- Home
- About
- Portfolio
Crush the Match – Medical School and Residency Platform
Food¢ense – Curbing Childhood Obesity and Food Waste
HealthStack – Shared and Jailed HIPAA Hosting $50
Marta Care – Let Us Help When You Can’t
MD Idea Lab – We Build Prototypes for Doctors
Nervcell – The Healthcare Web Browser
Patient Keto – Personalized Keto Medicine and Telehealth
SwipeChart – Rapid EMR Interface
Treatment Scores – Quantifying the Science of Medicine
Treatments – Diagnosed. Now What?
VIDRIO – Google Glass and EMR Interface
- Blog
- Contact
- Home
- Warp Core Health
- Blog
- 2023
- May
Month: May 2023
Transforming Healthcare in Rural America: The Role of Artificial Intelligence
- May 9, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Access to quality healthcare remains a significant challenge for rural communities in America. Limited resources, geographical barriers, and a shortage of healthcare professionals contribute to healthcare disparities in these areas. However, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) offers a transformative solution to address these challenges. This article explores how AI can improve healthcare in rural America, enhancing diagnosis and treatment, expanding access to specialized care, optimizing healthcare delivery, and empowering patients to take control of their health.
- Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment: AI algorithms have the potential to revolutionize the diagnostic process in rural healthcare settings. Machine learning models can analyze medical data, including patient records, lab results, and imaging scans, to assist healthcare providers in making accurate and timely diagnoses. AI can also support the identification of patterns and trends in population health data, helping healthcare professionals proactively address prevalent conditions in rural communities.
- Telemedicine and Remote Care: One of the most significant advantages of AI in rural healthcare is the ability to offer telemedicine and remote care services. Through AI-powered platforms, patients in remote areas can access virtual consultations with healthcare providers, eliminating the need for long-distance travel. This technology allows rural residents to receive timely medical advice, monitor chronic conditions, and access specialized care without the burden of geographical barriers.
- Optimization of Healthcare Delivery: AI can help optimize healthcare delivery in rural areas by streamlining processes and reducing inefficiencies. Predictive analytics can aid in resource allocation, ensuring that medical facilities have adequate staff, supplies, and equipment to meet the needs of the community. AI can also assist in predicting disease outbreaks and enabling targeted interventions, enabling rural healthcare providers to respond effectively to public health emergencies.
- Support for Rural Healthcare Professionals: AI can alleviate the burden on rural healthcare professionals by providing decision support tools and real-time access to medical information. AI-powered systems can analyze vast medical literature, recommend treatment options based on best practices, and offer guidance in complex medical scenarios. This assistance can enhance the capabilities of rural healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver high-quality care with greater confidence.
- Empowering Patients: AI technologies can empower rural patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey. Mobile health applications and wearable devices equipped with AI capabilities can help individuals monitor their vital signs, track their health conditions, and receive personalized health recommendations. By promoting self-care and providing health education, AI empowers rural residents to take control of their well-being and make informed decisions about their health.
Conclusion: Artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionize healthcare in rural America, addressing the unique challenges faced by these communities. Through enhanced diagnosis and treatment, telemedicine, optimized healthcare delivery, support for healthcare professionals, and patient empowerment, AI can bridge the gap in access to quality healthcare services. As rural areas strive for equitable healthcare, leveraging the power of AI becomes crucial. Collaborative efforts between healthcare organizations, policymakers, and technology experts are needed to ensure that AI is effectively integrated into rural healthcare systems, ultimately improving health outcomes and enhancing the well-being of rural Americans.
Author: Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Harnessing the Power of Probiotics: Exploring Mitochondrial Uncoupling and its Benefits
- May 7, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Probiotics have gained considerable attention for their potential health benefits, especially in the context of gut health. However, recent studies have revealed an intriguing connection between probiotics and mitochondrial uncoupling, a process that holds promise for various health benefits. In this article, we will explore the role of probiotics in mitochondrial uncoupling and delve into the potential advantages it offers.
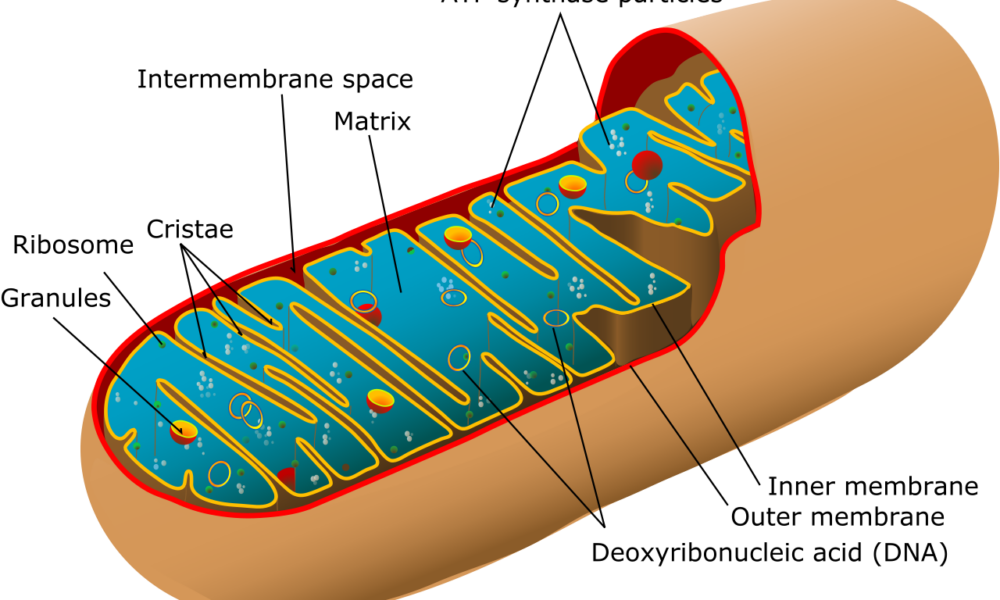
Understanding Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells, responsible for energy production. Normally, energy production occurs through a tightly regulated process called oxidative phosphorylation, where adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is generated. However, mitochondrial uncoupling refers to the disruption of this process, leading to the dissipation of energy as heat instead of ATP production. This phenomenon is facilitated by a protein called uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) and is primarily found in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and beige fat cells.
The Link Between Probiotics and Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Recent studies have demonstrated that certain probiotic strains can influence mitochondrial uncoupling and enhance the activity of UCP1. Specifically, probiotics like Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Akkermansia muciniphila have shown potential in promoting the browning of white adipose tissue, leading to increased thermogenesis and energy expenditure. These probiotics can modulate the gut microbiota composition and promote the release of specific metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), that play a role in mitochondrial uncoupling.
The Benefits of Probiotic-Induced Mitochondrial Uncoupling: Mitochondrial uncoupling, induced by probiotics, offers several potential benefits:
- Increased energy expenditure: By promoting thermogenesis and energy dissipation as heat, mitochondrial uncoupling can potentially boost overall energy expenditure, which may be beneficial for weight management and metabolic health.
- Improved glucose metabolism: Studies have suggested that probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling may improve glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, which could be particularly advantageous for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic disorders.
- Enhanced fat oxidation: Mitochondrial uncoupling can stimulate the breakdown of stored fat and enhance fat oxidation, potentially aiding in weight loss and reducing body fat.
- Regulation of inflammation: Probiotics that induce mitochondrial uncoupling have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved gut barrier function, which may have positive implications for various inflammatory conditions.
Conclusion: The emerging research on probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling highlights a fascinating link between gut health and metabolic processes. Probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Akkermansia muciniphila, show potential in promoting mitochondrial uncoupling and unlocking its associated benefits, including increased energy expenditure, improved glucose metabolism, enhanced fat oxidation, and regulation of inflammation. However, it is essential to note that further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term effects of probiotic-induced mitochondrial uncoupling.
As our understanding of the gut-brain axis and the intricate connections within our bodies continues to grow, harnessing the power of probiotics for mitochondrial uncoupling opens up new avenues for potential health interventions. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals or specialists in the field can provide personalized advice and guidance for incorporating probiotics and optimizing their benefits in relation to mitochondrial uncoupling.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
Vitamin D Supplementation: A Promising Strategy to Lower Diabetes Risk in Prediabetic Individuals
- May 1, 2023
- Stephen Fitzmeyer, MD
- No Comments
Introduction: Vitamin D, a vital nutrient with multifaceted functions in the body, has been found to play a role in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. Observational studies have consistently shown an association between low levels of vitamin D in the blood and an increased risk of developing diabetes. Given these findings, researchers set out to investigate whether administering vitamin D to individuals at high risk for diabetes could effectively reduce that risk. In this article, we discuss the results of a comprehensive meta-analysis that examined the impact of vitamin D supplementation on diabetes prevention in adults with prediabetes.
Study Details: The study authors conducted a systematic search of three databases, encompassing research published up until December 9, 2022. Their focus was to compare the use of vitamin D versus a placebo for diabetes prevention in individuals with prediabetes. The data were subjected to a rigorous meta-analysis and reanalysis to evaluate the pooled results of multiple trials. Importantly, the trials included were deemed to have a low risk of bias, enhancing the reliability of the findings.
Results: Over a period of three years, the study revealed that individuals in the vitamin D group had a lower incidence of new-onset diabetes compared to the placebo group. Specifically, 22.7% of participants in the vitamin D group developed diabetes, while 25% of those in the placebo group experienced new-onset diabetes. This translates to a 15% reduction in the risk of developing diabetes for individuals receiving vitamin D supplementation. To prevent one case of diabetes, approximately 30 adults with prediabetes would need to be treated with vitamin D.
Risk Reduction by Blood Levels: Furthermore, the study analyzed the effect of different blood levels of vitamin D on diabetes risk. Among participants who maintained a mean serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level of at least 125 nmol/L (≥50 ng/mL), cholecalciferol reduced the risk of diabetes by an impressive 76%, with a 3-year absolute risk reduction of 18.1%. In contrast, individuals with lower vitamin D levels (50 to 74 nmol/L or 20 to 29 ng/mL) still experienced a reduction in risk, albeit to a lesser extent.
Doses Used: The vitamin D supplementation regimens in the trials included 20,000 units of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) administered weekly, 4000 units of cholecalciferol daily, or 0.75 micrograms of eldecalcitol (a synthetic analogue of vitamin D) daily.
Adverse Events: While rare, the study did not provide definitive conclusions regarding the safety of vitamin D supplementation. Adverse events such as kidney stones, hypercalcemia, and hypercalciuria were not significantly different between the vitamin D and placebo groups.
Implications: The results of this study suggest that vitamin D supplementation can be an effective strategy for reducing the risk of developing diabetes in adults with prediabetes. These findings highlight the potential of a simple and accessible intervention that may have a significant impact on public health. However, further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, long-term effects, and safety profile of vitamin D supplementation in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion: Vitamin D supplementation has emerged as a promising avenue for lowering the risk of diabetes in individuals with prediabetes. The meta-analysis demonstrated a notable reduction in the incidence of new-onset diabetes among those receiving vitamin D supplementation compared to the placebo group. While the study sheds light on the efficacy of vitamin D, ongoing research is necessary to fully elucidate its role and establish specific guidelines for implementation. Nonetheless, these findings contribute to our understanding of diabetes prevention and underscore the potential benefits of incorporating an inexpensive and readily available solution like vitamin D supplementation in the overall approach to diabetes prevention. By considering the role of vitamin D in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism, individuals at high risk for diabetes, particularly those with prediabetes, may have an additional tool at their disposal to mitigate their risk.
As further research is conducted and more evidence accumulates, healthcare professionals can better inform their patients about the potential benefits and appropriate dosages of vitamin D supplementation. Implementing routine screening for vitamin D levels and providing personalized recommendations may become an integral part of preventive healthcare strategies aimed at reducing the burden of type 2 diabetes.
In conclusion, the meta-analysis and reanalysis of pooled data revealed that vitamin D supplementation was effective in lowering the risk of developing diabetes in adults with prediabetes. While additional studies are needed to confirm these findings and establish safety guidelines, the potential of an affordable and accessible intervention like vitamin D offers hope in the fight against type 2 diabetes. By addressing the role of vitamin D in diabetes prevention, healthcare providers can empower individuals with prediabetes to take proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Author: Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer, M.D.
Physician Informaticist
Founder of Patient Keto
Founder of Warp Core Health
Founder of Jax Code Academy, jaxcode.com
Connect with Dr. Stephen Fitzmeyer:
Twitter: @PatientKeto
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/sfitzmeyer/
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
Recent Posts
- Protected: Warp Core Health: Building a Custom AI Model for Transforming Healthcare
- The Intersection of Healthcare, AI, Clinical Informatics, and Machine Learning
- Accessing Siloed EMR Systems with FHIR: Connecting to Multiple EMRs
- How AI and Informatics Are Transforming Healthcare
- How AI Can Transform Healthcare Applications
Categories
- ApoB
- Artificial Intelligence
- Autophagy
- Biochemistry
- Biomedical Informatics
- Biostatistics
- Blood Glucose
- CAC
- Carbs
- CCD
- CDA
- Clinical Informatics
- Coding Bootcamp
- Coronary Artery Disease
- COVID-19
- Cybersecurity
- Data Science
- Diabetes
- Diet
- EHS
- EMR
- Epidemiology
- Evidence Based Medicine
- Fats
- FHIR
- Fiber
- Generative AI
- Global Health
- Health Administration
- Health Informatics
- Health IT
- HIPAA
- HL7
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- ICD 10
- Intermittent Fasting
- Ketogenic Diet
- Machine Learning
- Macronutrients
- MCT Oil
- Metabolic Health
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Minerals
- Mitochondria
- MySQL
- Neurology
- Nutritional Ketosis
- Nutritional Neurology
- Nutritional Psychiatry
- PHP
- PHR
- Programming
- Prompt Engineering
- Proteins
- Prototypes
- Public Health
- Python
- Recipes
- Sleep Health
- Stroke
- Uric Acid
- Vegan and Vegetarians
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K2
- Vitamins