- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
Year: 2023
Unveiling the Differences: The Dawn Phenomenon vs. The Somogyi Effect in Diabetes Management
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
Diabetes management encompasses various challenges, including understanding and addressing the intricacies of blood glucose fluctuations. Two phenomena that often perplex individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals are the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect. While both involve abnormal blood glucose levels, these phenomena differ in their timing, triggers, underlying mechanisms, and management strategies. In this article, we delve into these distinctions to shed light on the unique characteristics of the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect in diabetes management.
The Dawn Phenomenon: An Early Morning Rise in Blood Glucose
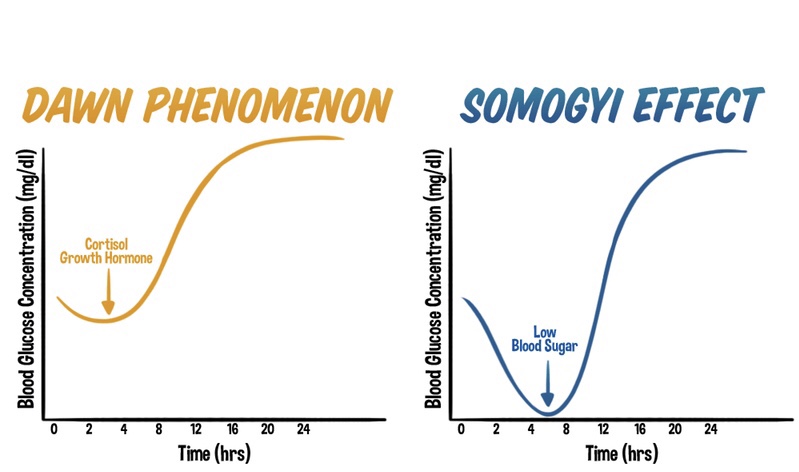
The dawn phenomenon is a well-known phenomenon observed in individuals with diabetes, characterized by an abnormal rise in blood glucose levels during the early morning hours, typically before waking up. Hormonal changes play a significant role in triggering this phenomenon. Increased release of hormones such as cortisol, growth hormone, and glucagon during the early morning hours leads to insulin resistance and stimulates gluconeogenesis. As a result, blood glucose levels rise without any preceding hypoglycemia.
The Somogyi Effect: Rebound Hyperglycemia Following Nocturnal Hypoglycemia
In contrast, the Somogyi effect involves a rebound hyperglycemia following a period of nocturnal hypoglycemia. This phenomenon occurs when blood glucose levels drop too low during the night, often due to excessive insulin administration or inadequate carbohydrate intake before bedtime. Nocturnal hypoglycemia triggers a counterregulatory response in the body, resulting in the release of hormones such as glucagon, cortisol, and growth hormone. These hormones stimulate gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, leading to a rebound rise in blood glucose levels during the morning or throughout the day.
Distinguishing Factors: Timing, Triggers, and Underlying Mechanisms
One of the primary distinctions between the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect lies in their timing and triggers. The dawn phenomenon occurs during the early morning hours, driven by natural hormonal changes, while the Somogyi effect occurs as a response to nocturnal hypoglycemia.
Underlying mechanisms also differ between the two phenomena. The dawn phenomenon involves overactive gluconeogenesis as a contributing factor, as the liver produces glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. In contrast, the Somogyi effect encompasses a complex interplay of factors, including the release of counterregulatory hormones that stimulate both gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
Management Strategies:
Effective management of the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect requires tailored approaches based on their unique characteristics.
Managing the dawn phenomenon involves adjusting insulin regimens, specifically optimizing basal insulin doses during the early morning hours. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also aid in stabilizing blood glucose levels.
The management of the Somogyi effect requires identifying patterns of nocturnal hypoglycemia through consistent blood glucose monitoring. Adjusting insulin doses, timing, or types can prevent hypoglycemia and subsequent rebound hyperglycemia. Ensuring sufficient carbohydrate intake before bedtime and maintaining consistent sleep patterns are essential strategies in managing the Somogyi effect.
Conclusion:
Understanding the distinctions between the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect is crucial in diabetes management. While both phenomena involve abnormal blood glucose fluctuations, their timing, triggers, underlying mechanisms, and management strategies differ significantly. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in recognizing these differences and tailoring individualized care plans to optimize blood glucose control. By comprehending the unique characteristics of the dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect, individuals with diabetes can work with their healthcare teams to effectively manage these phenomena and achieve improved overall well-being.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Rejuvenate Your Body: Harnessing the Power of Intermittent Fasting for Autophagy
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction
Intermittent fasting has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. One of the key aspects of intermittent fasting is its ability to stimulate a process called autophagy. Autophagy, which translates to “self-eating” in Greek, is a natural cellular process that plays a vital role in maintaining cellular health and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the importance of intermittent fasting for autophagy and how it can positively impact our health.
Understanding Autophagy
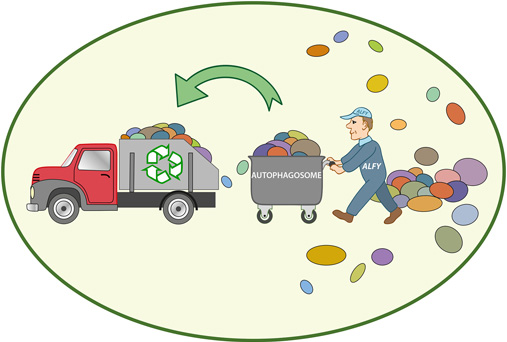
Autophagy is an intricate process by which cells remove and recycle damaged, dysfunctional, or unnecessary components, such as proteins and organelles. It acts as a cellular cleansing mechanism, promoting cellular renewal and enhancing the overall efficiency of our cells. This process is crucial for maintaining cellular health, preventing the accumulation of toxic substances, and reducing the risk of various diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
Autophagy and Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of fasting and eating. It doesn’t focus on what you eat but rather when you eat. Commonly, individuals adopt one of the popular intermittent fasting methods, such as the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) or the 5:2 diet (eating normally for five days and significantly reducing calorie intake for two non-consecutive days).
Studies have suggested that intermittent fasting can stimulate autophagy, thereby enhancing cellular health. When we fast, our body experiences a drop in insulin levels, leading to a state of increased autophagy. During this fasting period, the body shifts from utilizing glucose as a primary source of energy to utilizing stored fats through a process called ketosis. Ketosis has been shown to induce autophagy and promote cellular rejuvenation.
Benefits of Autophagy
- Cellular Regeneration: Autophagy allows for the removal of damaged or malfunctioning cellular components, promoting cellular regeneration and rejuvenation. This process helps to maintain cellular health and prevent the accumulation of toxic substances that can lead to various diseases.
- Anti-Aging Effects: Autophagy has been linked to anti-aging effects. By eliminating damaged cellular components and proteins, autophagy can help slow down the aging process and delay age-related diseases.
- Disease Prevention: Autophagy plays a crucial role in protecting against various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. By eliminating dysfunctional cells and reducing oxidative stress, autophagy helps to mitigate the risk of these diseases.
- Metabolic Health: Intermittent fasting and autophagy can have positive effects on metabolic health. It has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote healthy weight management.
- Clearance of Protein Aggregates: Intermittent fasting triggers autophagy, enabling cells to remove protein aggregates, including amyloid, tau, alpha-synuclein, and Lewy bodies. These aggregates are associated with neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other conditions. By effectively clearing these toxic substances, intermittent fasting helps decrease neuroinflammation and supports brain health.
- Reduction of Primed Glial Cells: Primed glial cells, when overactive, contribute to neuroinflammation. Intermittent fasting helps clear these primed glial cells, further decreasing neuroinflammation and offering neuroprotective effects. This reduction in neuroinflammation is key in preserving brain function and mitigating the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusion
Autophagy is a vital cellular process that promotes cellular health, rejuvenation, and disease prevention. Intermittent fasting serves as an effective tool to stimulate autophagy and reap its numerous benefits. By adopting intermittent fasting, individuals can harness the power of autophagy, enhancing their overall well-being and reducing the risk of various age-related diseases.
However, it is important to note that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with specific medical conditions or nutritional needs. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before implementing any significant dietary changes.
Incorporating intermittent fasting into one’s lifestyle, along with a balanced diet and regular exercise, can pave the way for improved cellular health and a healthier, more vibrant life.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
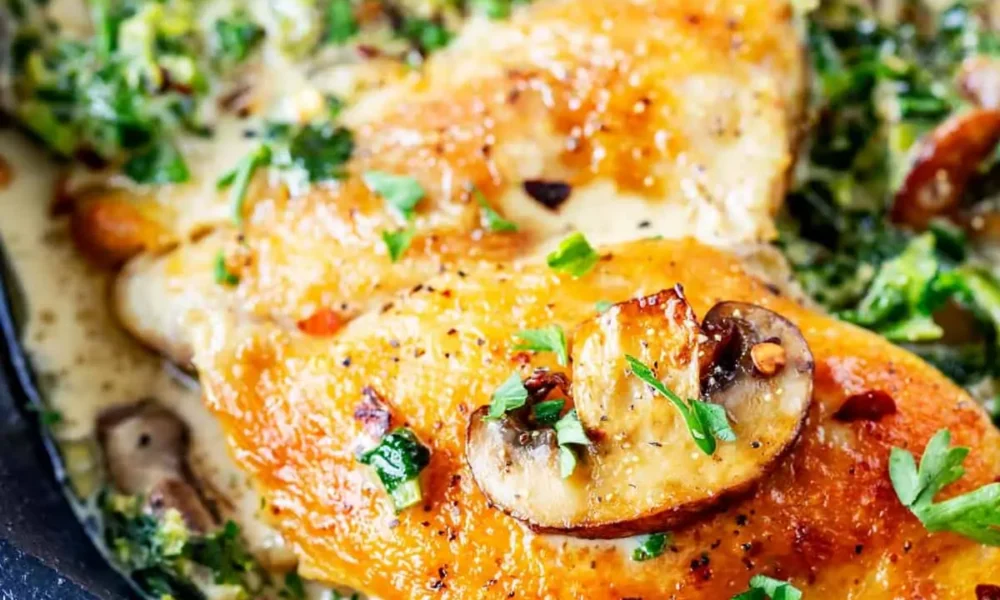
Chicken Thighs with Mushrooms and Spinach: A Flavorful Delight
By Lisa Fitzmeyer
Introduction: Chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach is a delicious and nutritious dish that combines tender chicken thighs, earthy mushrooms, and vibrant spinach. This recipe offers a harmonious blend of flavors and textures, making it a satisfying meal for any occasion. Follow this simple recipe to create a mouthwatering dish that will impress your family and friends.
Ingredients:
- 6-8 chicken thighs
- Avocado oil
- 2 tablespoons fresh rosemary, chopped
- 1 medium onion, sliced
- White button mushrooms, sliced
- 4 cloves of garlic, chopped
- Fresh spinach or kale
Instructions:
- Preheat the oven to 350°F (175°C).
- In a large skillet, heat 4 tablespoons of avocado oil over medium heat. Place the chicken thighs in the pan, skin side down, and cook until the skin is crispy and golden brown. This will take about 5-6 minutes. Flip the chicken thighs and cook for an additional 2-3 minutes. The chicken will not be fully cooked at this stage but will finish cooking in the oven.
- Transfer the chicken thighs to a baking dish, arranging them in a single layer.
- In the same skillet, add the sliced onions, chopped garlic, and fresh rosemary. Sauté them in the remaining oil until the onions become jammy and translucent. This process will take about 5 minutes.
- Add the sliced mushrooms to the skillet and sauté for an additional 3-4 minutes until they are tender and slightly browned.
- Spoon the onion, garlic, and mushroom mixture around the chicken thighs in the baking dish, distributing it evenly.
- Place the baking dish in the preheated oven and bake for 30 minutes, or until the chicken thighs are cooked through and reach an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
- Remove the baking dish from the oven and increase the oven temperature to 400°F (200°C).
- Meanwhile, coat the fresh spinach or kale with a drizzle of olive oil, ensuring that all leaves are lightly coated.
- Spread the oiled spinach or kale around the chicken and vegetables in the baking dish.
- Return the dish to the oven and bake for an additional 5 minutes, or until the spinach or kale wilts slightly.
- Carefully remove the baking dish from the oven. The chicken thighs should be juicy, and the mushrooms, onions, and spinach or kale will have melded together beautifully.
- Serve the chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach alongside your favorite keto-friendly sides, such as roasted cauliflower or zucchini noodles, or a fresh green salad dressed with olive oil and lemon juice. Enjoy the delightful flavors and wholesome goodness of this keto-friendly chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach dish!
Enjoy the delightful flavors and wholesome goodness of this chicken thighs with mushrooms and spinach dish!
Note: Feel free to adjust the quantities of ingredients to suit your preferences and the number of servings desired.
From Keto to Carnivore: Decoding Low Carb Diets for Ultimate Health and Vitality
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction:
In the quest for improved health and weight management, numerous dietary approaches have gained popularity. Among the most well-known are the low carb diets, including the ketogenic diet (keto) and the carnivore diet. However, it is important to understand the subtle nuances and benefits of each variation, as well as other popular low carb diets such as the Paleo, Mediterranean, and Standard American Diet (S.A.D.). In this article, we will explore the differences and benefits of these dietary choices, shedding light on the variables that make each one unique.
The Ketogenic Diet (Keto):
The ketogenic diet is a low carb, high fat diet that encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body shifts from using glucose as its primary fuel source to using ketones. This metabolic state has been associated with several benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased mental clarity. Additionally, keto has shown promise in managing epilepsy and certain neurological disorders.
The Carnivore Diet:
At the other end of the spectrum lies the carnivore diet, which emphasizes exclusively animal products and eliminates plant-based foods entirely. This ultra-low carb, high fat, and high protein approach aims to mimic the dietary patterns of our ancestors. Advocates claim that eliminating plant foods can reduce inflammation, promote weight loss, and improve digestion. However, it is important to note that the carnivore diet is highly restrictive and lacks the diversity of nutrients found in a balanced diet.
The Paleo Diet:
The Paleo diet seeks to emulate the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. It promotes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding grains, legumes, dairy products, and processed foods. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and eliminating potential allergens, the Paleo diet aims to support weight loss, improve digestion, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
The Mediterranean Diet:
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while incorporating moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products. This approach is rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber, which have been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, improved brain function, and overall longevity.
The Standard American Diet (S.A.D.):
The Standard American Diet, unfortunately, is characterized by a high intake of processed foods, refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and a low consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This diet is associated with a variety of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. It lacks the nutrient density and balance necessary for optimal health.
Benefits of Each Approach:
Keto: Weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, increased mental clarity, potential therapeutic benefits for epilepsy and neurological disorders.
Carnivore: Potential for reduced inflammation, weight loss, and improved digestion. However, it may lack essential nutrients and long-term sustainability.
Paleo: Improved weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases, increased nutrient intake, elimination of potential allergens.
Mediterranean: Heart health, improved brain function, longevity, reduced risk of chronic diseases, balanced nutrient intake.
S.A.D.: No significant benefits compared to the other diets mentioned. Associated with various health issues.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right low carb diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health considerations. While the ketogenic and carnivore diets offer unique metabolic effects, it is important to consider the
long-term sustainability and potential nutrient deficiencies. The Paleo and Mediterranean diets provide a balanced approach by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods and diverse nutrient profiles. In contrast, the Standard American Diet (S.A.D.) is associated with numerous health problems due to its reliance on processed and unhealthy foods.
It is essential to note that individual responses to different diets may vary. What works for one person may not yield the same results for another. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
Ultimately, the key to a successful and sustainable low carb diet lies in finding a balance that aligns with your health goals and preferences. Incorporating whole, nutrient-dense foods while reducing processed carbohydrates can have a positive impact on weight management, overall health, and disease prevention. By understanding the variables and benefits of different low carb diets, you can make an informed decision and embark on a journey towards improved well-being.
Comparison chart highlighting the macronutrient composition of each diet:
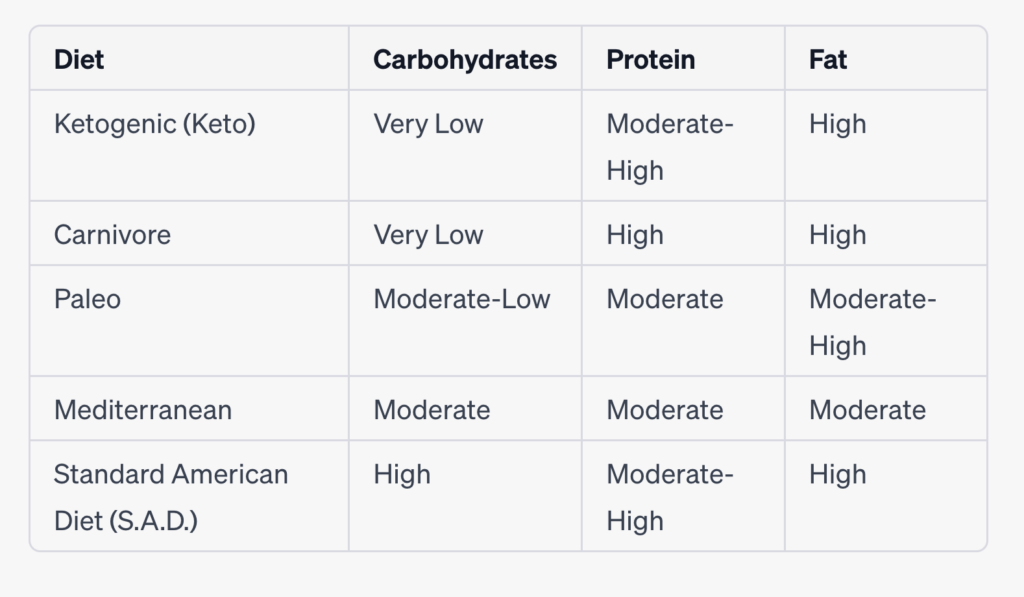
Please note that the macronutrient ratios mentioned above can vary based on individual preferences and specific interpretations of each diet. Additionally, the “Moderate” category indicates a more balanced distribution rather than being excessively high or low.
It’s important to keep in mind that macronutrient ratios can be adjusted within each diet based on individual needs, health goals, and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for determining the ideal macronutrient breakdown for your specific circumstances.
Remember that while macronutrients play a significant role in dietary choices, the quality of food, micronutrient content, and overall balance of the diet are also crucial factors to consider for long-term health and well-being.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Revolutionizing Patient Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-Generated Smart Forms
By Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
Introduction: The repetitive nature of filling out the same forms during each visit to a healthcare provider can be a time-consuming and tedious process for patients. However, Warp Core Health, an innovative healthcare technology company, is leading the charge in transforming the patient form experience. Through their groundbreaking AI-powered solutions, Warp Core Health is developing an AI-generated form that patients fill out once, and subsequently, only relevant information is presented for review and update based on the reason for the visit. This revolution in patient forms aims to streamline the healthcare experience, save time, and improve the overall efficiency of medical visits.
- The Current Challenge: Traditionally, patients are required to provide a comprehensive range of information during each visit, regardless of the reason for their appointment. This results in repetitive and time-consuming form filling, often causing frustration for patients who feel that the process is unnecessary and inefficient. Furthermore, healthcare providers must sift through extensive paperwork to locate the specific details relevant to the visit, creating an additional administrative burden.
- AI-Generated Smart Forms: Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms represent a significant advancement in the patient form process. With the power of artificial intelligence, these forms are designed to be dynamic and tailored to each patient’s specific needs. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, the smart forms intelligently analyze the reason for the visit and present only the relevant sections and questions for review and update.
- Personalized and Streamlined Experience: By eliminating the need to repeat previously provided information, patients can experience a more streamlined and personalized visit. With AI-generated smart forms, patients can focus on updating crucial details related to their current health condition, symptoms, or concerns. This targeted approach ensures that patients’ valuable time is maximized during their appointments, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering the most appropriate care.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Warp Core Health’s AI algorithms continually learn from patient data, allowing for improved accuracy and efficiency over time. As patients update their information during subsequent visits, the smart forms intelligently adapt and present new questions or prompts based on previous responses and the reason for the current visit. This iterative process ensures that patient information remains up-to-date and relevant, while minimizing redundant or unnecessary data entry.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Warp Core Health’s AI-generated smart forms seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems, creating a powerful synergy between patient information and form customization. As new data is added to the EHR, such as diagnoses, treatments, or test results, it further enhances the customization of smart forms for future visits. The AI algorithms analyze the updated EHR data and dynamically adjust the smart forms to ensure that patients are presented with the most relevant sections and questions specific to their follow-up or next visit. This dynamic customization optimizes the patient form experience, allowing for efficient updates and reviews of pertinent information while eliminating the need to navigate through irrelevant sections. By harnessing the power of EHR integration, Warp Core Health’s smart forms adapt to each patient’s evolving healthcare journey, ensuring a personalized and tailored experience throughout their medical visits.
- Data Security and Privacy: Warp Core Health places a high priority on maintaining the security and privacy of patient data. Their AI-generated smart forms are designed to adhere to stringent data protection regulations, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential. Robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards are implemented to safeguard patient privacy throughout the form-filling and data storage processes.
Conclusion: Warp Core Health’s pioneering efforts in developing AI-generated smart forms are set to revolutionize the patient form experience in healthcare. By leveraging artificial intelligence, these forms minimize repetitive data entry, present only relevant information for review and update, and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical visits. With seamless integration into electronic health record systems, Warp Core Health ensures that patient information remains up-to-date, contributing to improved continuity of care. As the healthcare industry embraces the power of AI technology, Warp Core Health’s innovative approach to patient forms promises to transform the patient experience, saving time, and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Author: Sharon Lojun, M.D., M.S.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health