irrelevant sections. By harnessing the power of EHR integration, Warp Core Health’s smart forms adapt to each patient’s evolving healthcare journey, ensuring a personalized and tailored experience throughout their medical visits.
- Data Security and Privacy: Warp Core Health places a high priority on maintaining the security and privacy of patient data. Their AI-generated smart forms are designed to adhere to stringent data protection regulations, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential. Robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards are implemented to safeguard patient privacy throughout the form-filling and data storage processes.
Conclusion: Warp Core Health’s pioneering efforts in developing AI-generated smart forms are set to revolutionize the patient form experience in healthcare. By leveraging artificial intelligence, these forms minimize repetitive data entry, present only relevant information for review and update, and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical visits. With seamless integration into electronic health record systems, Warp Core Health ensures that patient information remains up-to-date, contributing to improved continuity of care. As the healthcare industry embraces the power of AI technology, Warp Core Health’s innovative approach to patient forms promises to transform the patient experience, saving time, and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Author: Sharon Lojun, M.D., M.S.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health